Wobbly Robot Model¶
The wobbly robot model simulates a two-wheeled differential-drive mobile
robot with a low center of gravity. The body is designed with enough ground
clearance to tilt, but the low center of mass will wobble it back upright. The
body includes a mast with two distance sensors, a radio receiver and emitter,
GPS receiver for location, compass for heading, and three-axis accelerometer.
Each wheel has both a rotational motor and a position sensor.
The shape is constructed entirely of primitive cylinders.The same geometry is referenced to use as bounding objects for collision and automatic calculation of physics parameters.
The user-accessible parameters include the wheel radius, axle length, body color, and wheel color. The kinematics, shape, and physics will parametrically scale, but the actuator parameters do not change.
This model is demonstrated in the wobbly-demo.wbt world.
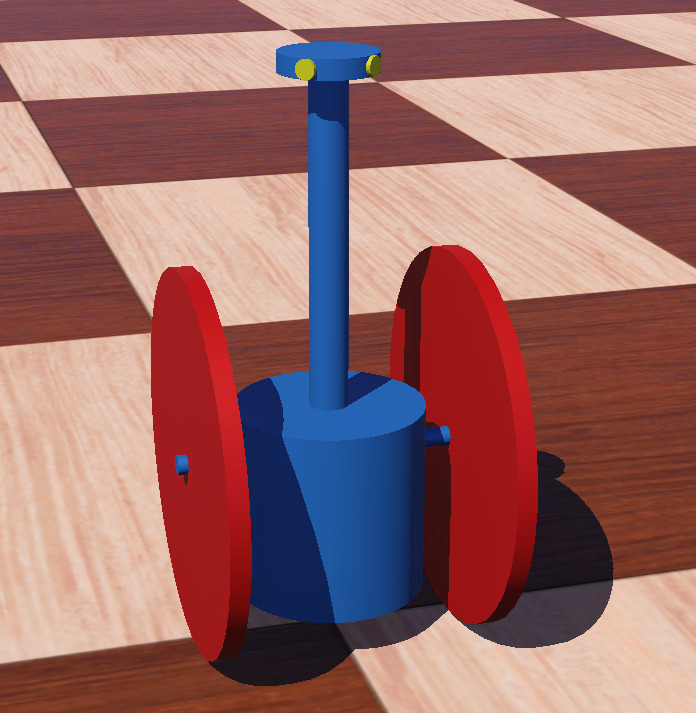
Screenshot of Webots model of a diff-drive ‘wobbly’ robot with low center of gravity.¶
System Kinematics and Components¶
The bodies are as follows:
name |
color |
notes |
|---|---|---|
body |
blue |
the core solid including counterweight, stalk, axle, and sensor disc |
left wheel |
red |
left wheel disc, cylinder with parameterized radius |
right wheel |
red |
right wheel disc, cylinder with parameterized radius |
The joints are as follows:
name |
parent |
child |
notes |
|---|---|---|---|
(6DOF free) |
world |
body |
mobile body; body +X axis is ‘forward’, +Z is ‘up’ |
left wheel |
body |
left wheel |
rotational joint on axle, parameterized Z position |
right wheel |
body |
right wheel |
rotational joint on axle, parameterized Z position |
The joint axes are as follows:
name |
direction |
notes |
|---|---|---|
left wheel |
along +Y |
along axle; direction chosen so positive rotation moves forward |
right wheel |
along +Y |
along axle; direction chosen so positive rotation moves forward |
The motors and sensors are named as follows:
name |
notes |
|---|---|
left wheel motor |
RotationalMotor on left wheel |
right wheel motor |
RotationalMotor on right wheel |
left wheel sensor |
PositionSensor on left wheel |
right wheel sensor |
PositionSensor on right wheel |
leftDistanceSensor |
DistanceSensor near top of body, aimed left of enter |
rightDistanceSensor |
DistanceSensor near top of body, aimed right of center |
gps |
GPS locator mounted on body in center of axle |
compass |
compass mounted on body in center of axle |
accelerometer |
three-axis accelerometer mounted on body in center of axle |
receiver |
radio Receiver |
emitter |
radio Emitter |
wobbly.proto¶
The robot model has been encapsulated in a .proto file for easy reuse. The model includes user-accessible scaling and color parameters.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 | #VRML_SIM R2021b utf8
# Two-wheeled differential-drive mobile robot with a low center of gravity. The
# body is designed with enough ground clearance to tilt, but the low center of
# mass will wobble it back upright. The body includes a mast with two distance
# sensors, a radio receiver and emitter, and a GPS receiver. Each wheel has
# both a rotational motor and a position sensor. The shape is constructed
# entirely of primitive cylinders.
# documentation url: https://courses.ideate.cmu.edu/16-375
# license: No copyright, 2020-2021 Garth Zeglin. This file is explicitly placed in the public domain.
PROTO wobbly [
field SFVec3f translation 0 0 0
field SFRotation rotation 0 1 0 0
field SFString controller "wobbly"
field SFString name "Wobbly"
field SFFloat wheelRadius 0.1
field SFFloat axleLength 0.14
field SFColor bodyColor 0.0820075 0.364731 0.8
field SFColor wheelColor 1 0 0
field SFString customData ""
]
{
Robot {
# connect properties to user-visible data fields
translation IS translation
rotation IS rotation
controller IS controller
name IS name
customData IS customData
# calculate derived parameters
%{
local counterweightHeight = fields.wheelRadius.value
local counterweightOffset = 0.75*fields.wheelRadius.value
local counterweightTop = 1.25*fields.wheelRadius.value
local sensorHeight = 3*fields.wheelRadius.value
local stalkHeight = sensorHeight - counterweightTop
local stalkOffset = counterweightTop + 0.5*stalkHeight
}%
children [
# The body group contains three cylinders: the massive counterweight at
# bottom, a thin stalk rising above it, topped by the sensor disc.
# All these shapes participate in collision; the axle is kept separate
# as it is just for rendering.
DEF bodyShape Group {
children [
# counterweight
Transform {
translation 0 0 %{= counterweightOffset }%
rotation 1 0 0 1.5708
children [
Shape {
appearance DEF bodyAppearance PBRAppearance {
baseColor IS bodyColor
roughness 0.5
metalness 0.5
}
geometry Cylinder {
height %{= counterweightHeight }%
radius 0.05
}
}
]
}
# sensor disc
Transform {
translation 0 0 %{= sensorHeight }%
rotation 1 0 0 1.5708
children [
Shape {
appearance USE bodyAppearance
geometry Cylinder {
height 0.01
radius 0.025
}
}
]
}
# stalk
Transform {
translation 0 0 %{= stalkOffset }%
rotation 1 0 0 1.5708
children [
Shape {
appearance USE bodyAppearance
geometry Cylinder {
height %{= stalkHeight }%
radius 0.01
}
}
]
}
]
}
# Visible axle shape, not part of the boundingObject.
DEF axleShape Transform {
translation 0 0 %{= fields.wheelRadius.value }%
children [
Shape {
appearance USE bodyAppearance
geometry Cylinder {
height %{= fields.axleLength.value + 0.02 }%
radius 0.005
}
}
]
}
# Define the left wheel axis, pointing in the +Y direction along the axle.
HingeJoint {
jointParameters HingeJointParameters {
axis 0 1 0
anchor 0 0 %{= fields.wheelRadius.value }%
}
device [
RotationalMotor {
name "left wheel motor"
acceleration 10
maxTorque 2
}
PositionSensor {
name "left wheel sensor"
}
]
# Define the left wheel solid, offset along +Y along the axle.
endPoint DEF leftWheel Solid {
translation 0 %{= 0.5*fields.axleLength.value }% %{= fields.wheelRadius.value }%
rotation 0 -1 0 0
children [
# Define the left wheel shape and appearance, which is used by the right wheel solid.
DEF wheelShape Transform {
rotation 0 0 1 0
children [
Shape {
appearance PBRAppearance {
baseColor IS wheelColor
roughness 0.5
metalness 0.5
}
geometry Cylinder {
height 0.01
radius %{= fields.wheelRadius.value }%
}
}
]
}
]
name "left wheel"
boundingObject USE wheelShape
physics DEF wheelPhysics Physics {
density 600
}
}
}
# Define the right wheel axis, also pointing in the +Y direction along the axle
# so positive wheel rotations will move forward.
HingeJoint {
jointParameters HingeJointParameters {
axis 0 1 0
anchor 0 0 %{= fields.wheelRadius.value }%
}
device [
RotationalMotor {
name "right wheel motor"
acceleration 10
maxTorque 2
}
PositionSensor {
name "right wheel sensor"
}
]
# Define the right wheel solid, offset along -Y along the axle.
# The wheel shape is inherited from the left wheel.
endPoint DEF rightWheel Solid {
translation 0 %{= -0.5*fields.axleLength.value }% %{= fields.wheelRadius.value }%
rotation 0 0 1 3.14159
children [
USE wheelShape
]
name "right wheel"
boundingObject USE wheelShape
physics USE wheelPhysics
}
}
# Define the two range sensors. They are located on the sensor disc on
# top of the body stalk, each pointed off-axis by 1.0 radian.
DEF leftEyeSensor DistanceSensor {
translation 0.019 0.016 %{= sensorHeight }%
rotation 0 0 1 0.7
children [
DEF eyeShape Transform {
rotation 0 0 1 1.57
children [
Shape {
appearance PBRAppearance {
baseColor 0.975691 0.981481 0.0252992
roughness 0.5
metalness 0.5
}
geometry Cylinder {
height 0.004
radius 0.005
}
}
]
}
]
name "leftDistanceSensor"
lookupTable [
0 0.025 0
1 1 0
]
numberOfRays 2
aperture 0.4
}
DEF rightEyeSensor DistanceSensor {
translation 0.019 -0.016 %{= sensorHeight }%
rotation 0 0 1 -0.7
children [
USE eyeShape
]
name "rightDistanceSensor"
lookupTable [
0 0.025 0
1 1 0
]
numberOfRays 2
aperture 0.4
}
# add a default radio receiver and transmitter
Receiver {
}
Emitter {
}
# add a position-sensing 'GPS' device located at the center of the axle
GPS {
translation 0 0 %{= fields.wheelRadius.value }%
}
# add a rotation-sensing 'compass' returning only the X and Y components of the North vector
Compass {
zAxis FALSE
}
# add an accelerometer located at the center of the axle to measure both gravity and reactive forces
Accelerometer {
translation 0 0 %{= fields.wheelRadius.value }%
}
] # close children list of Robot
boundingObject USE bodyShape
physics Physics {
density -1
mass 3
}
} # close Robot
}
|
Sample Control Code¶
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 | # wobbly.py
# Sample Webots controller file for driving the wobbly diff-drive
# mobile robot.
# No copyright, 2020-2021, Garth Zeglin. This file is
# explicitly placed in the public domain.
print("loading wobbly.py...")
# Import the Webots simulator API.
from controller import Robot
# Import standard Python libraries.
import math, random, time
# Define the time step in milliseconds between controller updates.
EVENT_LOOP_DT = 200
################################################################
class Wobbly(Robot):
def __init__(self):
super(Wobbly, self).__init__()
self.robot_name = self.getName()
print("%s: controller connected." % (self.robot_name))
# Attempt to randomize the random library sequence.
random.seed(time.time())
# Initialize geometric constants. These should match
# the current geometry of the robot.
self.wheel_radius = 0.1
self.axle_length = 0.14
# Fetch handles for the wheel motors
self.l_motor = self.getDevice('left wheel motor')
self.r_motor = self.getDevice('right wheel motor')
# Adjust the low-level controller gains.
print("%s: setting PID gains." % (self.robot_name))
self.l_motor.setControlPID(1.0, 0.0, 0.1)
self.r_motor.setControlPID(1.0, 0.0, 0.1)
# Fetch handles for the wheel joint sensors.
self.l_pos_sensor = self.getDevice('left wheel sensor')
self.r_pos_sensor = self.getDevice('right wheel sensor')
# Specify the sampling rate for the joint sensors.
self.l_pos_sensor.enable(EVENT_LOOP_DT)
self.r_pos_sensor.enable(EVENT_LOOP_DT)
# Connect to the eye sensors.
self.l_eye_sensor = self.getDevice('leftDistanceSensor')
self.r_eye_sensor = self.getDevice('rightDistanceSensor')
self.l_eye_sensor.enable(EVENT_LOOP_DT)
self.r_eye_sensor.enable(EVENT_LOOP_DT)
# Connect to the radio emitter and receiver.
self.receiver = self.getDevice('receiver')
self.emitter = self.getDevice('emitter')
self.radio_interval = 1000
self.radio_timer = 0
self.receiver.enable(self.radio_interval)
# Maintain a table of peer robot locations received over the radio.
self.peers = {}
# Connect to the GPS position sensor.
self.gps = self.getDevice('gps')
self.gps_timer = 0
self.gps_interval = 1000
self.gps.enable(self.gps_interval)
self.gps_location = [0, 0, 0.1] # reference pose value
# Connect to the compass orientation sensor.
self.compass = self.getDevice('compass')
self.compass_timer = 0
self.compass_interval = 200
self.compass.enable(self.compass_interval)
# State variables for reporting compass readings. The heading is the
# body forward (body +X) direction expressed in degrees clockwise from
# North (world +Y). The compass_vector is the direction of North
# expressed in body coordinates. The neutral pose points East.
self.heading = 90
self.compass_vector = [0,1] # reference pose value
self.heading_error = 0
# Connect to the accelerometer sensor.
self.accelerometer = self.getDevice('accelerometer')
self.accelerometer_timer = 0
self.accelerometer_interval = 200
self.accelerometer.enable(self.accelerometer_interval)
self.accel_vector = [0, 0, 9.81] # reference pose value
# Initialize generic behavior state machine variables.
self.state_timer = 0 # timers in milliseconds
self.state_index = 0 # current state
self.target_heading = 0
self.target_velocity = 0
return
#================================================================
# Polling function to process sensor input at different timescales.
def poll_sensors(self):
self.gps_timer -= EVENT_LOOP_DT
if self.gps_timer < 0:
self.gps_timer += self.gps_interval
location = self.gps.getValues()
if not math.isnan(location[0]):
self.gps_location = location
# print("%s GPS: %s" % (self.robot_name, location))
self.compass_timer -= EVENT_LOOP_DT
if self.compass_timer < 0:
self.compass_timer += self.compass_interval
orientation = self.compass.getValues()
if not math.isnan(orientation[0]) and not math.isnan(orientation[1]):
# For heading, 0 degrees is North, 90 is East, 180 is South, 270 is West.
# The world is assumed configured 'ENU' so X is East and Y is North.
# The robot 'front' is along body +X, so the neutral pose is facing East.
self.heading = math.fmod(2*math.pi + math.atan2(orientation[1], orientation[0]), 2*math.pi) * (180.0/math.pi)
self.compass_vector = orientation[0:2]
# print("%s Compass: %s, heading %3.0f deg" % (self.robot_name, self.compass_vector, heading))
self.accelerometer_timer -= EVENT_LOOP_DT
if self.accelerometer_timer < 0:
self.accelerometer_timer += self.accelerometer_interval
self.accel_vector = self.accelerometer.getValues()
# The accelerometer will read [0, 0, 9.81] when stationary in the reference pose.
# print("%s Accelerometer: %s" % (self.robot_name, self.accel_vector))
return
#================================================================
# Polling function to process radio and network input at different timescales.
def poll_communication(self):
self.radio_timer -= EVENT_LOOP_DT
if self.radio_timer < 0:
self.radio_timer += self.radio_interval
while self.receiver.getQueueLength() > 0:
packet = self.receiver.getData()
# print("%s Receiver: %s" % (self.robot_name, packet))
tokens = packet.split()
if len(tokens) != 5:
print("%s malformed packet: %s" % (self.robot_name, packet))
else:
name = tokens[0].decode() # convert bytestring to Unicode
if self.peers.get(name) is None:
print("%s receiver: new peer observed: %s" % (self.robot_name, name))
self.peers[name] = {'location' : [float(tokens[1]), float(tokens[2]), float(tokens[3])],
'heading' : float(tokens[4]),
'timestamp' : self.getTime(),
}
# done with packet processing
self.receiver.nextPacket()
# Transmit a status message at the same rate
name_token = self.robot_name.replace(" ","_")
status = "%s %.2f %.2f %.2f %.0f" % (name_token, self.gps_location[0], self.gps_location[1],
self.gps_location[2] - self.wheel_radius, self.heading)
# emitter requires a bytestring, not a Python Unicode string
data = status.encode()
# print("%s emitter: sending %s" % (self.robot_name, data))
self.emitter.send(data)
#================================================================
# motion primitives
def go_forward(self, velocity):
"""Command the motor to turn at the rate which produce the ground velocity
specified in meters/sec. Negative values turn backward. """
# velocity control mode
self.l_motor.setPosition(math.inf)
self.r_motor.setPosition(math.inf)
# calculate the rotational rate in radians/sec based on the wheel radius
theta_dot = velocity / self.wheel_radius
self.l_motor.setVelocity(theta_dot)
self.r_motor.setVelocity(theta_dot)
return
def go_rotate(self, rot_velocity):
"""Command the motors to turn in place at the rate which produce the rotational
velocity specified in radians/sec. Negative values turn
backward."""
# velocity control mode
self.l_motor.setPosition(math.inf)
self.r_motor.setPosition(math.inf)
# calculate the difference in linear velocity of the wheels
linear_velocity = self.axle_length * rot_velocity
# calculate the net rotational rate in radians/sec based on the wheel radius
theta_dot = linear_velocity / self.wheel_radius
# apply the result symmetrically to the wheels
self.l_motor.setVelocity( 0.5*theta_dot)
self.r_motor.setVelocity(-0.5*theta_dot)
return
def heading_difference(self, target, current):
"""Calculate a directional error in degrees, always returning a value on (-180, 180]."""
err = target - current
# fold the range of values to (-180, 180]
if err > 180.0:
return err - 360
elif err <= -180.0:
return err + 360
else:
return err
def go_heading(self, target_heading):
"""Rotate toward the heading specifed in positive degrees, with 0 at North (+Y),
90 at East (+X). This assume the compass-reading process is
active."""
# find the directional error in degrees
self.heading_error = self.heading_difference(target_heading, self.heading)
# apply a linear mapping from degrees error to rotational velocity in radians/sec
rot_vel = 0.02 * self.heading_error
self.go_rotate(rot_vel)
# print("go_heading: %f, %f, %f" % (target_heading, self.heading, rot_vel))
return
def go_still(self):
"""Actively damp any wobble to come to rest in place."""
# map an error in X acceleration to a linear velocity
vel = -0.05 * self.accel_vector[0]
self.go_forward(vel)
# print("go_still: %f, %f" % (self.accel_vector[0], vel))
return
#================================================================
def peer_heading_distance(self, record):
"""Given a peer record, return a tuple (heading, distance) with the compass
heading and distance in meters of the peer from this robot current
location."""
loc = record['location']
dx = loc[0] - self.gps_location[0]
dy = loc[1] - self.gps_location[1]
distance = math.sqrt(dx*dx + dy*dy)
heading = math.fmod(2*math.pi + math.atan2(dx, dy), 2*math.pi) * (180.0/math.pi)
return heading, distance
def nearest_peer(self, range=2.0):
"""Locate the nearest peer (as reported by radio) within the given range.
Returns either None or a dictionary with the location record."""
result = None
best = math.inf
for name in self.peers:
record = self.peers[name]
heading, dist = self.peer_heading_distance(record)
if dist < best:
result = record
best = dist
return result
#================================================================
def poll_wandering_activity(self):
"""State machine update function to aimlessly wander around the world."""
# This machine always transitions at regular intervals.
timer_expired = False
if self.state_timer < 0:
self.state_timer += 3000
timer_expired = True
# Evaluate the side-effects and transition rules for each state.
if self.state_index == 0:
print("Init state, entering cycle.")
self.state_index = 1
elif self.state_index == 1:
self.go_forward(0.2)
if timer_expired:
self.state_index += 1
elif self.state_index == 2:
self.go_heading(self.target_heading)
if timer_expired:
self.state_index += 1
elif self.state_index == 3:
self.go_still()
if timer_expired:
self.state_index += 1
elif self.state_index == 4:
self.go_rotate(math.pi / 6)
if timer_expired:
self.state_index = 1
self.target_heading = random.randint(0,360)
else:
print("%s: invalid state, resetting." % (self.robot_name))
self.state_index = 0
if timer_expired:
print("%s: transitioning to state %s" % (self.robot_name, self.state_index))
return
#================================================================
def poll_following_activity(self):
"""State machine update function to always move toward the nearest peer."""
if self.state_timer < 0:
self.state_timer += 1000
# periodically test if there is a nearby peer
nearest = self.nearest_peer()
if nearest is None:
self.state_index = 1
else:
self.state_index = 2
heading, distance = self.peer_heading_distance(nearest)
self.target_heading = heading
self.target_velocity = 0.1 * distance
print("%s: peer to follow at %f deg, %f meters" % (self.robot_name, heading, distance))
# always either stabilize, turn, or move
if self.state_index < 1:
self.go_still()
else:
heading_err = self.heading_difference(self.target_heading, self.heading)
if abs(heading_err) > 20.0 or abs(self.target_velocity) < 0.05:
self.go_heading(self.target_heading)
else:
self.go_forward(self.target_velocity)
#================================================================
def run(self):
# Run loop to execute a periodic script until the simulation quits.
# If the controller returns -1, the simulator is quitting.
while self.step(EVENT_LOOP_DT) != -1:
# Read simulator clock time.
self.sim_time = self.getTime()
# Read sensor values.
self.poll_sensors()
# Check the radio and/or network.
self.poll_communication()
# Update the activity state machine.
self.state_timer -= EVENT_LOOP_DT
# This will run some open-loop motion. One robot will be the leader, the rest will follow.
mode = self.getCustomData()
if mode == 'leader':
self.poll_wandering_activity()
else:
self.poll_following_activity()
################################################################
# Start the script.
robot = Wobbly()
robot.run()
|