Flat-Pack Joinery¶
Joinery refers to techniques for rigidly connecting individual flat parts to build a structure. Moving connections are treated separately as joints.
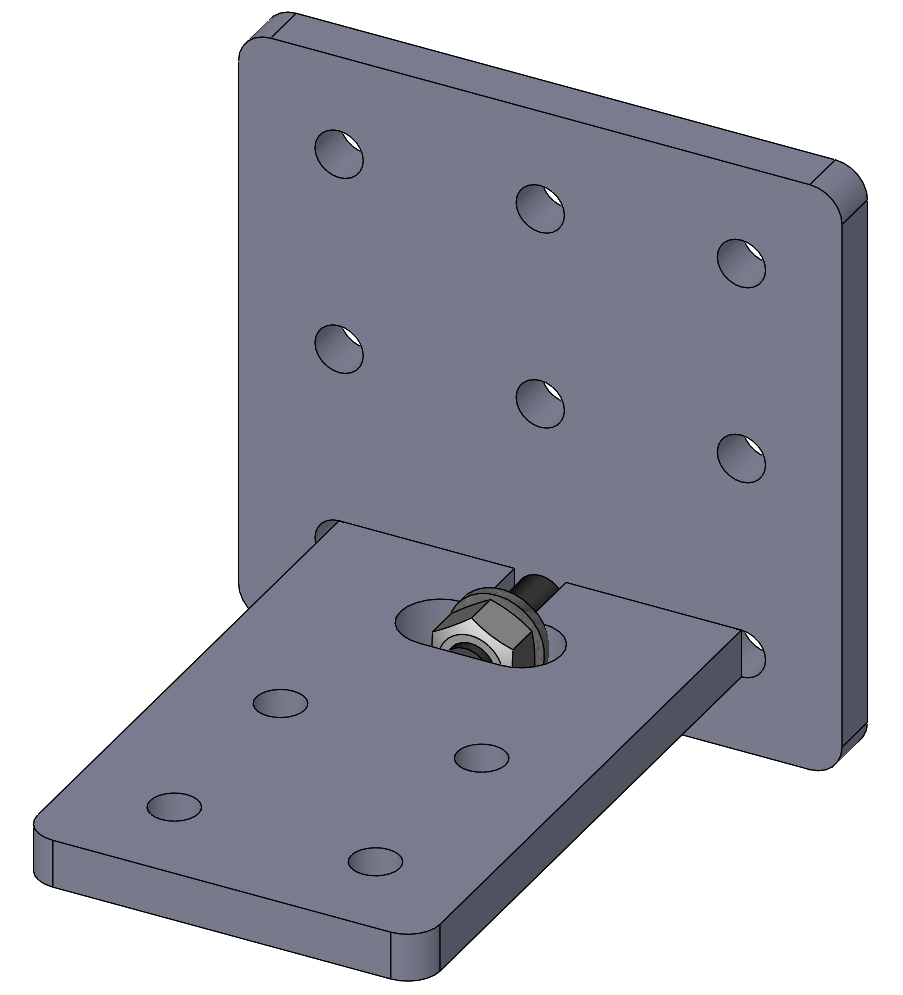
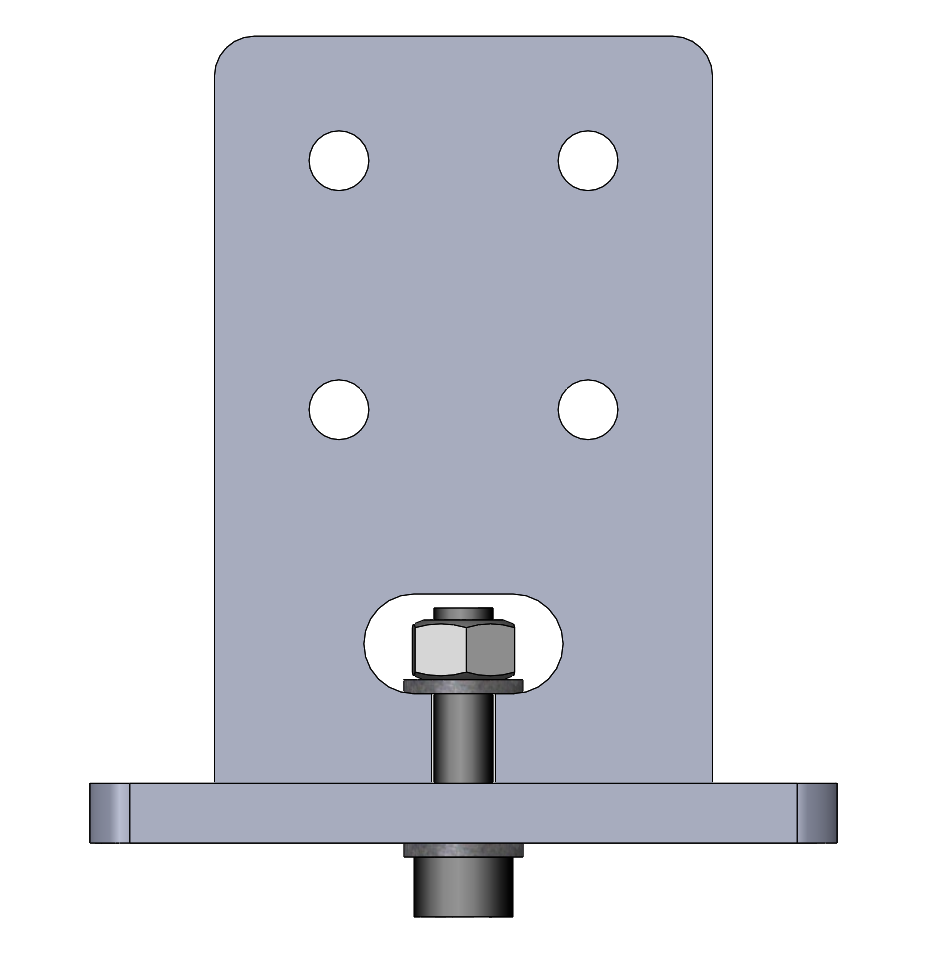
Captive-Screw Joints. The purpose of a captive-screw connection is to create a butt joint clamped by a screw and nut within the plane of one of the two parts. The primary advantages are a joint which can be tightly clamped with a wide tolerance for variations in material thickness. It can also be easily disassembled and re-assembled, and the fasteners re-used many times. The primary disadvantages are the weight and cost of steel fasteners, the need to provide access to the screw head and nut for tightening, and the weakness to resisting rotation around the screw axis.
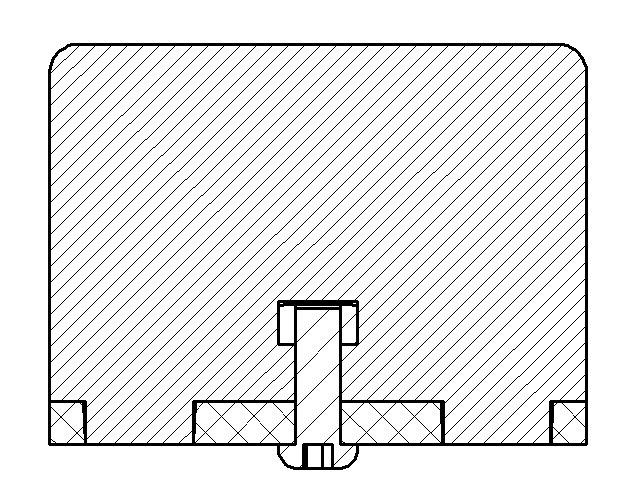
Laser-Cut Captive-Screw Mortise and Tenon¶
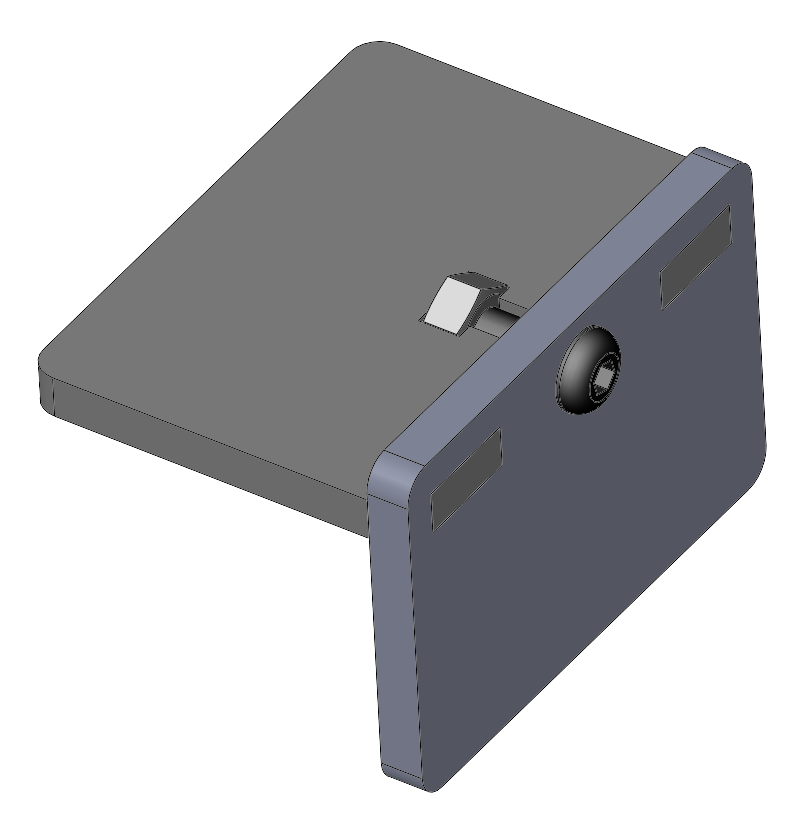
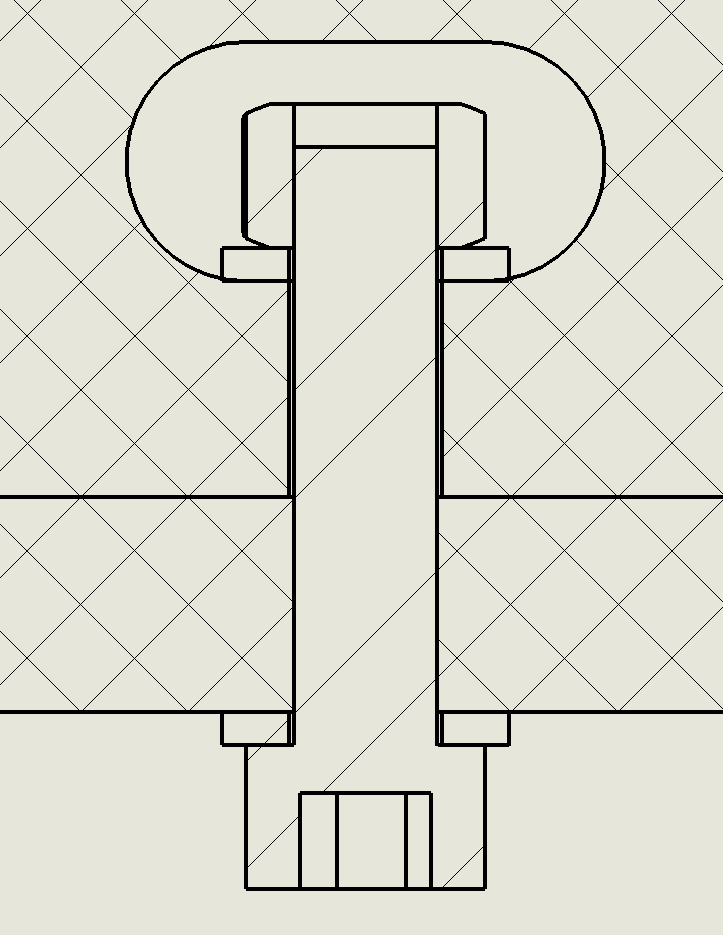
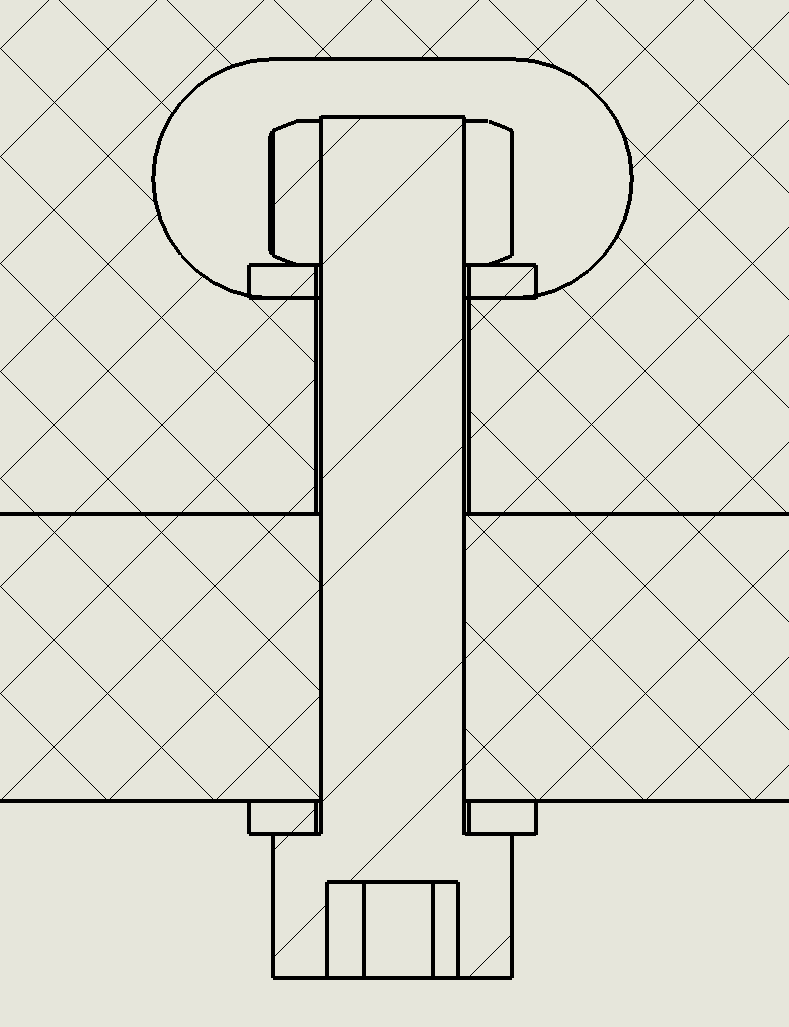
Example of a captive-screw connection incorporating two mortise and tenon joints. The captive screw slot is laser-cut to tightly fit a 1/4-20 nut.
This captive-screw joint includes a pair of press-fit mortise and tenon joints. Each tenon tongue is slightly tapered and can be tapped into the corresponding mortise slot. The screw clamps the two parts firmly together.
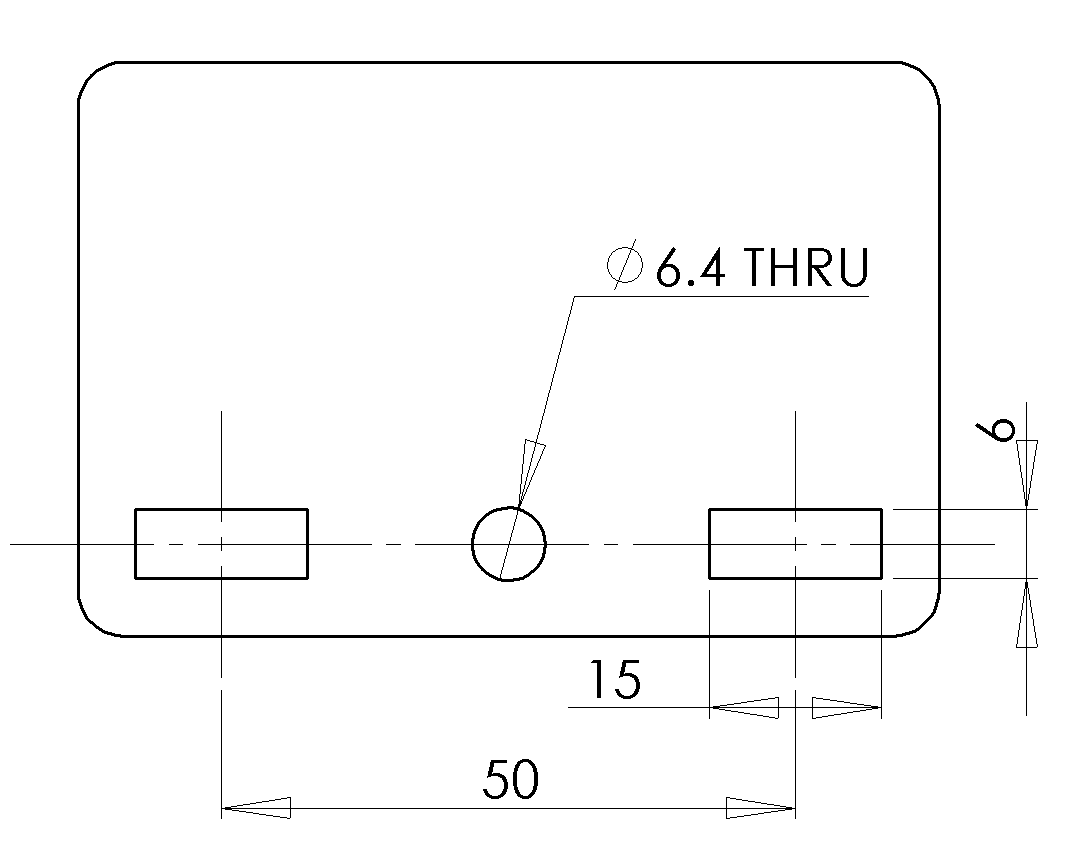
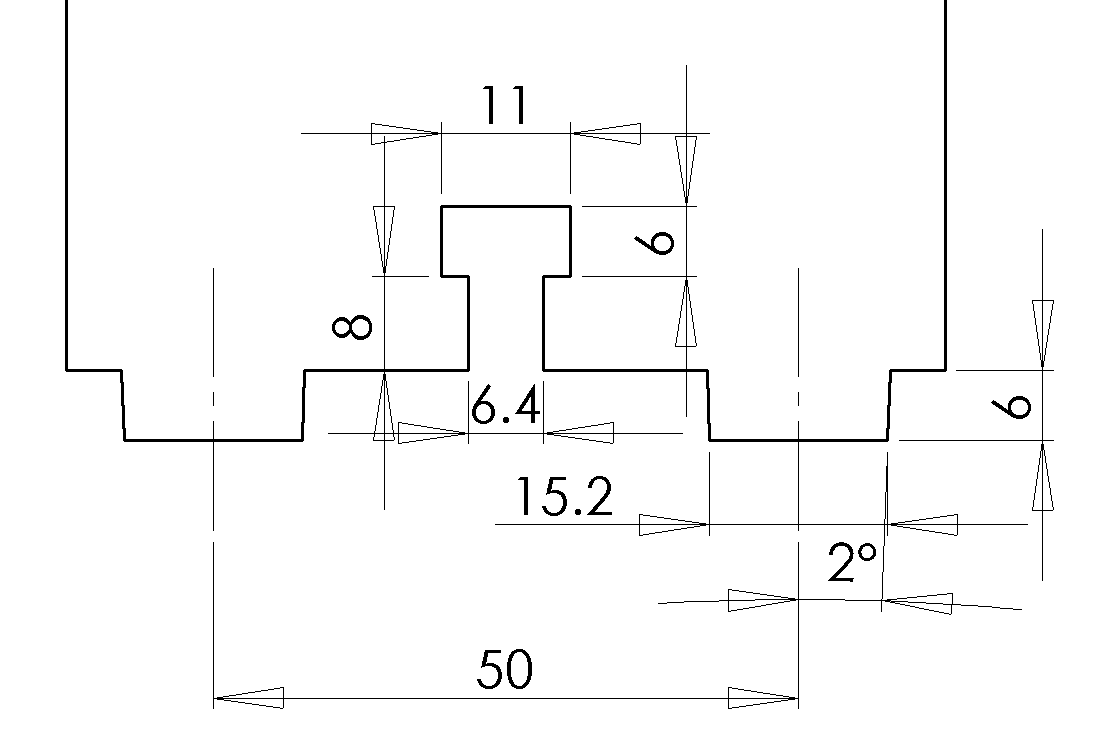
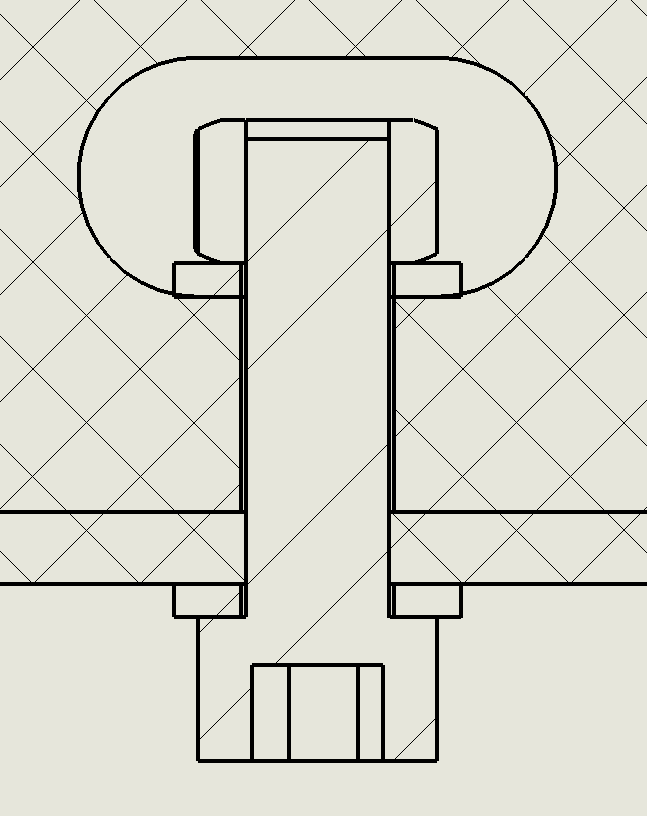
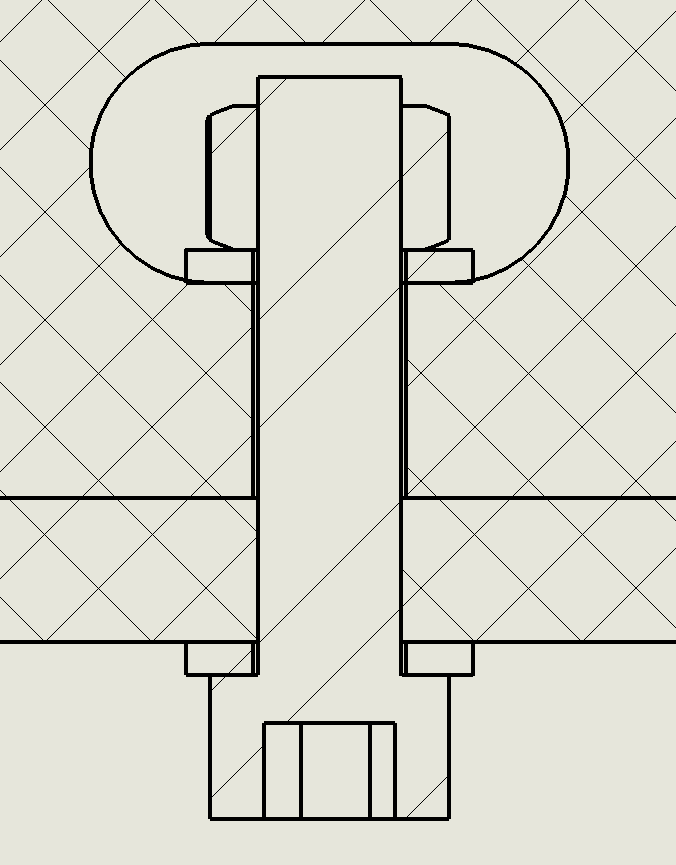
Typical dimensions for the features are shown below, assuming the use of 6 mm plywood stock and a 3/4” long 1/4-20 screw. Please note the 2 degree taper on the tenons.
CNC-Cut Captive-Screw Joinery¶
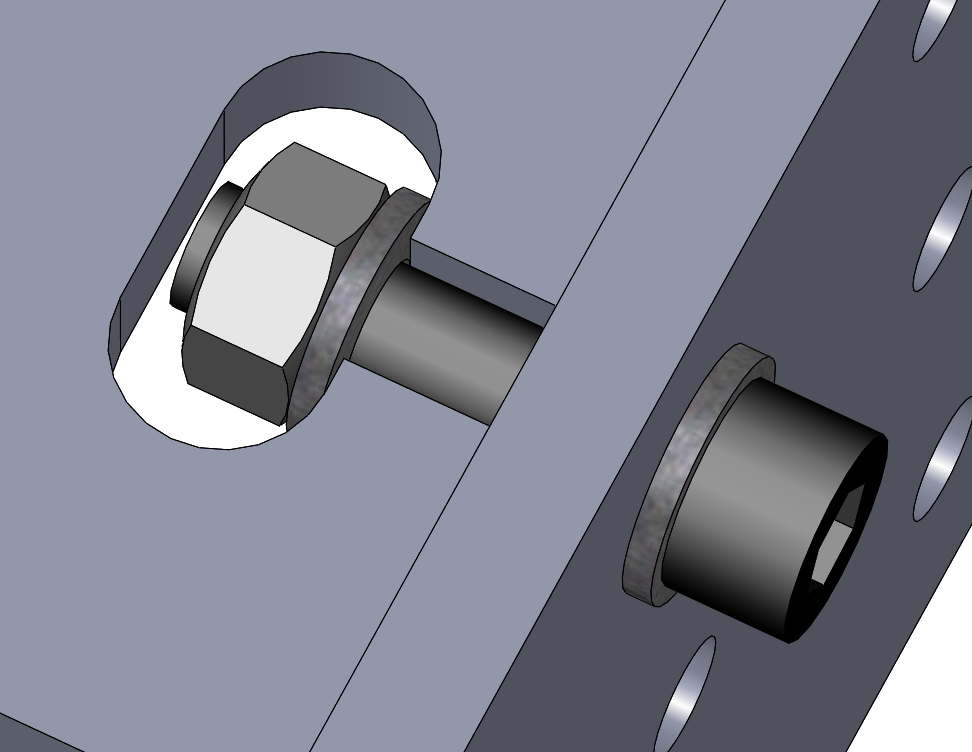
This example uses a circular slot geometry to maintain compatibility with milling and routing; the feature can be contour-routed with a 6.35 mm (1/4”) or smaller end mill. This approach takes more space than a tightly-fitting square slot design possible with the laser cutter. But a side benefit is avoiding stress concentrations at sharp inside corners. This example lacks the tenons and is susceptible to rotating out of place unless further constraint is provided.
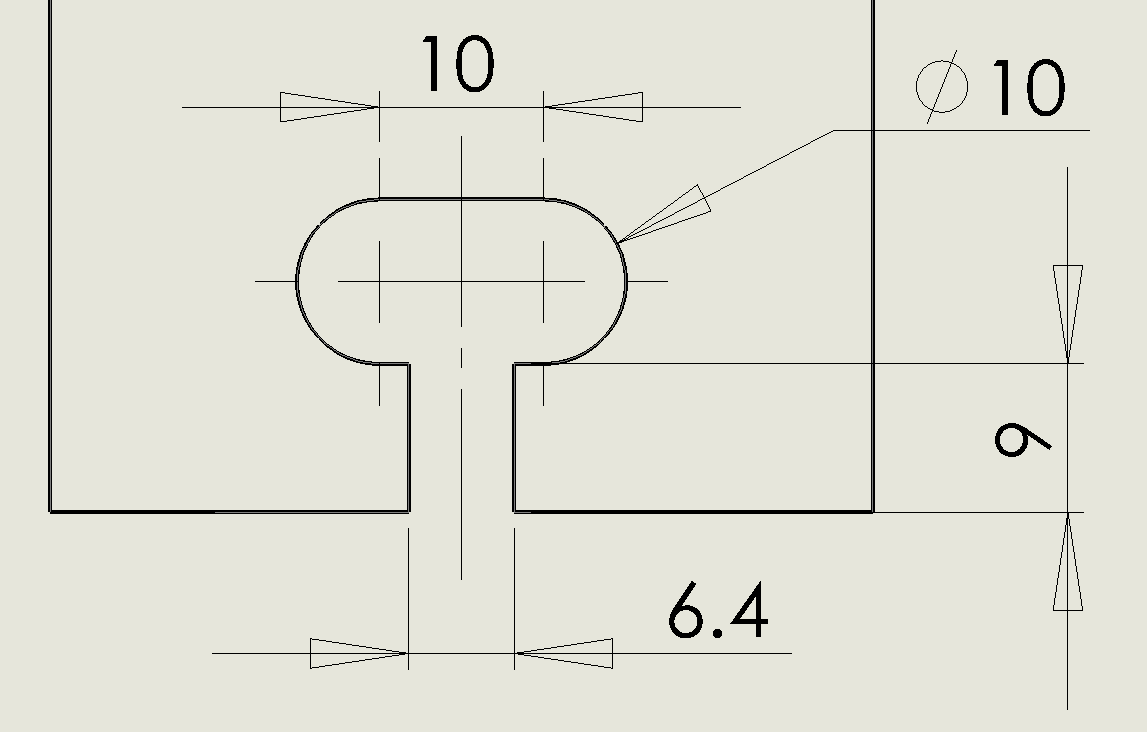
Typical dimensions for a captive-screw slot for a M6 or 1/4-20 screw. All dimensions are in millimeters.
Following are examples of captive-screw joints for different stock thicknesses. Washers are included to distribute the nut and head forces over wider faces of each end of the slot, although in some use cases they may be omitted:
The screw lengths are as follows:
Stock Screw 3 mm M6 x 20 6 mm M6 x 25 9 mm M6 x 25 12 mm M6 x 30
Note that the screw has a partial fit on the nut for the 9mm case, which could be improved by omitting a washer.
Standard Hole Patterns¶
(need sketch or photos for: standard hole pattern, lap-joint slot, etc.)
Other Online Resources¶
- Make magazine joinery tutorial
- 50 Digital Joints (mostly for 3-axis CNC, some for laser) (alternate link)(alternate link)(alternate link)
- Curved/Bending hard materials with Laser Cutter