Arm Camera¶
This sample world includes a ZYY arm with an attached camera and visual targets. This model is a testbed for exploring vision-guided behaviors.
The control script uses the OpenCV Python module for image processing. This can
be installed in your Python system using pip3 install opencv-python.
The world file is arm-camera.wbt, which can be found within the Webots.zip archive.
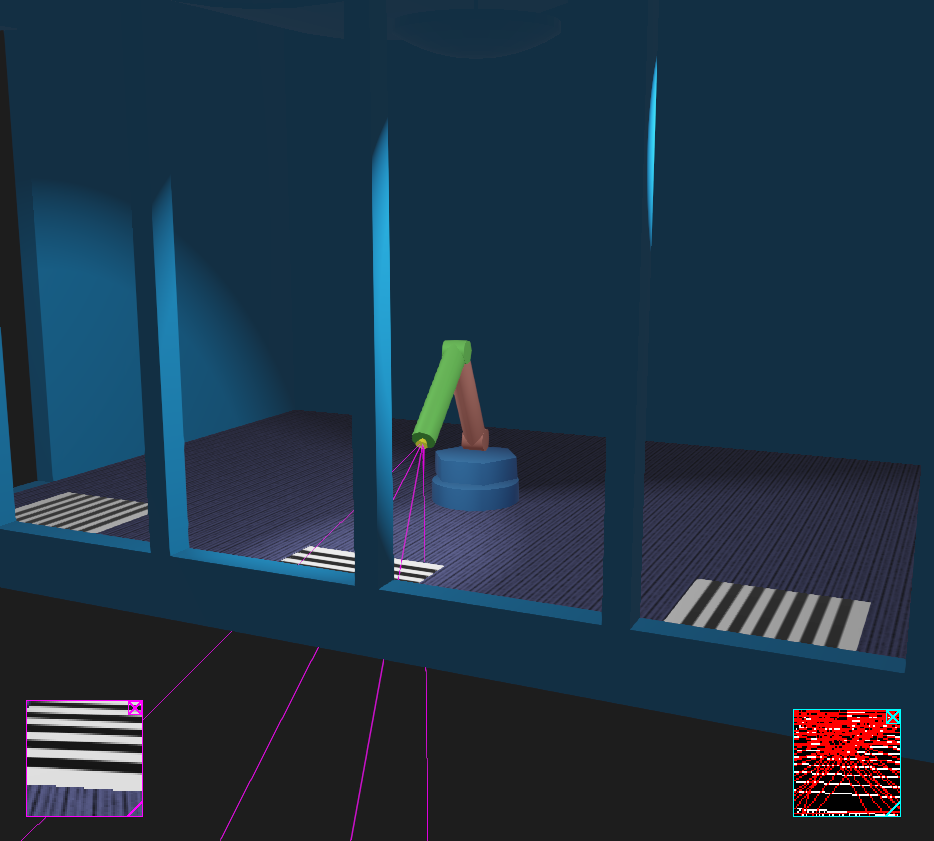
Screenshot of Webots model of the arm-camera robot. The arm has a low-resolution camera on the end, represented by the yellow cone. The optional camera frustrum rendering is enabled so the magenta lines indicate the volume visible to the camera. The display box in the lower left shows the current camera view, and the display box in the lower right shows the processed camera view. Several visual targets are placed on the floor.¶
World File¶
The world file specifies all the elements of the scene: camera position, background scenery, lighting, fixed objects, the robot arm, and a kinematics-only Cartesian robot to position a vision target.
The robot arm is defined within the world file as a modified form of the ZYY Robot Arm Model. The modified model adds a camera and display and removes a distance sensor.
1#VRML_SIM R2023b utf8
2
3EXTERNPROTO "../protos/HL-A11-room.proto"
4EXTERNPROTO "../protos/cartesian-target.proto"
5
6WorldInfo {
7}
8Viewpoint {
9 orientation 0.0967171354651438 0.028945079794029917 -0.9948909377731483 2.6640220350656656
10 position 6.685541706721584 3.239781663991078 2.4623641250844526
11 followType "None"
12}
13Background {
14 skyColor [
15 0.1 0.1 0.1
16 ]
17}
18SpotLight {
19 attenuation 0 0 1
20 beamWidth 0.3
21 cutOffAngle 0.4
22 direction -0.5 -2 -1.2
23 intensity 5
24 location 1.5 2 2
25}
26SpotLight {
27 attenuation 0 0 1
28 beamWidth 0.3
29 cutOffAngle 0.4
30 direction -0.5 2 -1.2
31 intensity 5
32 location 1.5 -2 2
33}
34HL-A11-room {
35}
36Robot {
37 rotation 0 1 0 0
38 children [
39 Receiver {
40 }
41 Emitter {
42 }
43 DEF fixedBaseShape Pose {
44 translation 0 0 0.05
45 children [
46 Shape {
47 appearance DEF blueAppearance PBRAppearance {
48 baseColor 0.21529 0.543008 0.99855
49 roughness 0.5
50 metalness 0.5
51 }
52 geometry Cylinder {
53 height 0.1
54 radius 0.2
55 }
56 }
57 ]
58 }
59 HingeJoint {
60 jointParameters HingeJointParameters {
61 axis 0 0 1
62 minStop -2.0943951023931953
63 maxStop 2.0943951023931953
64 }
65 device [
66 PositionSensor {
67 name "joint1"
68 }
69 RotationalMotor {
70 name "motor1"
71 acceleration 2
72 controlPID 100 0 25
73 maxVelocity 3.14
74 maxTorque 20
75 }
76 ]
77 endPoint Solid {
78 translation 0 0 0.12
79 children [
80 DEF rotatingBaseShape Pose {
81 translation 0 0 0.05
82 children [
83 Shape {
84 appearance USE blueAppearance
85 geometry Cylinder {
86 height 0.1
87 radius 0.2
88 subdivision 6
89 }
90 }
91 ]
92 }
93 HingeJoint {
94 jointParameters HingeJointParameters {
95 axis 0 1 0
96 anchor 0 0 0.17
97 minStop -0.08726646259971647
98 maxStop 1.5707963267948966
99 }
100 device [
101 PositionSensor {
102 name "joint2"
103 }
104 RotationalMotor {
105 name "motor2"
106 acceleration 2
107 controlPID 50 0 15
108 maxVelocity 3.14
109 maxTorque 20
110 }
111 ]
112 endPoint Solid {
113 translation 0 0 0.42
114 rotation 0 1 0 0
115 children [
116 HingeJoint {
117 jointParameters HingeJointParameters {
118 axis 0 1 0
119 anchor 0 0 0.25
120 minStop -0.08726646259971647
121 maxStop 2.0943951023931953
122 dampingConstant 0.1
123 }
124 device [
125 PositionSensor {
126 name "joint3"
127 }
128 RotationalMotor {
129 name "motor3"
130 acceleration 2
131 controlPID 50 0 15
132 maxVelocity 6.28
133 maxTorque 15
134 }
135 ]
136 endPoint Solid {
137 translation 0 0 0.5
138 rotation 0 1 0 0
139 children [
140 DEF link2Shape Pose {
141 children [
142 Shape {
143 appearance DEF greenAppearance PBRAppearance {
144 baseColor 0.413001 1 0.33489
145 roughness 0.5
146 metalness 0.5
147 }
148 geometry Cylinder {
149 height 0.5
150 radius 0.05
151 }
152 }
153 ]
154 }
155 Pose {
156 translation 0 0 -0.25
157 rotation 1 0 0 1.5708
158 children [
159 Shape {
160 appearance USE greenAppearance
161 geometry Cylinder {
162 height 0.1
163 radius 0.05
164 }
165 }
166 ]
167 }
168 Camera {
169 translation 0 0 0.25
170 rotation 0 1 0 -1.5708
171 children [
172 Pose {
173 rotation 0 1 0 -1.5707953071795862
174 children [
175 Shape {
176 appearance PBRAppearance {
177 baseColor 1 0.99028 0.0584421
178 roughness 0.5
179 metalness 0.5
180 emissiveColor 1 0.99028 0.0584421
181 emissiveIntensity 0.2
182 }
183 geometry Cone {
184 bottomRadius 0.025
185 height 0.05
186 }
187 }
188 ]
189 }
190 ]
191 fieldOfView 0.75
192 far 5
193 }
194 ]
195 name "link2"
196 boundingObject USE link2Shape
197 physics Physics {
198 density 211.7
199 }
200 }
201 }
202 DEF link1Shape Pose {
203 children [
204 Shape {
205 appearance DEF redAppearance PBRAppearance {
206 baseColor 0.990494 0.516915 0.468254
207 roughness 0.5
208 metalness 0.5
209 }
210 geometry Cylinder {
211 height 0.5
212 radius 0.05
213 }
214 }
215 ]
216 }
217 Pose {
218 translation 0 0 -0.25
219 rotation 1 0 0 1.5708
220 children [
221 Shape {
222 appearance USE redAppearance
223 geometry Cylinder {
224 height 0.1
225 radius 0.05
226 }
227 }
228 ]
229 }
230 ]
231 name "link1"
232 boundingObject USE link1Shape
233 physics Physics {
234 density 211.7
235 }
236 }
237 }
238 ]
239 name "base"
240 boundingObject USE rotatingBaseShape
241 physics Physics {
242 density -1
243 mass 2
244 }
245 }
246 }
247 Display {
248 }
249 ]
250 name "camera-on-arm"
251 boundingObject USE fixedBaseShape
252 controller "arm_camera"
253}
254Solid {
255 translation 1 1.5 0.01
256 rotation 0.7071072811860408 1.223050486354381e-06 0.7071062811856431 3.14159
257 children [
258 Shape {
259 appearance PBRAppearance {
260 baseColorMap ImageTexture {
261 url [
262 "textures/stripes.png"
263 ]
264 filtering 1
265 }
266 metalness 0
267 }
268 geometry IndexedFaceSet {
269 coord Coordinate {
270 point [
271 0 -0.3 -0.3
272 0 0.3 -0.3
273 0 0.3 0.3
274 0 -0.3 0.3
275 ]
276 }
277 texCoord TextureCoordinate {
278 point [
279 0 0
280 1 0
281 1 1
282 0 1
283 ]
284 }
285 coordIndex [
286 0, 1, 2, 3
287 ]
288 texCoordIndex [
289 0, 1, 2, 3
290 ]
291 }
292 }
293 ]
294 name "right target"
295}
296Solid {
297 translation 1.25 0 0.01
298 rotation -0.5773509358554485 0.5773489358556708 -0.5773509358554485 -2.094395307179586
299 children [
300 Shape {
301 appearance PBRAppearance {
302 baseColorMap ImageTexture {
303 url [
304 "textures/circle.png"
305 ]
306 filtering 1
307 }
308 metalness 0
309 }
310 geometry IndexedFaceSet {
311 coord Coordinate {
312 point [
313 0 -0.3 -0.3
314 0 0.3 -0.3
315 0 0.3 0.3
316 0 -0.3 0.3
317 ]
318 }
319 texCoord TextureCoordinate {
320 point [
321 0 0
322 1 0
323 1 1
324 0 1
325 ]
326 }
327 coordIndex [
328 0, 1, 2, 3
329 ]
330 texCoordIndex [
331 0, 1, 2, 3
332 ]
333 }
334 }
335 ]
336 name "center target"
337}
338Solid {
339 translation 1 -1.5 0.0100094
340 rotation 0.7071072811860408 1.223050486354381e-06 0.7071062811856431 3.14159
341 children [
342 Shape {
343 appearance PBRAppearance {
344 baseColorMap ImageTexture {
345 url [
346 "textures/stripes.png"
347 ]
348 filtering 1
349 }
350 metalness 0
351 }
352 geometry IndexedFaceSet {
353 coord Coordinate {
354 point [
355 0 -0.3 -0.3
356 0 0.3 -0.3
357 0 0.3 0.3
358 0 -0.3 0.3
359 ]
360 }
361 texCoord TextureCoordinate {
362 point [
363 0 0
364 1 0
365 1 1
366 0 1
367 ]
368 }
369 coordIndex [
370 0, 1, 2, 3
371 ]
372 texCoordIndex [
373 0, 1, 2, 3
374 ]
375 }
376 }
377 ]
378 name "left target"
379}
380cartesian-target {
381 translation 2 0 0
382 radius 0.2
383}
Sample Arm Camera Controller¶
The controller reads the camera images and uses them to trigger different reactive movements.
1# arm_camera.py
2#
3# Sample Webots controller file for driving a two-link arm with three driven
4# joints and an end-mounted camera.
5
6# No copyright, 2020-2024, Garth Zeglin. This file is
7# explicitly placed in the public domain.
8
9print("zyy_camera.py waking up.")
10
11# Import the Webots simulator API.
12from controller import Robot, Display
13
14# Import the standard Python math library.
15import math, random, time
16
17# Import the third-party numpy library for matrix calculations.
18# Note: this can be installed using 'pip3 install numpy' or 'pip3 install scipy'.
19import numpy as np
20
21# Import the third-party OpenCV library for image operations.
22# Note: this can be installed using 'pip3 install opencv-python'
23import cv2 as cv
24
25# Import the bezier module from the same directory. Note: this requires numpy.
26import bezier
27
28# Import the vision module from the same directory. Note: this requires OpenCV.
29import vision
30
31# Define the time step in milliseconds between controller updates.
32EVENT_LOOP_DT = 50
33
34################################################################
35class ZYY(Robot):
36 def __init__(self):
37
38 super(ZYY, self).__init__()
39 self.robot_name = self.getName()
40 print("%s: controller connected." % (self.robot_name))
41
42 # Attempt to randomize the random library sequence.
43 random.seed(time.time())
44
45 # Initialize geometric constants. These should match
46 # the current geometry of the robot.
47 self.base_z = 0.29 # joint2 axis height: 0.12 fixed base height + 0.17 j2 z offset
48 self.link1 = 0.5 # link1 length, i.e. distance between j2 and j3
49 self.link2 = 0.5 # link2 length, i.e. distance between j3 and end
50
51 # Fetch handles for the joint motors.
52 self.motor1 = self.getDevice('motor1')
53 self.motor2 = self.getDevice('motor2')
54 self.motor3 = self.getDevice('motor3')
55
56 # Adjust the motor controller properties.
57 self.motor1.setAvailableTorque(20.0)
58 self.motor2.setAvailableTorque(15.0)
59 self.motor3.setAvailableTorque(10.0)
60
61 # Adjust the low-level controller gains.
62 print("%s: setting PID gains." % (self.robot_name))
63 self.motor1.setControlPID(100.0, 0.0, 25.0)
64 self.motor2.setControlPID( 50.0, 0.0, 25.0)
65 self.motor3.setControlPID( 50.0, 0.0, 25.0)
66
67 # Fetch handles for the joint sensors.
68 self.joint1 = self.getDevice('joint1')
69 self.joint2 = self.getDevice('joint2')
70 self.joint3 = self.getDevice('joint3')
71
72 # Save the most recent target position.
73 self.joint_target = np.zeros(3)
74
75 # Specify the sampling rate for the joint sensors.
76 self.joint1.enable(EVENT_LOOP_DT)
77 self.joint2.enable(EVENT_LOOP_DT)
78 self.joint3.enable(EVENT_LOOP_DT)
79
80 # Enable the overhead camera and set the sampling frame rate.
81 self.camera = self.getDevice('camera')
82 self.camera_frame_dt = EVENT_LOOP_DT # units are milliseconds
83 self.camera_frame_timer = 0
84 self.camera.enable(self.camera_frame_dt)
85 self.frame_count = 0
86 self.vision_target = None
87
88 # Connect to the display object to show debugging data within the Webots GUI.
89 # The display width and height should match the camera.
90 self.display = self.getDevice('display')
91
92 # Initialize behavior state machines.
93 self.state_timer = 2*EVENT_LOOP_DT
94 self.state_index = 0
95 self._init_spline()
96 return
97
98 #================================================================
99 def endpoint_forward_kinematics(self, q):
100 """Compute the forward kinematics for the end point. Returns the
101 body-coordinate XYZ Cartesian position of the end point for a given joint
102 angle vector.
103 :param q: three-element list with [q1, q2, q3] joint angles in radians
104 :return: three-element list with endpoint [x,y,z] location
105
106 """
107 j1 = q[0]
108 j2 = q[1]
109 j3 = q[2]
110
111 return [(self.link1*math.sin(j2) + self.link2*math.sin(j2 + j3))*math.cos(j1),
112 (self.link1*math.sin(j2) + self.link2*math.sin(j2 + j3))*math.sin(j1),
113 self.base_z + self.link1*math.cos(j2) + self.link2*math.cos(j2 + j3)]
114
115 #================================================================
116 def endpoint_inverse_kinematics(self, target):
117 """Compute the joint angles for a target end position. The target is a
118 XYZ Cartesian position vector in body coordinates, and the result vector
119 is a joint angles as list [j1, j2, j3]. If the target is out of reach,
120 returns the closest pose. With j1 between -pi and pi, and j2 and j3
121 limited to positive rotations, the solution is always unique.
122 """
123
124 x = target[0]
125 y = target[1]
126 z = target[2]
127
128 # the joint1 base Z rotation depends only upon x and y
129 j1 = math.atan2(y, x)
130
131 # distance within the XY plane from the origin to the endpoint projection
132 xy_radial = math.sqrt(x*x + y*y)
133
134 # find the Z offset from the J2 horizontal plane to the end point
135 end_z = z - self.base_z
136
137 # angle between the J2 horizonta plane and the endpoint
138 theta = math.atan2(end_z, xy_radial)
139
140 # radial distance from the J2 axis to the endpoint
141 radius = math.sqrt(x*x + y*y + end_z*end_z)
142
143 # use the law of cosines to compute the elbow angle solely as a function of the
144 # link lengths and the radial distance from j2 to end
145 # R**2 = l1**2 + l2**2 - 2*l1*l2*cos(pi - elbow)
146 acosarg = (radius*radius - self.link1**2 - self.link2**2) / (-2 * self.link1 * self.link2)
147 if acosarg < -1.0: elbow_supplement = math.pi
148 elif acosarg > 1.0: elbow_supplement = 0.0
149 else: elbow_supplement = math.acos(acosarg)
150
151 print("theta:", theta, "radius:", radius, "acosarg:", acosarg)
152
153 # use the law of sines to find the angle at the bottom vertex of the triangle defined by the links
154 # radius / sin(elbow_supplement) = l2 / sin(alpha)
155 if radius > 0.0:
156 alpha = math.asin(self.link2 * math.sin(elbow_supplement) / radius)
157 else:
158 alpha = 0.0
159
160 # calculate the joint angles
161 return [j1, math.pi/2 - theta - alpha, math.pi - elbow_supplement]
162
163
164 #================================================================
165 # motion primitives
166
167 def go_joints(self, target):
168 """Issue a position command to move to the given endpoint position expressed in joint angles as radians."""
169
170 self.motor1.setPosition(target[0])
171 self.motor2.setPosition(target[1])
172 self.motor3.setPosition(target[2])
173 self.joint_target = target
174 # print("%s: moving to (%f, %f, %f)" % (self.robot_name, target[0], target[1], target[2]));
175
176
177 #================================================================
178 # Polling function to process camera input. The API doesn't seem to include
179 # any method for detecting frame capture, so this just samples at the
180 # expected frame rate. It is possible it might retrieve duplicate frames or
181 # experience time aliasing.
182
183 def poll_camera(self):
184 self.camera_frame_timer -= EVENT_LOOP_DT
185 if self.camera_frame_timer < 0:
186 self.camera_frame_timer += self.camera_frame_dt
187 # read the camera
188 image = self.camera.getImage()
189 if image is not None:
190 # print("read %d byte image from camera" % (len(image)))
191 self.frame_count += 1
192
193 # convert the image data from a raw bytestring into a 3D matrix
194 # the pixel format is BGRA, which is the default for OpenCV
195 width = self.camera.getWidth()
196 height = self.camera.getHeight()
197 frame = np.frombuffer(image, dtype=np.uint8).reshape(height, width, 4)
198
199 # temporary: write image to file for offline testing
200 # cv.imwrite("capture-images/%04d.png" % (self.frame_count), frame)
201
202 # convert to grayscale and normalize levels
203 frame = cv.cvtColor(frame, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
204
205 # extract features from the image
206 render = self._find_round_image_targets(frame)
207
208 # display a debugging image in the Webots display
209 imageRef = self.display.imageNew(render.tobytes(), format=Display.RGB, width=width, height=height)
210 self.display.imagePaste(imageRef, 0, 0, False)
211
212 #================================================================
213 # Analyze a grayscale image for circular targets.
214 # Updates the internal state. Returns and annotated debugging image.
215 def _find_round_image_targets(self, grayscale):
216 circles = vision.find_circles(grayscale)
217
218 # generate controls from the feature data
219 if circles is None:
220 if self.vision_target is not None:
221 print("target not visible, tracking dropped")
222 self.vision_target = None
223 else:
224 # find the offset of the first circle center from the image center in pixels,
225 # ignoring the radius value
226 height, width = grayscale.shape
227 halfsize = np.array((width/2, height/2))
228 offset = circles[0][0:2] - halfsize
229
230 # normalize to unit scale, i.e. range of each dimension is (-1,1)
231 self.vision_target = offset / halfsize
232
233 # invert the Y coordinate so that positive values are 'up'
234 self.vision_target[1] *= -1.0
235 # print("target: ", self.vision_target)
236
237 # produce a debugging image
238 return vision.annotate_circles(grayscale, circles)
239
240 #================================================================
241
242 # Define joint-space movement sequences as a Bezier cubic spline
243 # trajectories specified in degrees. Each sequence should have three rows
244 # per spline segment.
245
246 # This initial motion brings the arm from the vertical home position to a
247 # 'work' pose with the camera pointing forward.
248
249 _home_to_work = np.array(
250 [
251 [ 0, 0, 0],
252 [ 0, 10, 60],
253 [ 0, 10, 60], # waypoint
254 ])
255
256 # This begins and ends at the 'work' pose, and is looped by poll_spline_path().
257 _path = np.array([
258 [ 0, 10, 60],
259 [ 15, 10, 60],
260 [ 15, 10, 60], # waypoint
261
262 [ 15, 10, 60],
263 [ -15, 10, 60],
264 [ -15, 10, 60], # waypoint
265
266 [ 15, 10, 60],
267 [ 0, 10, 60],
268 [ 0, 10, 60], # waypoint
269
270 [ 0, 10, 60],
271 [ 0, 10, 60],
272 [ 0, 10, 60], # waypoint
273 ])
274
275
276 def _init_spline(self):
277 """Create the Bezier spline interpolator and add the initial path from the home position."""
278 self.interpolator = bezier.PathSpline(axes=3)
279 self.interpolator.set_tempo(45.0)
280 self.interpolator.add_spline(self._home_to_work)
281 self._last_segment_count = self.interpolator.segments()
282
283 def poll_spline_path(self):
284 """Update function to loop a cubic spline trajectory."""
285 degrees = self.interpolator.update(dt=EVENT_LOOP_DT*0.001)
286 radians = [math.radians(theta) for theta in degrees]
287
288 # mirror the base rotation of the right robot for symmetric motion
289 if 'right' in self.robot_name:
290 radians[0] *= -1
291
292 self.go_joints(radians)
293 # print("u: ", self.interpolator.u, "knots:", self.interpolator.knots.shape[0])
294
295 segment_count = self.interpolator.segments()
296 if segment_count != self._last_segment_count:
297 self._last_segment_count = segment_count
298 print("Starting next spline segment.")
299
300 if self.interpolator.is_done():
301 print("Restarting the spline path.")
302 self.interpolator.add_spline(self._path)
303
304 #================================================================
305 # Define joint-space movement sequences. For convenience the joint angles
306 # are specified in degrees, then converted to radians for the controllers.
307 _right_poses = [[0, 0, 0],
308 [-45, 0, 60],
309 [45, 60, 60],
310 [0, 60, 0],
311 ]
312
313 _left_poses = [[0, 0, 0],
314 [45, 0, 60],
315 [-45, 60, 60],
316 [0, 60, 0],
317 ]
318
319 #================================================================
320 def poll_sequence_activity(self):
321 """State machine update function to walk through a series of poses at regular intervals."""
322
323 # Update the state timer
324 self.state_timer -= EVENT_LOOP_DT
325
326 # If the timer has elapsed, reset the timer and update the outputs.
327 if self.state_timer < 0:
328 self.state_timer += 2000
329
330 # Look up the next pose.
331 if 'left' in self.robot_name:
332 next_pose = self._left_poses[self.state_index]
333 self.state_index = (self.state_index + 1) % len(self._left_poses)
334 else:
335 next_pose = self._right_poses[self.state_index]
336 self.state_index = (self.state_index + 1) % len(self._right_poses)
337
338 # Convert the pose to radians and issue to the motor controllers.
339 angles = [math.radians(next_pose[0]), math.radians(next_pose[1]), math.radians(next_pose[2])]
340 self.go_joints(angles)
341
342 #================================================================
343 def apply_target_tracking(self):
344 # self.vision_target is a 2D vector representing the normalized target
345 # displacement from the image center. The following approximates the
346 # robot yaw and pitch error in radians using the half-angle of the field
347 # of view. The negative sign results from the robot kinematics, e.g. a
348 # positive yaw moves the camera to the left, so a positive image plane
349 # error needs a negative yaw to track toward the right.
350
351 field_of_view = 0.75 # horizontal FOV of Webots camera in radians
352 yaw_error, pitch_error = -0.5 * field_of_view * self.vision_target
353
354 # print("yaw and pitch error:", yaw_error, pitch_error)
355
356 # Calculate a joint velocity to reduce angular error. For now, this
357 # uses the base Z axis to control yaw and the elbow Y axis to control
358 # pitch; the shoulder Y axis is unchanged. The feedback gain scales
359 # angular error to angular velocity.
360 joint_velocity = np.array((0.5 * yaw_error, 0.0, 0.5 * pitch_error))
361 print("target tracking joint velocity:", joint_velocity)
362
363 # Update the position targets for this cycle for the given velocity.
364 dt = 0.001 * EVENT_LOOP_DT
365 new_joint_target = self.joint_target + dt * joint_velocity
366
367 self.go_joints(new_joint_target)
368 return
369
370
371 #================================================================
372 def run(self):
373 # Run loop to execute a periodic script until the simulation quits.
374 # If the controller returns -1, the simulator is quitting.
375 while self.step(EVENT_LOOP_DT) != -1:
376 # Read simulator clock time.
377 self.sim_time = self.getTime()
378
379 # Process available camera data.
380 self.poll_camera()
381
382 # If a target is visible, try tracking it
383 if self.vision_target is not None:
384 self.apply_target_tracking()
385
386 else:
387 # Update the spline trajectory generator.
388 self.poll_spline_path()
389
390################################################################
391# Start the script.
392robot = ZYY()
393robot.run()
Machine Vision Module¶
1# vision.py
2# OpenCV machine vision image processing functions.
3# No copyright, 2024, Garth Zeglin. This file is explicitly placed in the public domain.
4
5# Import the standard Python math library.
6import math
7
8# Import the third-party numpy library for matrix calculations.
9# Note: this can be installed using 'pip3 install numpy' or 'pip3 install scipy'.
10import numpy as np
11
12# Import the third-party OpenCV library for image operations.
13# Note: this can be installed using 'pip3 install opencv-python'
14import cv2 as cv
15
16################################################################
17def find_circles(grayscale_image):
18
19 # normalize levels to full range of pixel values
20 frame = cv.normalize(grayscale_image, None, 0, 255, cv.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv.CV_8U)
21
22 # reduce noise
23 img = cv.medianBlur(frame,5)
24
25 circles = cv.HoughCircles(img,
26 method=cv.HOUGH_GRADIENT,
27 dp=1, # accumulator has same resolution as the image
28 minDist=8, # minimum center to center distance
29 param1=200, # with HOUGH_GRADIENT, Canny edge threshold
30 param2=20, # with HOUGH_GRADIENT, accumulator threshold
31 minRadius=0,
32 maxRadius=0)
33
34 if circles is None:
35 return None
36 else:
37 # the result seems to be a 1 x num-circles x 3 matrix
38 # this reshapes it to a 2D matrix, each row is then [x y r]
39 num_circles = circles.shape[1]
40 return circles.reshape((num_circles, 3))
41
42################################################################
43def annotate_circles(grayscale_image, circles):
44
45 # create color image for visualization
46 cimg = cv.cvtColor(grayscale_image,cv.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
47 if circles is not None:
48 circles = np.uint16(np.round(circles))
49 for i in circles:
50 # draw the perimeter in green
51 cv.circle(cimg,(i[0],i[1]),i[2],(0,255,0),2)
52
53 # draw the center of the circle in red
54 cv.circle(cimg,(i[0],i[1]),2,(255,0,0),3)
55 return cimg
56
57################################################################
58def find_lines(grayscale_image):
59 # convert to binary image
60 # ret, frame = cv.threshold(frame, 127, 255, cv.THRESH_BINARY)
61
62 # normalize levels to full range of pixel values
63 frame = cv.normalize(grayscale_image, None, 0, 255, cv.NORM_MINMAX, dtype=cv.CV_8U)
64
65 # find edges, return binary edge image
66 frame = cv.Canny(frame, 100, 200)
67
68 # extract possible lines
69 lines = cv.HoughLines(frame, rho=1, theta=math.radians(10), threshold=20)
70 if lines is not None:
71 print("found %d possible lines, shape is %s" % (len(lines), lines.shape))
72 # print(lines)
73 else:
74 print("no lines found")
75 return lines
76
77################################################################
78def annotate_lines(grayscale_image, lines):
79
80 # show the image in the debugging viewer window
81 render = cv.cvtColor(grayscale_image, cv.COLOR_GRAY2RGB)
82 if lines is not None:
83 for line in lines:
84 rho, theta = line[0] # line is a matrix with shape (1, 2)
85 a = np.cos(theta)
86 b = np.sin(theta)
87 x0 = a*rho
88 y0 = b*rho
89 x1 = int(x0 + 100*(-b))
90 y1 = int(y0 + 100*(a))
91 x2 = int(x0 - 100*(-b))
92 y2 = int(y0 - 100*(a))
93 cv.line(render,(x1,y1),(x2,y2),(255,0,0),1)
94
95 return render
96
97################################################################
98# Test script to perform when run this file is run as a standalone script.
99if __name__ == "__main__":
100 import argparse
101 import os.path
102 parser = argparse.ArgumentParser( description = """Test vision processing using a test image.""")
103 parser.add_argument('paths', nargs="+", help="One or more image files to analyze.")
104 args = parser.parse_args()
105
106 # read a test image
107 for path in args.paths:
108 frame = cv.imread(path)
109 if frame is None:
110 print("Unable to load %s." % (path))
111 else:
112 print("Read image %s with shape: %s" % (path, frame.shape))
113
114 # convert to grayscale and normalize levels
115 frame = cv.cvtColor(frame, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
116
117 circles = find_circles(frame)
118
119 if circles is None:
120 print("no circles detected")
121 else:
122 print("detected %d circle(s):" % (circles.shape[0]))
123 print(circles)
124
125 cimg = annotate_circles(frame, circles)
126 debug_path = os.path.join("debug-images", os.path.basename(path))
127 print("Writing ", debug_path)
128 cv.imwrite(debug_path, cimg)
Bezier Spline Module¶
1# bezier.py
2#
3# Support for Bezier cubic spline interpolation and path generation.
4
5# Import the third-party numpy library for matrix calculations.
6# Note: this can be installed using 'pip3 install numpy' or 'pip3 install scipy'.
7import numpy as np
8
9#================================================================
10class PathSpline:
11 """Representation of a multi-axis multi-segment Bezier cubic spline
12 trajectory. This may be useful for interpolating a path through joint space
13 or Cartesian space.
14 """
15
16 def __init__(self, axes=3):
17 # Initialize a default spline buffer. The invariant is that this will
18 # always retain at least one segment. It should always have (1+3*segs)
19 # rows where segs is the number of path segments.
20 self.knots = np.zeros((4, axes))
21
22 # Set the default execution rate in spline segments per second.
23 self.rate = 1.0
24
25 # Initialize the current position at the end of the path. The position
26 # advances by one unit per segment.
27 self.u = 1.0
28
29 # Initialize the current interpolated value.
30 self.value = np.zeros((axes))
31
32 def set_tempo(self, spm):
33 """Set the execution rate of the spline interpolator in units of
34 segments/minute. The initial default value is 60 segs/min (1 per
35 second)."""
36 self.rate = max(min(spm/60.0, 5), 0.0001)
37
38 def axes(self):
39 """Return the number of axes."""
40 return self.knots.shape[1]
41
42 def segments(self):
43 """Return the number of spline segments in the path."""
44 return (self.knots.shape[0]-1)//3
45
46 def update(self, dt):
47 """Advance the spline position given the elapsed interval dt (in
48 seconds) and recalculate the spline interpolation. Returns the current
49 interpolated value."""
50 if dt > 0.0:
51 self.u += self.rate * dt
52 # Determine whether to roll over to the next segment or not. This will
53 # always leave one segment remaining.
54 segs = (self.knots.shape[0]-1) // 3
55 if segs > 1:
56 if self.u >= 1.0:
57 # u has advanced to next segment, drop the first segment by dropping the first three knots
58 self.knots = self.knots[3:]
59 self.u -= 1.0
60
61 # always limit u to the first active segment
62 self.u = min(max(self.u, 0.0), 1.0)
63
64 # update interpolation
65 self._recalculate()
66 return self.value
67
68 def is_done(self):
69 """Returns True if the evaluation has reached the end of the last spline segment."""
70 return (self.u >= 1.0) and (self.knots.shape[0] == 4)
71
72 def _recalculate(self):
73 """Apply the De Casteljau algorithm to calculate the position of
74 the spline at the current path point."""
75
76 # unroll the De Casteljau iteration and save intermediate points
77 num_axes = self.knots.shape[1]
78 beta = np.ndarray((3, num_axes))
79
80 # note: could use more numpy optimizations
81 u = self.u
82 for k in range(3):
83 beta[k] = self.knots[k] * (1 - u) + self.knots[k+1] * u
84
85 for k in range(2):
86 beta[k] = beta[k] * (1 - u) + beta[k+1] * u;
87
88 self.value[:] = beta[0] * (1 - u) + beta[1] * u
89
90 def set_target(self, value):
91 """Reset the path generator to a single spline segment from the current
92 value to the given value. The path defaults to 'ease-out', meaning the
93 rate of change is discontinuous at the start and slows into the target
94
95 :param value: iterable with one value per axis"""
96 self.knots[0,:] = self.value # start at the current levels
97 self.knots[1,:] = value # derivative discontinuity
98 self.knots[2,:] = value # ease at the target
99 self.knots[3,:] = value # target endpoint
100
101 # reset the path position to start the new segment
102 self.u = 0.0;
103
104 def set_value(self, value):
105 """Reset the path generator immediately to the given value with no
106 interpolation.
107
108 :param value: iterable with one value per axis"""
109
110 self.knots[0,:] = value
111 self.knots[1,:] = value
112 self.knots[2,:] = value
113 self.knots[3,:] = value
114
115 # reset the path position to start the new segment
116 self.u = 1.0;
117
118 # reset current value
119 self.value[:] = value
120
121 def add_spline(self, knots):
122 """Append a sequence of Bezier spline segments to the path
123 generator, provided as a numpy matrix with three rows per segment and
124 one column per axis."""
125
126 self.knots = np.vstack((self.knots, knots))
127
128 # Note: the path position and current value are left unchanged. If the
129 # interpolator is at the end of the current segment, it will now begin
130 # to advance into these new segments.
131 return
Vision Target Animation¶
The arm-camera.wbt world includes an instance of a controllable vision
target robot using 2D Cartesian gantry kinematics as defined in
cartesian-target.proto. This model has no dynamics but can be positioned.
The following script produces a fixed target motion pattern.
1# cartesian_target.py
2# Copyright, 2024, Garth Zeglin.
3# Sample Webots controller file for moving a spherical vision target using a 2D cartesian mechanism.
4
5print("cartesian_target.py waking up.")
6
7# Import standard Python libraries.
8import math
9
10# Import the Webots simulator API.
11from controller import Robot
12
13# Define the time step in milliseconds between controller updates.
14EVENT_LOOP_DT = 20
15
16# Request a proxy object representing the robot to control.
17robot = Robot()
18robot_name = robot.getName()
19print("%s: controller connected." % (robot_name))
20
21# Fetch handles for the motors.
22ymotor = robot.getDevice('ymotor')
23zmotor = robot.getDevice('zmotor')
24
25# Set time constants for the overall oscillation.
26lateral_period = 30.0
27
28# run loop to execute a periodic script until the simulation quits.
29# If the controller returns -1, the simulator is quitting.
30while robot.step(EVENT_LOOP_DT) != -1:
31 # Read simulator clock time.
32 t = robot.getTime()
33
34 # Move the target through a Lissajous pattern.
35 yphase = t * (2*math.pi/lateral_period)
36 ymotor.setPosition(1.0 * math.sin(yphase))
37 zmotor.setPosition(1.0 + 0.25 * math.sin(2.25*yphase))