Day 8: (Mon Sep 23, Week 5) Motor Puppets; Raspberry Pi Pico; Hobby Servos¶
Notes for 2024-09-23.
New Assignments¶
New assignment, due Mon Sep 30: Children’s School Classroom Observation Session. Please bring your notes on paper to class.
Please write a variation of the servo_step.py program (below) to produce a hobby servo motion pattern of your choice to be demonstrated at the start of the next class.
Administrative¶
Please note: for the next class on Wed Sep 25 we will be visiting the Children’s School for the entire class period. On Wednesday please meet at the south lobby of Margaret Morrison, one floor down from the rotunda entrance. Please be prompt, we will enter the MMC-17 secure school area precisely at 10:00AM.
Agenda¶
Review results of Exercise: Motor Puppet
Discussion of the observation assignment.
Brief introduction to the Raspberry Pi Pico and CircuitPython.
Each person pick up a Pico and a USB cable.
Installing the Mu Python Editor.
Crash course in CircuitPython basics.
Introduction to hobby servos.
Figures¶
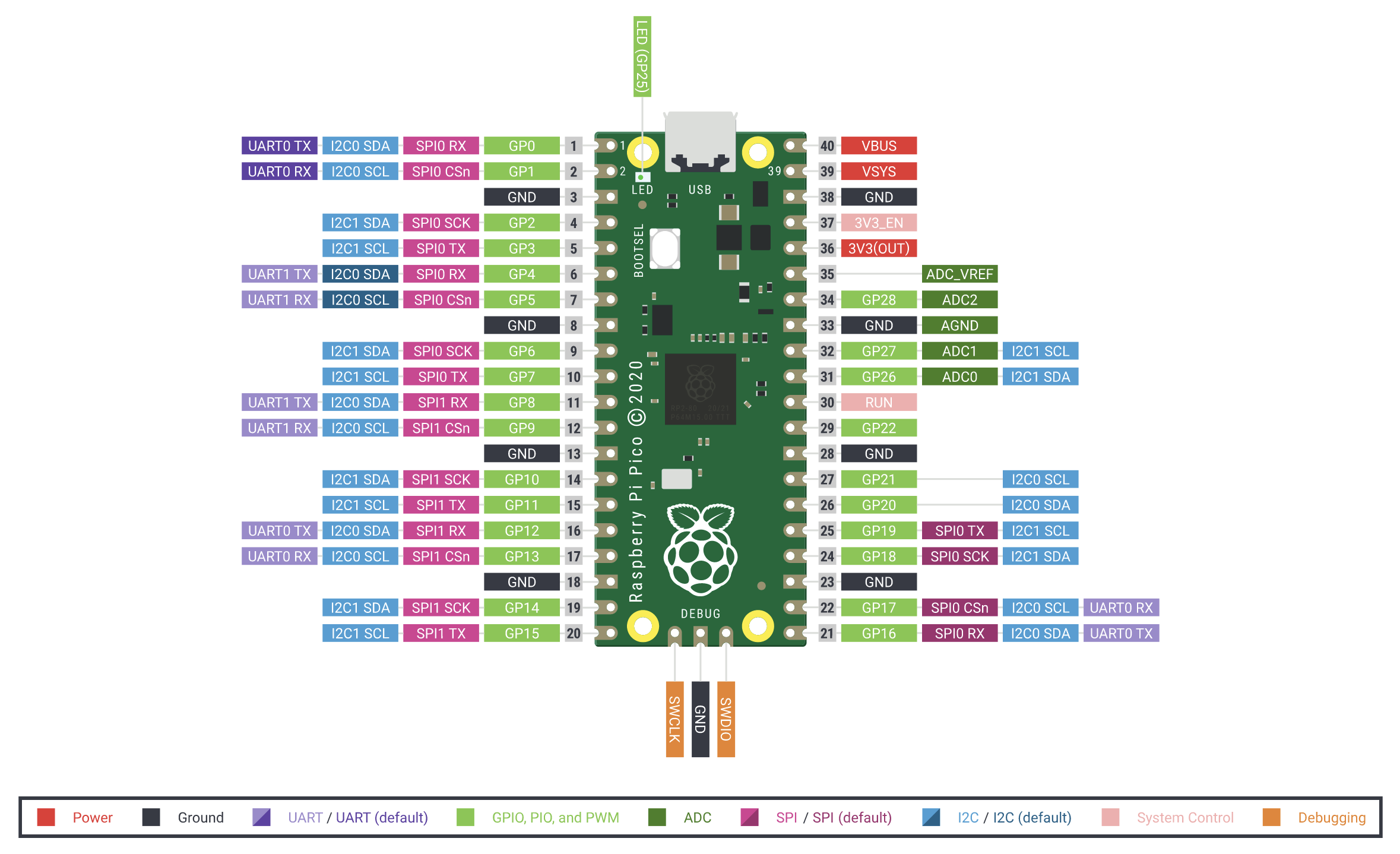
Lecture code samples¶
Blink¶
1# pico_blink.py
2
3# Raspberry Pi Pico - Blink demo
4
5# Blink the onboard LED and print messages to the serial console.
6
7import board
8import time
9from digitalio import DigitalInOut, Direction, Pull
10
11#---------------------------------------------------------------
12# Set up the hardware: script equivalent to Arduino setup()
13# Set up built-in green LED
14led = DigitalInOut(board.LED) # GP25
15led.direction = Direction.OUTPUT
16
17#---------------------------------------------------------------
18# Run the main loop: script equivalent to Arduino loop()
19
20while True:
21 led.value = True
22 print("On")
23 time.sleep(1.0)
24
25 led.value = False
26 print("Off")
27 time.sleep(1.0)
Servo Step¶
1# servo_step.py
2#
3# Raspberry Pi Pico - hobby servo motion demo
4#
5# Demonstrates stepping a hobby servo back and forth.
6#
7# This assumes a tiny 9G servo has been wired up to the Pico as follows:
8# Pico pin 40 (VBUS) -> servo red (+5V)
9# Pico pin 38 (GND) -> servo brown (GND)
10# Pico pin 1 (GP0) -> servo orange (SIG)
11
12# links to CircuitPython module documentation:
13# time https://circuitpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/shared-bindings/time/index.html
14# math https://circuitpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/shared-bindings/math/index.html
15# board https://circuitpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/shared-bindings/board/index.html
16# pwmio https://circuitpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/shared-bindings/pwmio/index.html
17
18################################################################################
19# load standard Python modules
20import math, time
21
22# load the CircuitPython hardware definition module for pin definitions
23import board
24
25# load the CircuitPython pulse-width-modulation module for driving hardware
26import pwmio
27
28#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
29# Define a function to issue a servo command by updating the PWM signal output.
30# This function maps an angle specified in degrees between 0 and 180 to a servo
31# command pulse width between 1 and 2 milliseconds, and then to the
32# corresponding duty cycle fraction, specified as a 16-bit fixed-point integer.
33
34def servo_write(servo, angle, debug=False):
35 # calculate the desired pulse width in units of seconds
36 pulse_width = 0.001 + angle * (0.001 / 180.0)
37
38 # fetch the current pulse repetition rate from the hardware driver
39 pulse_rate = servo.frequency
40
41 # calculate the duration in seconds of a single pulse cycle
42 cycle_period = 1.0 / pulse_rate
43
44 # calculate the desired ratio of pulse ON time to cycle duration
45 duty_cycle = pulse_width / cycle_period
46
47 # convert the ratio into a 16-bit fixed point integer
48 duty_fixed = int(2**16 * duty_cycle)
49
50 # limit the ratio range and apply to the hardware driver
51 servo.duty_cycle = min(max(duty_fixed, 0), 65535)
52
53 # print some diagnostics to the console
54 if debug:
55 print(f"Driving servo to angle {angle}")
56 print(f" Pulse width {pulse_width} seconds")
57 print(f" Duty cycle {duty_cycle}")
58 print(f" Command value {servo.duty_cycle}\n")
59
60#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
61# Create a PWMOut object on Pin GP0 to drive the servo. The frequency argument
62# specifies the pulse repetition rate in Hz (pulses per second).
63
64servo = pwmio.PWMOut(board.GP0, duty_cycle=0, frequency=50)
65
66# Begin the main processing loop.
67while True:
68 servo_write(servo, 0.0, debug=True)
69 time.sleep(2.0)
70
71 servo_write(servo, 180.0, debug=True)
72 time.sleep(2.0)