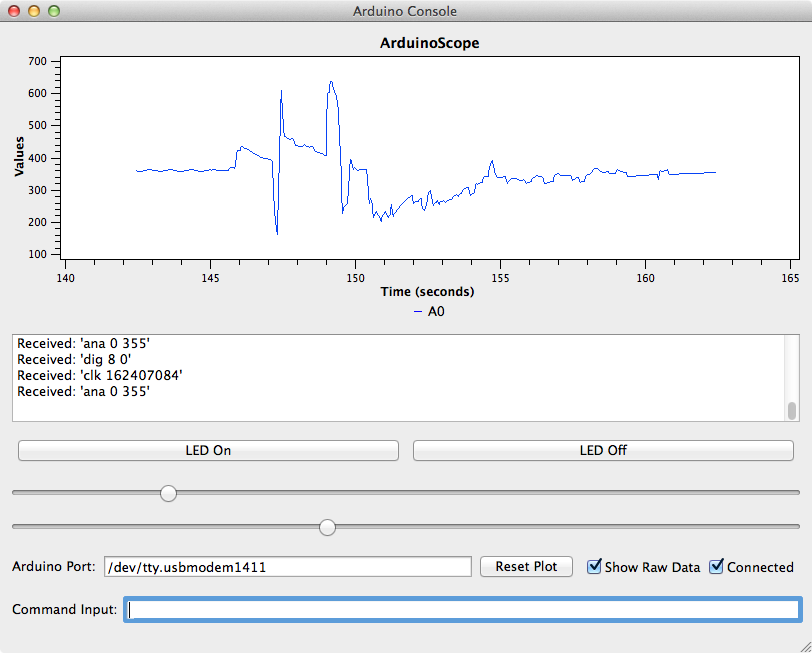
5.2. OneInOneOutGUI Example¶
This module provides a graphical interface to an Arduino running
the OneInOneOutASCII Arduino Sketch. It is built on top of the ArduinoGUI
module.
5.2.2. OneInOneOutGUI.py¶
OneInOneOutGUI.py
GUI controller for the OneInOneOutASCII Arduino sketch. This interface shell communicates over a serial port to an Arduino running a sketch which includes line-oriented text input and output.
Copyright (c) 2015, Garth Zeglin. All rights reserved. Licensed under the terms of the BSD 3-clause license.
-
class
OneInOneOutGUI.OneInOneOutGUI.OneInOneOutGUIController(port=None, **kwargs)[source]¶ Application-specific control object to manage the GUI for OneInOneOutASCII. This class creates a generic ArduinoConsole GUI, adds application-specific GUI controls, and manages basic I/O.
Parameters: - port – the name of the serial port device
- kwargs – collect any unused keyword arguments
Callback function activated to disable the LED.
Callback function activated to enable the LED.
5.2.3. run_gui.py¶
This script launches the GUI.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 | #!/usr/bin/env python
"""\
run_gui.py
Sample script to create and operate a graphical user interface for an Arduino
program. This interface shell communicates over a serial port to an Arduino
running a sketch which includes line-oriented text input and output.
Copyright (c) 2015, Garth Zeglin. All rights reserved. Licensed under the terms
of the BSD 3-clause license.
"""
from __future__ import print_function
import os, sys, argparse
# This requires the PyQt4 module to interface to the Qt GUI toolkit. For
# documentation on the PyQt4 API, see http://pyqt.sourceforge.net/Docs/PyQt4/index.html
from PyQt4 import QtGui
# Make sure that the Python libraries also contained within this course package
# are on the load path. This adds the parent folder to the load path, assuming that this
# script is still located within a subfolder of the Python library tree.
sys.path.insert(0, os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__))))
# Import the custom GUI class.
from OneInOneOutGUI.OneInOneOutGUI import OneInOneOutGUIController
################################################################
# Main script follows. This sequence is executed when the script is initiated from the command line.
if __name__ == "__main__":
# process command line arguments
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description = """Run the GUI for the OneInOneOutGUIASCII Arduino sketch.""")
parser.add_argument( '-v', '--verbose', action='store_true', help='Enable more detailed output.' )
parser.add_argument( '-p', '--port', default='/dev/tty.usbmodem1411', \
help='Specify the name of the Arduino serial port device (default is /dev/tty.usbmodem1411).')
args = parser.parse_args()
# initialize the Qt system itself
app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
# create the interface window
window = OneInOneOutGUIController(port=args.port)
print("""Starting up OneInOneOutGUI.
Toggle the 'Connected' switch to open the Arduino serial port.
Click 'Enable' while connected to enable motor drivers.
""")
# run the event loop until the user is done
sys.exit(app.exec_())
|