Group: Xin Hui Lim, Soonho Kwon, and Wade Lacey
Goals:
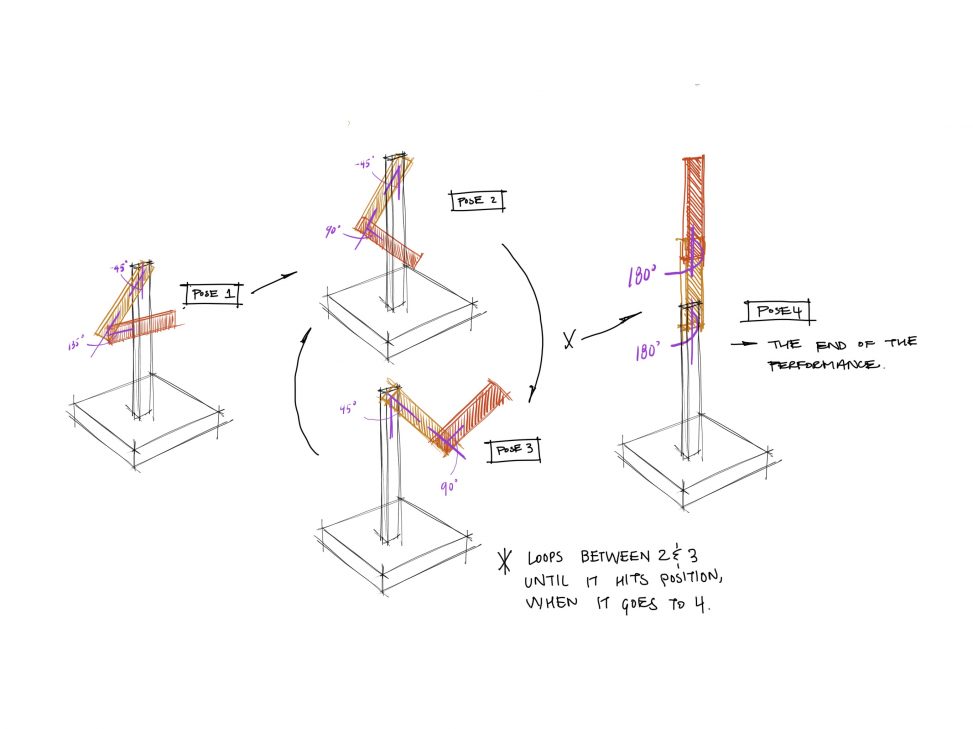
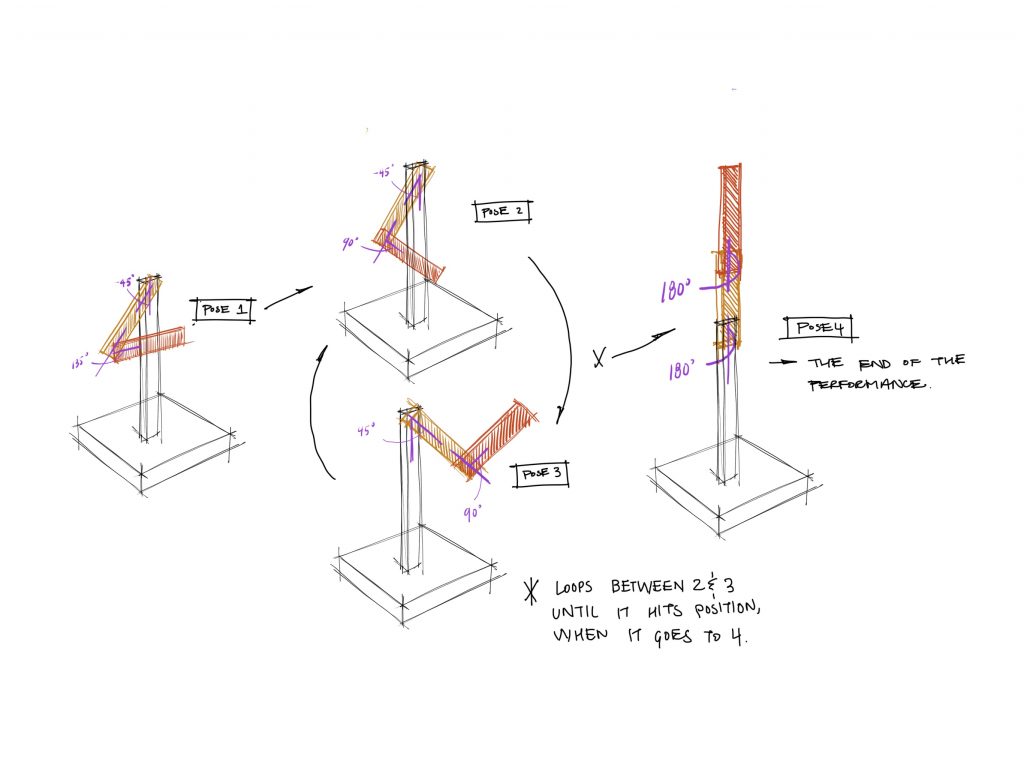
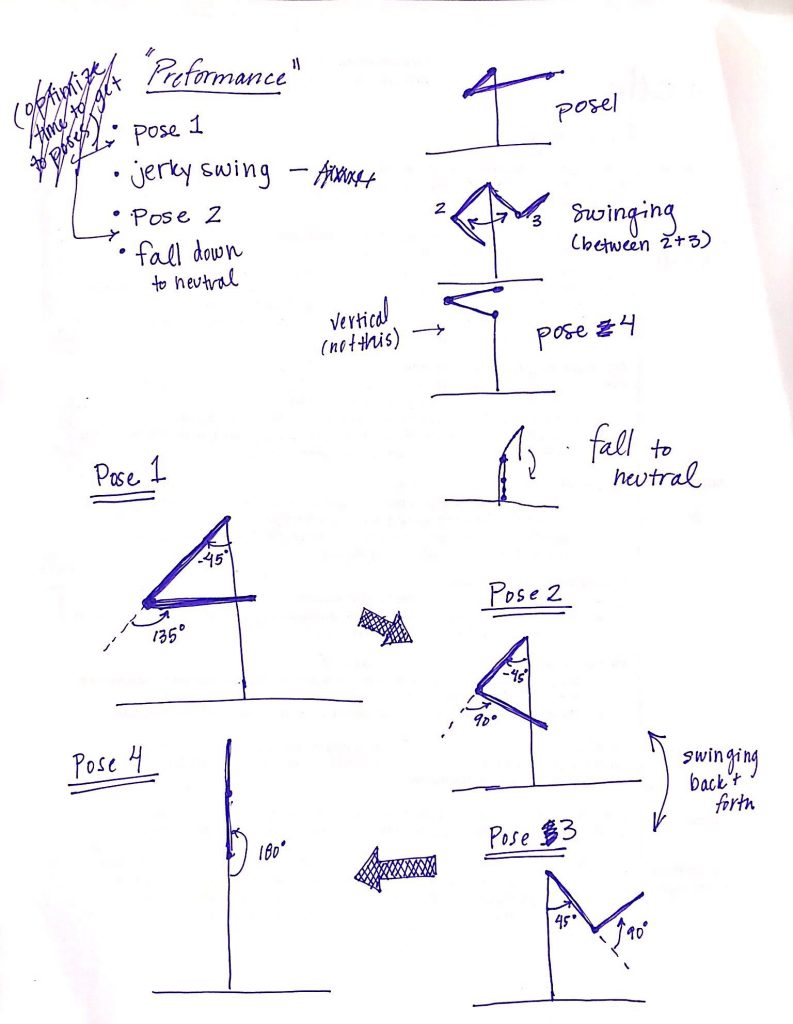
We wanted to simulate our double pendulum to go through four predetermined poses. For pose one the pedulum would move up to a bent pose and hold for five seconds before proceding. Then to make this cycle of movements more interesting we decided the simulation should move back and forth between the second and third pose an undefined number of times until it reached a specific position when then it could proceed onto the next pose, pose four. After the simulation reached pose four we then wanted it to fall back down to neutral. When the double pendulum goes back down to the neutral point the whole process will restart. To incorporate the optimization, we decide to apply optimization techniques to the number of times the pendulum swings between pose two and three before reaching the position to trigger pose four.
Outcomes:
We got the simulation to progress through the poses as we had planned. The movement this created is acrobatic in a sense. To us it looks like a gymnast gaining momentum and propelling themself up into a vertical handstand above the bar. Then returning to neutral by swining back down. Next time learning to get better and better or more efficient at propelling itself up into and through the vertical position.
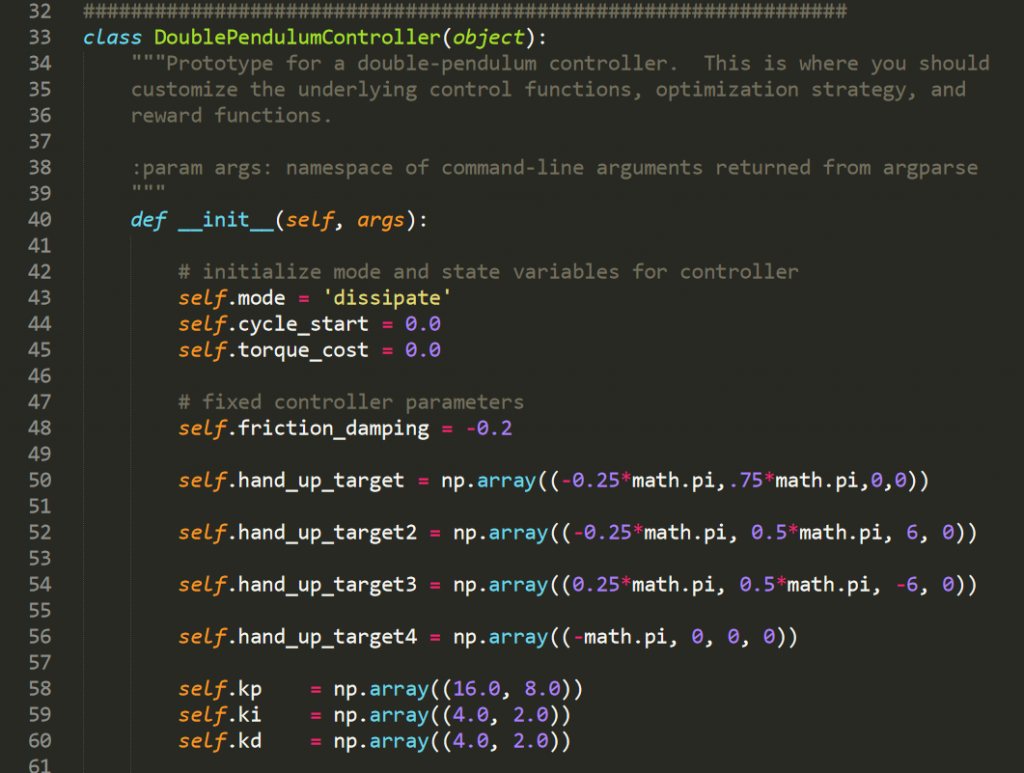
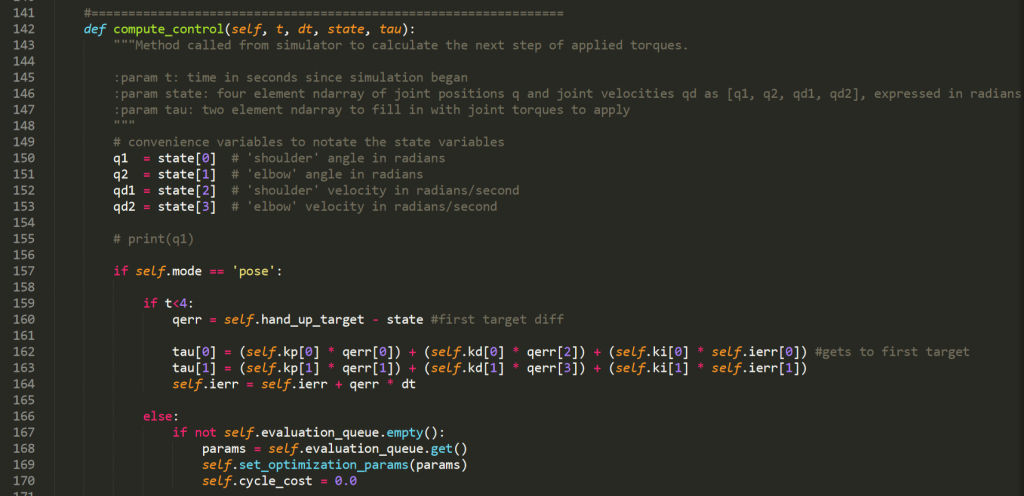
Final Code:
Defining the 4 poses or targets we wanted the double pendulum to move through.
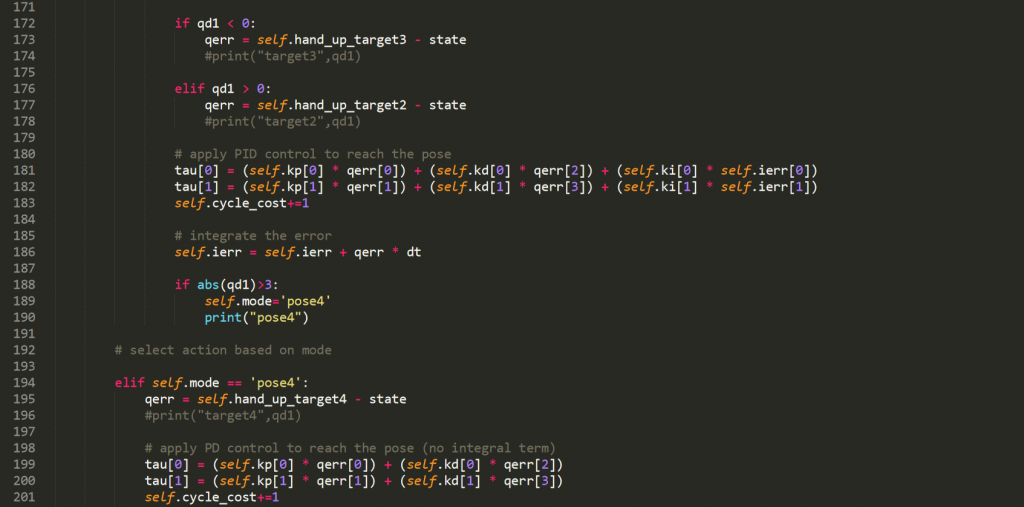
The code that gives the simulation the torques to move it to the poses we wanted in the order and manner desired. Use of PID and PD controllers to find the torques needed to get to the poses correctly. Optimization using cost function for the number of swings between pose 2 and 3 before moving on to pose 4.
Original plan sketch:
#Soonho Kwon, Xin Hui Lim, Wade Lacey
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# Enable basic compatibility features to work with either Python 2 or 3.
from __future__ import print_function, absolute_import, unicode_literals
# Standard library modules.
import math, time, argparse, threading, queue
# Third-party library modules.
import numpy as np
import time
# Use the scipy fmin optimizer if available.
# ref: https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/generated/scipy.optimize.fmin.html
try:
import scipy.optimize
have_optimizer = True
except ImportError:
print("Unable to load scipy.optimize.")
have_optimizer = False
# This uses python-osc to communicate with a Max/MSP patch.
# installation: pip3 install python-osc
# source code: https://github.com/attwad/python-osc
# pypi description: https://pypi.org/project/python-osc/
from pythonosc import udp_client
from pythonosc import dispatcher
from pythonosc import osc_server
################################################################
class DoublePendulumController(object):
"""Prototype for a double-pendulum controller. This is where you should
customize the underlying control functions, optimization strategy, and
reward functions.
:param args: namespace of command-line arguments returned from argparse
"""
def __init__(self, args):
# initialize mode and state variables for controller
self.mode = 'dissipate'
self.cycle_start = 0.0
self.cycle_cost = 0.0
# fixed controller parameters
self.friction_damping = -0.2
self.hand_up_target = np.array((-0.25*math.pi,.75*math.pi,0,0))
self.hand_up_target2 = np.array((-0.25*math.pi, 0.5*math.pi, 6, 0))
self.hand_up_target3 = np.array((0.25*math.pi, 0.5*math.pi, -6, 0))
self.hand_up_target4 = np.array((-math.pi, 0, 0, 0))
self.kp = np.array((16.0, 8.0))
self.ki = np.array((4.0, 2.0))
self.kd = np.array((4.0, 2.0))
# integrated error
self.ierr = np.array((0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0))
# keep track of the worst case cost to know when to cancel a trial
self.worst_cost = None
# Construct default parameter vector for the optimization problem. This
# builds a single array with all the default parameter values. See the
# set_optimization_params() method to update the mapping from parameter
# vector back to controller parameters.
self.default_params = np.hstack((self.kp, self.ki, self.kd))
# launch a thread to run the optimizer as a co-routine
self.evaluation_queue = queue.Queue() # next parameter array to evaluate
self.result_queue = queue.Queue() # next computed cost value
self.optimizer_thread = threading.Thread(target=self.optimizer_task)
self.optimizer_thread.daemon = True
self.optimizer_thread.start()
return
#================================================================
def message(self, msgaddr, *args):
"""Process messages from the Max/MSP display received via OSC over UDP.
:param msgaddr: the address string of the OSC message, eg '/control/mode'
:param args: tuple of OSC message arguments
"""
print("Controller received message %s: %s" % (msgaddr, args))
if msgaddr == "/control/kp1":
self.kp[0] = args[0]
elif msgaddr == "/control/kd1":
self.kd[0] = args[0]
elif msgaddr == "/control/mode":
self.mode = args[0]
#================================================================
def optimizer_task(self):
"""Entry point for starting the optimizer on a background thread. It communicates with the simulator using a pair of queues."""
print("Starting optimizer thread.")
if have_optimizer:
result = scipy.optimize.fmin(func=self.optimizer_eval, x0=self.default_params)
print("Optimizer finished:", result)
else:
print("Optimizer not available, evaluating default parameters.")
result = self.optimizer_eval(self.default_params)
return
def optimizer_eval(self, params):
"""Optimizer callback function to evaluate a parameter vector. This pushes the
vector into a queue and blocks the optimizer thread waiting for a cost result.
:param params: numpy ndarray for the optimization problem parameters
:returns: a scalar cost value
"""
print("Optimizer requesting evaluation of:", params)
self.evaluation_queue.put(params)
# wait for result
cost = self.result_queue.get()
print("Trial yielded cost:", cost)
return cost
def set_optimization_params(self, params):
"""Configure controller gains for a single trial of the optimization problem.
Called from within the controller state machine when a new parameter
vector is received for evaluation.
:param params: numpy ndarray of optimization parameters
"""
self.kp = params[0:2]
self.ki = params[2:4]
self.kd = params[4:6]
print("Set optimization params: kp is %s, ki is %s, kd is %s" % (self.kp, self.ki, self.kd))
return
#================================================================
def compute_control(self, t, dt, state, tau):
"""Method called from simulator to calculate the next step of applied torques.
:param t: time in seconds since simulation began
:param state: four element ndarray of joint positions q and joint velocities qd as [q1, q2, qd1, qd2], expressed in radians and radians/sec
:param tau: two element ndarray to fill in with joint torques to apply
"""
# convenience variables to notate the state variables
q1 = state[0] # 'shoulder' angle in radians
q2 = state[1] # 'elbow' angle in radians
qd1 = state[2] # 'shoulder' velocity in radians/second
qd2 = state[3] # 'elbow' velocity in radians/second
# print(q1)
if self.mode == 'pose':
if t<4:
qerr = self.hand_up_target - state #first target diff
tau[0] = (self.kp[0] * qerr[0]) + (self.kd[0] * qerr[2]) + (self.ki[0] * self.ierr[0]) #gets to first target
tau[1] = (self.kp[1] * qerr[1]) + (self.kd[1] * qerr[3]) + (self.ki[1] * self.ierr[1])
self.ierr = self.ierr + qerr * dt
else:
if not self.evaluation_queue.empty():
params = self.evaluation_queue.get()
self.set_optimization_params(params)
self.cycle_cost = 0.0
if qd1 < 0:
qerr = self.hand_up_target3 - state
#print("target3",qd1)
elif qd1 > 0:
qerr = self.hand_up_target2 - state
#print("target2",qd1)
# apply PID control to reach the pose
tau[0] = (self.kp[0] * qerr[0]) + (self.kd[0] * qerr[2]) + (self.ki[0] * self.ierr[0])
tau[1] = (self.kp[1] * qerr[1]) + (self.kd[1] * qerr[3]) + (self.ki[1] * self.ierr[1])
self.cycle_cost+=1
# integrate the error
self.ierr = self.ierr + qerr * dt
if abs(qd1)>3:
self.mode='pose4'
print("pose4")
# select action based on mode
elif self.mode == 'pose4':
qerr = self.hand_up_target4 - state
#print("target4",qd1)
# apply PD control to reach the pose (no integral term)
tau[0] = (self.kp[0] * qerr[0]) + (self.kd[0] * qerr[2])
tau[1] = (self.kp[1] * qerr[1]) + (self.kd[1] * qerr[3])
self.cycle_cost+=1
if abs(qerr[0])<0.1:
self.mode='home'
print('home')
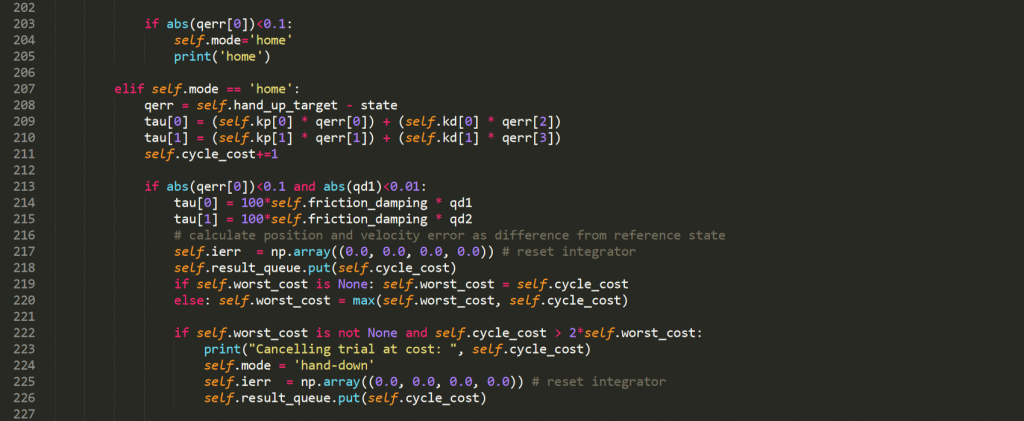
elif self.mode == 'home':
qerr = self.hand_up_target - state
tau[0] = (self.kp[0] * qerr[0]) + (self.kd[0] * qerr[2])
tau[1] = (self.kp[1] * qerr[1]) + (self.kd[1] * qerr[3])
self.cycle_cost+=1
if abs(qerr[0])<0.1 and abs(qd1)<0.01:
tau[0] = 100*self.friction_damping * qd1
tau[1] = 100*self.friction_damping * qd2
# calculate position and velocity error as difference from reference state
self.ierr = np.array((0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0)) # reset integrator
self.result_queue.put(self.cycle_cost)
if self.worst_cost is None: self.worst_cost = self.cycle_cost
else: self.worst_cost = max(self.worst_cost, self.cycle_cost)
if self.worst_cost is not None and self.cycle_cost > 2*self.worst_cost:
print("Cancelling trial at cost: ", self.cycle_cost)
self.mode = 'hand-down'
self.ierr = np.array((0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0)) # reset integrator
self.result_queue.put(self.cycle_cost)
print("end of cycle")
self.mode = 'pose'
else: # free-swinging, no torques
tau[0] = 0.0
tau[1] = 0.0
# accumulate sum of squared torques cost
#self.torque_cost += tau.dot(tau)
return
################################################################
class DoublePendulumSimulator(object):
"""Dynamic simulation of a frictionless double pendulum. This object can send
state updates to an external server for rendering. It communicates with a
user-supplied control object to compute applied joint torques.
:param args: namespace of command-line arguments returned from argparse
:param cartoon: python-osc UDP client object for sending messages to GUI
:param control: instance of DoublePendulumControl for computing applied torques
"""
def __init__(self, args, cartoon, control):
# save the OSC client object used to update the display
self.cartoon = cartoon
# save the object used to calculate joint torques
self.control = control
# save selected command line flags
self.verbose = args.verbose
self.fast = args.fast
# set default dynamics
self.set_default_dynamic_parameters()
# configure transient state
self.reset()
return
def reset(self):
"""Reset or initialize all simulator state variables."""
self.t = 0.0
self.dt = 0.001
self.state = np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
self.tau = np.array([0.0, 0.0])
self.dydt = np.ndarray((4,))
return
def set_default_dynamic_parameters(self):
"""Set the default dynamics coefficients defining the rigid-body model physics."""
self.l1 = 1.0 # proximal link length, link1
self.l2 = 1.0 # distal link length, link2
self.lc1 = 0.5 # distance from proximal joint to link1 COM
self.lc2 = 0.5 # distance from distal joint to link2 COM
self.m1 = 1.0 # link1 mass
self.m2 = 1.0 # link2 mass
self.I1 = (self.m1 * self.l1**2) / 12 # link1 moment of inertia
self.I2 = (self.m2 * self.l2**2) / 12 # link2 moment of inertia
self.gravity = -9.81
return
#================================================================
def deriv(self):
"""Calculate the accelerations for a rigid body double-pendulum dynamics model.
:returns: system derivative vector as a numpy ndarray
"""
q1 = self.state[0]
q2 = self.state[1]
qd1 = self.state[2]
qd2 = self.state[3]
LC1 = self.lc1
LC2 = self.lc2
L1 = self.l1
M1 = self.m1
M2 = self.m2
d11 = M1*LC1*LC1 + M2*(L1*L1 + LC2*LC2 + 2*L1*LC2*math.cos(q2)) + self.I1 + self.I2
d12 = M2*(LC2*LC2 + L1*LC2*math.cos(q2)) + self.I2
d21 = d12
d22 = M2*LC2*LC2 + self.I2
h1 = -M2*L1*LC2*math.sin(q2)*qd2*qd2 - 2*M2*L1*LC2*math.sin(q2)*qd2*qd1
h2 = M2*L1*LC2*math.sin(q2)*qd1*qd1
phi1 = -M2*LC2*self.gravity*math.sin(q1+q2) - (M1*LC1 + M2*L1) * self.gravity * math.sin(q1)
phi2 = -M2*LC2*self.gravity*math.sin(q1+q2)
# now solve the equations for qdd:
# d11 qdd1 + d12 qdd2 + h1 + phi1 = tau1
# d21 qdd1 + d22 qdd2 + h2 + phi2 = tau2
rhs1 = self.tau[0] - h1 - phi1
rhs2 = self.tau[1] - h2 - phi2
# Apply Cramer's Rule to compute the accelerations using
# determinants by solving D qdd = rhs. First compute the
# denominator as the determinant of D:
denom = (d11 * d22) - (d21 * d12)
# the derivative of the position is trivially the current velocity
self.dydt[0] = qd1
self.dydt[1] = qd2
# the derivative of the velocity is the acceleration.
# the numerator of qdd[n] is the determinant of the matrix in
# which the nth column of D is replaced by RHS
self.dydt[2] = ((rhs1 * d22 ) - (rhs2 * d12)) / denom
self.dydt[3] = (( d11 * rhs2) - (d21 * rhs1)) / denom
return self.dydt
#================================================================
def timer_tick(self, delta_t):
"""Run the simulation for an interval.
:param delta_t: length of interval in simulated time seconds
"""
while delta_t > 0:
# calculate next control outputs
self.control.compute_control(self.t, self.dt, self.state, self.tau)
# calculate dynamics model
qd = self.deriv()
# Euler integration
self.state = self.state + self.dt * qd
delta_t -= self.dt
self.t += self.dt
def update_display(self):
"""Send the current state to the GUI using a UDP OSC message."""
radian_to_degrees = 180.0 / math.pi
pose = (self.state[0]*radian_to_degrees, self.state[1]*radian_to_degrees)
self.cartoon.send_message("/q", pose)
if self.verbose: print("Position: ", pose)
return
def event_loop(self):
"""Simulator run loop; never exits."""
frame_interval = 0.040 if not self.fast else 10.0
while True:
self.timer_tick(frame_interval)
self.update_display()
if not self.fast: time.sleep(frame_interval)
#================================================================
# Methods to process messages from the Max/MSP display received via OSC over UDP.
def message(self, msgaddr, *args):
"""Process messages from the Max/MSP display received via OSC over UDP.
:param msgaddr: the address string of the OSC message, eg '/sim/verbose'
:param args: tuple of OSC message arguments
"""
print("Simulator received message %s: %s" % (msgaddr, args))
if msgaddr == "/sim/verbose":
self.verbose = (args[0] != 0)
def unknown_message(self, msgaddr, *args):
"""Default handler for unrecognized OSC messages."""
print("Simulator received unmapped message %s: %s" % (msgaddr, args))
################################################################
def start_osc_server(args, sim, control):
"""Start a background thread running an OSC server listening for messages on an UDP socket."""
# Initialize the OSC message dispatch system.
dispatch = dispatcher.Dispatcher()
dispatch.map("/sim/*", sim.message)
dispatch.map("/control/*", control.message)
dispatch.set_default_handler(sim.unknown_message)
# Start and run the server.
server = osc_server.ThreadingOSCUDPServer((args.simaddr, args.simport), dispatch)
server_thread = threading.Thread(target=server.serve_forever)
server_thread.daemon = True
server_thread.start()
################################################################
# Script entry point.
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Double-pendulum or two-link arm simulator.")
parser.add_argument('--verbose', action='store_true', help='Enable debugging output.')
parser.add_argument('--maxport', type=int, default=16375, help='UDP port for Max/MSP patch (default 16375).')
parser.add_argument('--maxaddr', default="127.0.0.1", help='IP address for the Max/MSP patch (default localhost).')
parser.add_argument('--simport', type=int, default=54375, help='UDP port for Python simulator (default 54375).')
parser.add_argument('--simaddr', default="127.0.0.1", help='IP address for the simulator (default localhost).')
parser.add_argument('--fast', action='store_true', help='Run as fast as possible.')
args = parser.parse_args()
# create an OSC client endpoint to send display updates to Max/MSP
cartoon = udp_client.SimpleUDPClient(args.maxaddr, args.maxport)
# initializes the simulator
control = DoublePendulumController(args)
sim = DoublePendulumSimulator(args, cartoon, control)
# set up the OSC message server to receive parameters from Max/MSP
start_osc_server(args, sim, control)
# begin the simulation
sim.event_loop()

Comments are closed.