About water jet cutter
A water jet cutter, also known as a water jet or waterjet, is an industrial tool capable of cutting a wide variety of materials using a very high‐pressure jet of water, or a mixture of water with an abrasive substance.
The term abrasive jet refers specifically to the use of a mixture of water and abrasive to cut hard materials, such as metal or granite, while the terms pure waterjet and water‐only cutting refer to waterjet cutting without any use of added abrasives, often used for softer materials, such as food or rubber.
Waterjet cutting is often used while manufacturing machine parts. It is the preferred method when the materials being cut are sensitive to the high temperatures generated by other methods. Waterjet cutting is used in various industries, including mining and aerospace, for cutting, shaping, and reaming operations.

Advantages:
- Waterjet cutting doesn’t affect a material’s basic makeup, it creates no heat along its cut path to affect the material’s original integrity
- Waterjet cutting doesn’t have the material limitations of other methods, both in variety of material and thickness
- Waterjet cutting can produce remarkably complex cuts with up to 5 axis axes of motion
- Waterjet cutting has a small cut kerf so material loss is greatly minimized
- Waterjet cutting can produce high depth-to-diameter ratio through holes that won’t damage threading taps
- Waterjet cutting can achieve high accuracy parts while being able to obtain almost square inside corners when needed
- Waterjet cutting can cut a wide range of materials such as steel, titanium, aluminum, and fiberglass up to 12″ thick
How a waterjet works
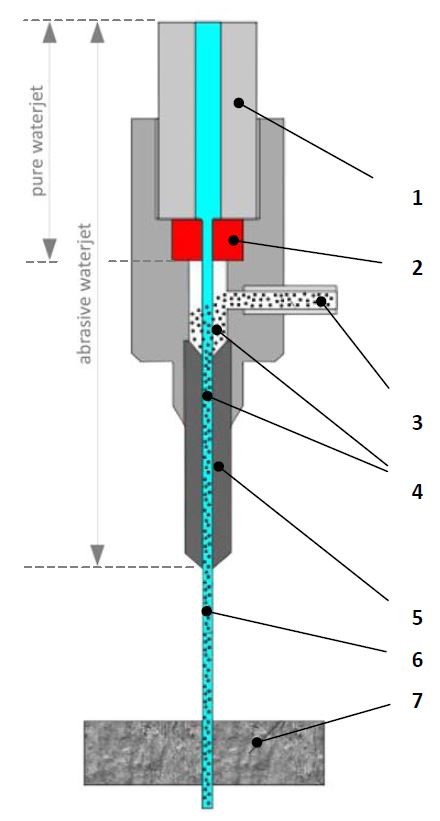
(1)High‐pressure Water Inlet
High pressure is produced by a pressure intensifier.
(2)Primary Nozzle (“Orifice”, “Jewel”)
The primary nozzle transforms the water pressure energy into kinetic energy and is made of synthetic sapphire or diamond, with a diameter from 0.2 to 0.5 mm; the water is transformed into a stream with a speed of up to 900 m/s—one traveling over 2,000 mph—depending on the pressure.
(3)Abrasive
Only used for cutting hard materials.
(4)Mixing Chamber and Focusing Tube
The mixing chamber and focuting tube is the place where the abrasive particles are mixed with water, accelerated and their path aligned in order to achieve a coherent jet.
(5)Focusing Nozzle
(6)Cutting Water Jet
(7)Cut Material
So then, a waterjet cutting machine operates by supplying up to 90,000+ psi water through a plumbing system to the cutting head. Inside the cutting head, a sapphire, ruby or diamond orifice restricts the high pressure water flow to a diameter ranging from 0.004″ to 0.020″. This focused stream of supersonic water is capable of cutting rubber, soft plastics, food, insulation, synthetic turf, carpet, and countless other soft materials. As most of these materials are so easily cut, a large number of waterjet systems purchased for cutting soft materials are configured with two or more cutting heads, thereby greatly increasing the production capability of the machine.
Harder materials can be cut when an abrasive powder, such as garnet, is mixed into the stream of water. To aid in this process, the abrasive cutting head incorporates a mixing chamber below the orifice. The flow of high pressure water through this chamber creates a venturi vacuum effect, which in turn draws the garnet powder into the stream. This abrasive-enriched waterjet stream is then re-focused by a mixing tube, which typically has an internal diameter between 0.020″ to 0.050″. The exiting abrasive stream produces a kerf width that is roughly the same size as the mixing tube ID and is ideal for cutting aluminum, steel, titanium, granite, composites, wood, glass, and many other materials.
Abrasive usage is typically between 0.5 to 2.0 pounds per minute, depending on the orifice/mixing tube combination, garnet mesh size, and the application’s requirements.
Location: 192 Bakery Square Blvd, Techshop.
