DC Motor Examples - Raspberry Pi Pico¶
The following short Python programs will demonstrate essential operation of the
Raspberry Pi Pico board. These assume one or DC motor actuators are externally
attached. Each can be run by copying the program into code.py on the
CIRCUITPY drive offered by the board. The text can be pasted directly from this
page, or each file can be downloaded from the CircuitPython sample code folder on this site.
Related Pages
Sample MOSFET Motor Driver Circuit¶
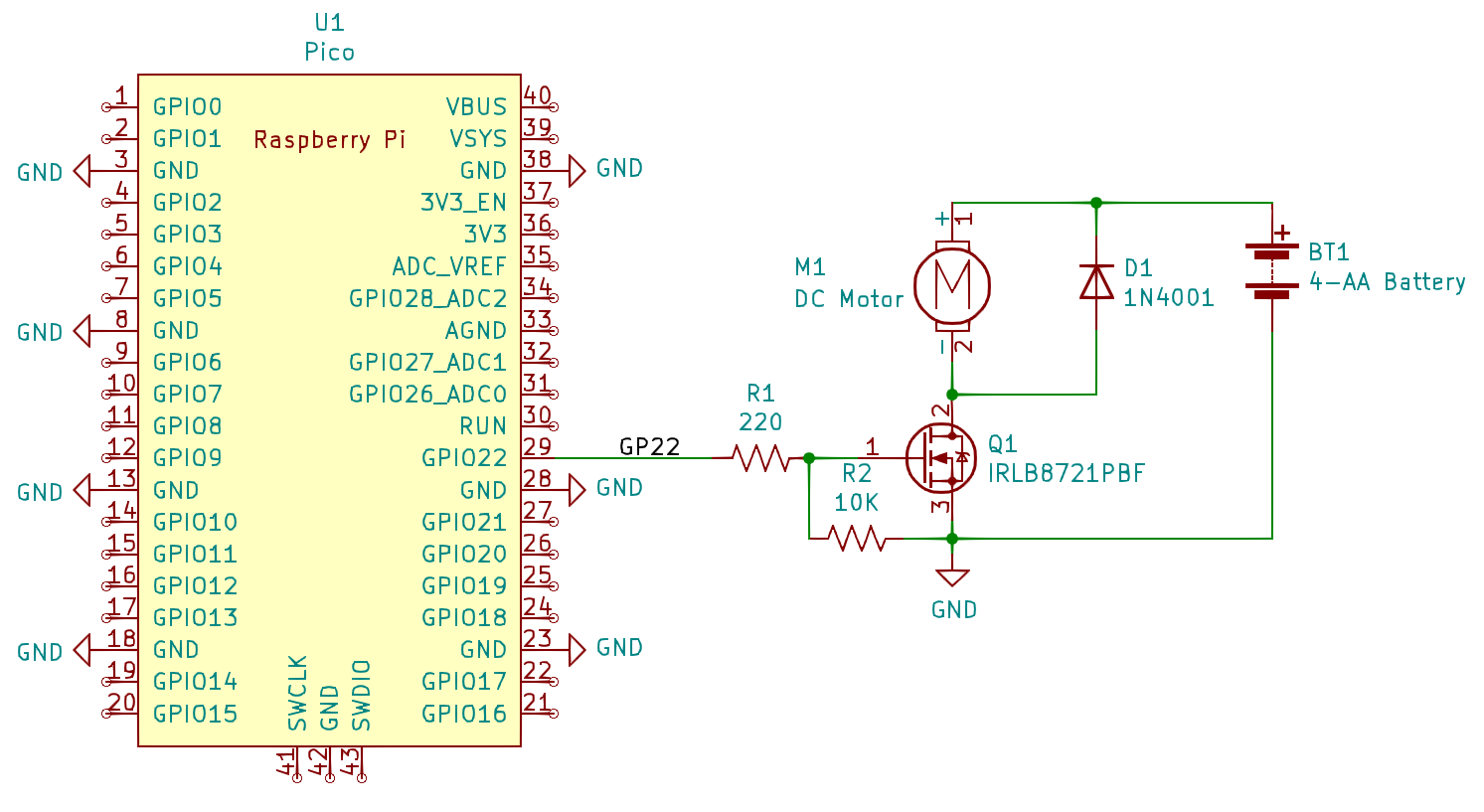
Sample MOSFET driver circuit. Note that any GPIO pin may be used to control the IRLB8721PBF MOSFET transistor driver. The circuit is shown with a battery for motor power, but a an 5 or 12V adapter is also suitable if appropriate for the chosen motor. Please be careful with the power wiring, motor voltages can destroy the Pico. The IRLB8721PBF is specifically selected because it will operate with the Pico 3.3V output signals.¶
Sample DRV8833 Motor Driver Circuit¶
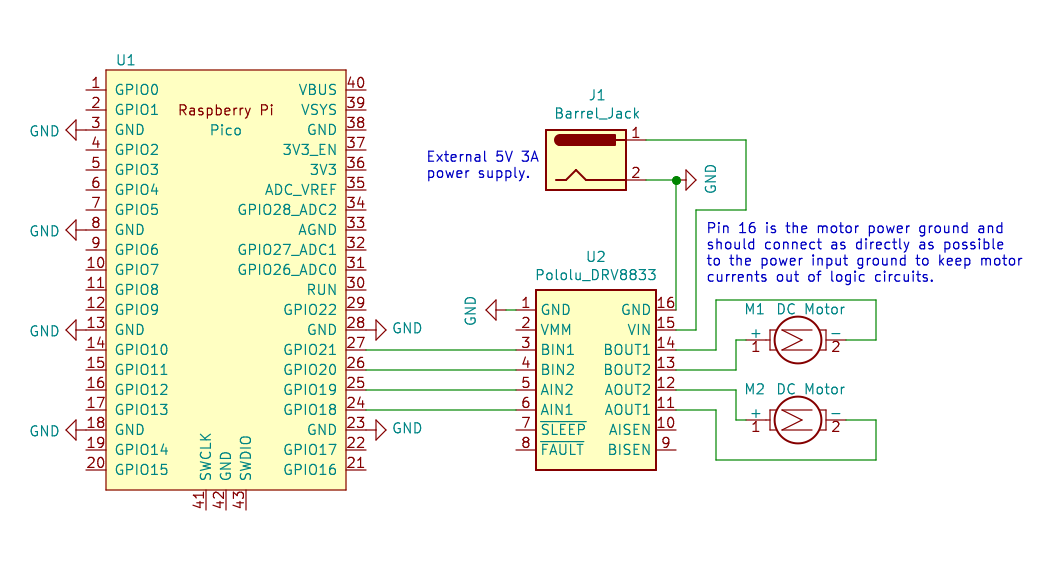
Sample driver circuit. Note that any four GPIO pins may be used to control the DRV8833 dual motor driver. Please be careful with the power wiring, motor voltages can destroy the Pico.¶
Pump Control Example¶
This self-contained example operates one DC motor in a single direction at variable speed. This is usually all that is needed for operating pumps or fans. For bidirectional control, please see the DRV8833 examples. The example uses GP22 for output, but any of the GPIO outputs can be programmed for pulse-width-modulation (PWM) output.
Direct download: pump_control.py.
1# pump_control.py
2
3# Demonstrate variable-speed single-directional control of a DC motor driven via
4# a MOSFET transistor driver circuit. For a reversible motion, please see the
5# DRV8833 example, but some applications (e.g. pumps and fans) only require a
6# single direction of rotation at variable speed.
7
8# Related documentation:
9# https://circuitpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/shared-bindings/pwmio/index.html#module-pwmio
10
11# ----------------------------------------------------------------
12# Import standard Python modules.
13import time, math
14
15# Load the CircuitPython hardware definition module for pin definitions.
16import board
17
18# Load the CircuitPython pulse-width-modulation module for driving hardware.
19import pwmio
20
21# ----------------------------------------------------------------
22# Initialize hardware.
23
24# Create a PWMOut object on GP22. This will create a pulsing signal with
25# variable duty cycle. The switching rate of 20kHz is chosen to be
26# supra-audible.
27pwm = pwmio.PWMOut(board.GP22, duty_cycle=0, frequency=20000)
28
29# Utility function to calculate and apply a new duty cycle setting. Converts a
30# unit-range (0.0 to 1.0) pwm_level to a 16-bit integer representing a fraction
31# needed by the PWM driver.
32def set_motor_speed(pwm_device, pwm_level):
33 pwm_device.duty_cycle = min(max(int(pwm_level * 2**16), 0), 2**16-1)
34 print("Applied duty cycle of %d for pwm_level %f" % (pwm_device.duty_cycle, pwm_level))
35
36# ----------------------------------------------------------------
37# Enter the main event loop.
38while True:
39
40 # Turn the motor on halfway.
41 set_motor_speed(pwm, 0.5)
42 time.sleep(1.0)
43
44 # Turn the motor off again.
45 set_motor_speed(pwm, 0.0)
46 time.sleep(1.0)
47
48 # Turn the motor on a little faster.
49 set_motor_speed(pwm, 0.75)
50 time.sleep(1.0)
51
52 # Turn the motor off again.
53 set_motor_speed(pwm, 0.0)
54 time.sleep(1.0)
55
56 # Turn the motor full.
57 set_motor_speed(pwm, 1.0)
58 time.sleep(1.0)
59
60 # Turn the motor off again.
61 set_motor_speed(pwm, 0.0)
62 time.sleep(1.0)
Dual Spin Example¶
This self-contained example operates two small DC motors.
Direct download: dual_spin.py.
1# dual_spin.py
2#
3# Raspberry Pi Pico - DC motor motion demo
4#
5# Demonstrates operating two DC motors driven by a DRV8833.
6#
7# This assumes a Pololu DRV8833 dual motor driver has been wired up to the Pico as follows:
8# Pico pin 24, GPIO18 -> AIN1
9# Pico pin 25, GPIO19 -> AIN2
10# Pico pin 26, GPIO20 -> BIN2
11# Pico pin 27, GPIO21 -> BIN1
12# any Pico GND -> GND
13
14# DRV8833 carrier board: https://www.pololu.com/product/2130
15
16################################################################
17# CircuitPython module documentation:
18# time https://circuitpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/shared-bindings/time/index.html
19# math https://circuitpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/shared-bindings/math/index.html
20# board https://circuitpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/shared-bindings/board/index.html
21# pwmio https://circuitpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/shared-bindings/pwmio/index.html
22
23################################################################################
24# print a banner as reminder of what code is loaded
25print("Starting dual_spin script.")
26
27# load standard Python modules
28import math, time
29
30# load the CircuitPython hardware definition module for pin definitions
31import board
32
33# load the CircuitPython pulse-width-modulation module for driving hardware
34import pwmio
35
36#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
37# Class to represent a single dual H-bridge driver.
38
39class DRV8833():
40 def __init__(self, AIN1=board.GP18, AIN2=board.GP19, BIN2=board.GP20, BIN1=board.GP21, pwm_rate=20000):
41 # Create a pair of PWMOut objects for each motor channel.
42 self.ain1 = pwmio.PWMOut(AIN1, duty_cycle=0, frequency=pwm_rate)
43 self.ain2 = pwmio.PWMOut(AIN2, duty_cycle=0, frequency=pwm_rate)
44
45 self.bin1 = pwmio.PWMOut(BIN1, duty_cycle=0, frequency=pwm_rate)
46 self.bin2 = pwmio.PWMOut(BIN2, duty_cycle=0, frequency=pwm_rate)
47
48 def write(self, channel, rate):
49 """Set the speed and direction on a single motor channel.
50
51 :param channel: 0 for motor A, 1 for motor B
52 :param rate: modulation value between -1.0 and 1.0, full reverse to full forward."""
53
54 # convert the rate into a 16-bit fixed point integer
55 pwm = min(max(int(2**16 * abs(rate)), 0), 65535)
56
57 if channel == 0:
58 if rate < 0:
59 self.ain1.duty_cycle = pwm
60 self.ain2.duty_cycle = 0
61 else:
62 self.ain1.duty_cycle = 0
63 self.ain2.duty_cycle = pwm
64 else:
65 if rate < 0:
66 self.bin1.duty_cycle = pwm
67 self.bin2.duty_cycle = 0
68 else:
69 self.bin1.duty_cycle = 0
70 self.bin2.duty_cycle = pwm
71
72
73#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
74# Create an object to represent a dual motor driver.
75print("Creating driver object.")
76driver = DRV8833()
77
78#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
79# Begin the main processing loop. This is structured as a looping script, since
80# each movement primitive 'blocks', i.e. doesn't return until the action is
81# finished.
82
83print("Starting main script.")
84while True:
85 # initial pause
86 time.sleep(2.0)
87
88 print("Testing motor A.")
89 driver.write(0, 1.0)
90 time.sleep(2.0)
91
92 driver.write(0, 0.0)
93 time.sleep(2.0)
94
95 driver.write(0, -1.0)
96 time.sleep(2.0)
97
98 driver.write(0, 0.0)
99 time.sleep(2.0)
100
101 print("Testing motor B.")
102 driver.write(1, 1.0)
103 time.sleep(2.0)
104
105 driver.write(1, 0.0)
106 time.sleep(2.0)
107
108 driver.write(1, -1.0)
109 time.sleep(2.0)
110
111 driver.write(1, 0.0)
112 time.sleep(2.0)
113
114 print("Ramp test.")
115
116 for i in range(10):
117 driver.write(0, i*0.1)
118 driver.write(1, i*0.1)
119 time.sleep(0.5)
120
121 driver.write(0, 0.0)
122 driver.write(1, 0.0)
123 time.sleep(2.0)
124
125 for i in range(10):
126 driver.write(0, -i*0.1)
127 driver.write(1, -i*0.1)
128 time.sleep(0.5)
129
130 driver.write(0, 0.0)
131 driver.write(1, 0.0)
132 time.sleep(2.0)
drv8833 module¶
This module provides a class for controlling a DRV8833 dual H-bridge DC motor driver. This device can drive two low-power DC motor bidirectionally with variable speed. Note that this file will normally be copied to the top-level folder of the CIRCUITPY filesystem so it can be imported by other scripts.
- class drv8833.DRV8833¶
This class represents a single dual H-bridge driver. It configures four pins for PWM output and can be used to control two DC motors bidirectionally at variable speed.
N.B. this does not implement any other timing process, it simply sets motor PWM levels but does not apply feedback, duration, or trajectory.
Direct download: drv8833.py.
1# drv8833.py
2#
3# Raspberry Pi Pico - dual H-bridge motor driver support
4#
5# This module provides a class for controlling a DRV8833 dual H-bridge DC motor driver.
6# This device can drive two low-power DC motor bidirectionally with variable speed.
7#
8# A typical usage requires four digital outputs. The defaults assumes a Pololu
9# DRV8833 dual motor driver has been wired up to the Pico as follows:
10# Pico pin 24, GPIO18 -> AIN1
11# Pico pin 25, GPIO19 -> AIN2
12# Pico pin 26, GPIO20 -> BIN2
13# Pico pin 27, GPIO21 -> BIN1
14# any Pico GND -> GND
15
16# DRV8833 carrier board: https://www.pololu.com/product/2130
17
18################################################################
19# CircuitPython module documentation:
20# time https://circuitpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/shared-bindings/time/index.html
21# math https://circuitpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/shared-bindings/math/index.html
22# board https://circuitpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/shared-bindings/board/index.html
23# pwmio https://circuitpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/shared-bindings/pwmio/index.html
24#
25# Driver lifecycle documentation:
26# https://circuitpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/docs/design_guide.html#lifetime-and-contextmanagers
27#
28################################################################################
29# load standard Python modules
30import math, time
31
32# load the CircuitPython hardware definition module for pin definitions
33import board
34
35# load the CircuitPython pulse-width-modulation module for driving hardware
36import pwmio
37
38#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
39class DRV8833:
40 def __init__(self,
41 AIN1=board.GP18, AIN2=board.GP19, # control pins for motor A
42 BIN2=board.GP20, BIN1=board.GP21, # control pins for motor B
43 pwm_rate=20000):
44 """This class represents a single dual H-bridge driver. It configures four pins
45 for PWM output and can be used to control two DC motors bidirectionally
46 at variable speed.
47
48 N.B. this does not implement any other timing process, it simply sets
49 motor PWM levels but does not apply feedback, duration, or trajectory.
50 """
51 self.ain1 = pwmio.PWMOut(AIN1, duty_cycle=0, frequency=pwm_rate)
52 self.ain2 = pwmio.PWMOut(AIN2, duty_cycle=0, frequency=pwm_rate)
53
54 self.bin1 = pwmio.PWMOut(BIN1, duty_cycle=0, frequency=pwm_rate)
55 self.bin2 = pwmio.PWMOut(BIN2, duty_cycle=0, frequency=pwm_rate)
56
57 def write(self, channel, rate):
58 """Set the speed and direction on a single motor channel.
59
60 :param int channel: 0 for motor A, 1 for motor B
61 :param float rate: modulation value between -1.0 and 1.0, full reverse to full forward."""
62
63 # convert the rate into a 16-bit fixed point integer
64 pwm = min(max(int(2**16 * abs(rate)), 0), 65535)
65
66 if channel == 0 or channel == 'A' or channel == 'a':
67 if rate < 0:
68 self.ain1.duty_cycle = pwm
69 self.ain2.duty_cycle = 0
70 else:
71 self.ain1.duty_cycle = 0
72 self.ain2.duty_cycle = pwm
73 else:
74 if rate < 0:
75 self.bin1.duty_cycle = pwm
76 self.bin2.duty_cycle = 0
77 else:
78 self.bin1.duty_cycle = 0
79 self.bin2.duty_cycle = pwm
80
81 def deinit(self):
82 """Manage resource release as part of object lifecycle."""
83 self.ain1.deinit()
84 self.ain2.deinit()
85 self.bin1.deinit()
86 self.bin2.deinit()
87 self.ain1 = None
88 self.ain2 = None
89 self.bin1 = None
90 self.bin2 = None
91
92 def __enter__(self):
93 return self
94
95 def __exit__(self):
96 # Automatically deinitializes the hardware when exiting a context.
97 self.deinit()
98