ZYY Robot Arm Model¶
The zyy robot model simulates a three-DOF robot arm structured as a two-link arm on a rotating base. The base joint1 rotates around the vertical Z axis, followed by a shoulder joint2 around the horizontal Y axis and elbow joint3, parallel to joint2 around the Y axis. The reference pose is straight up. The arm has a distance sensor at the end. The model is intended as a demonstration testbed for zyy kinematics.
The link geometry uses only cylinder primitives. The same geometry is referenced to use as bounding objects for collision and automatic calculation of physics parameters. The base object has a NULL Physics object so it does not move, simulating a rigid connection to the ground.
The end sensor is represented by a yellow cone. It is implemented as a DistanceSensor of limited range, pointing outward along the link axis from the end of the second link.
This model is demonstrated in the zyy.wbt world.
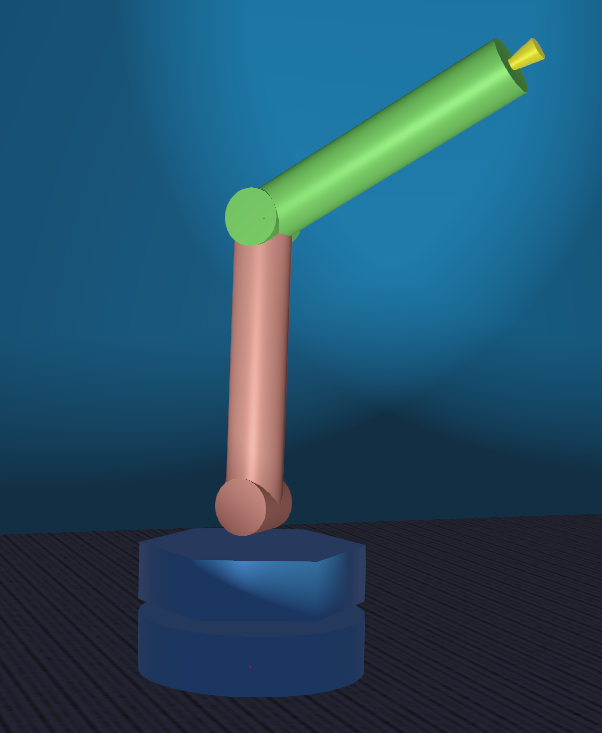

Screenshot of Webots zyy robot arm robot model.¶
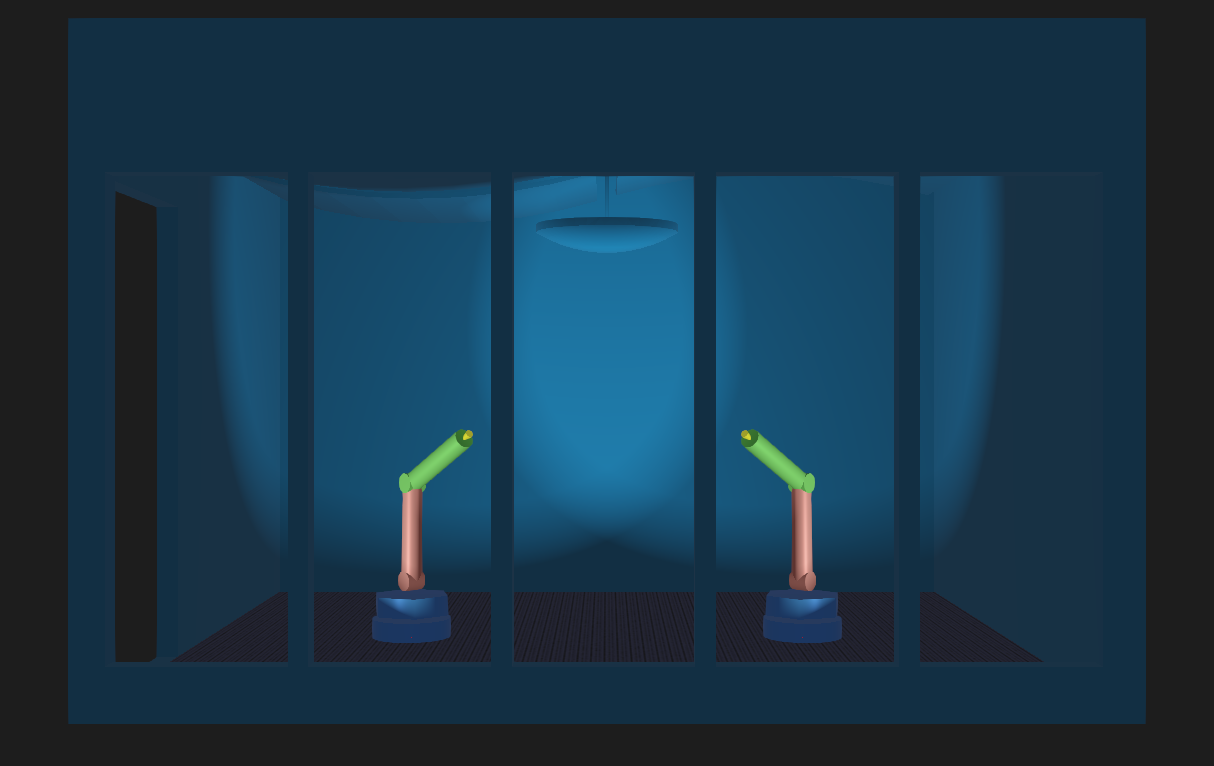

Screenshot of Webots sample world zyy.wbt with two zyy robot arms in the HL A11 room.¶
System Kinematics¶
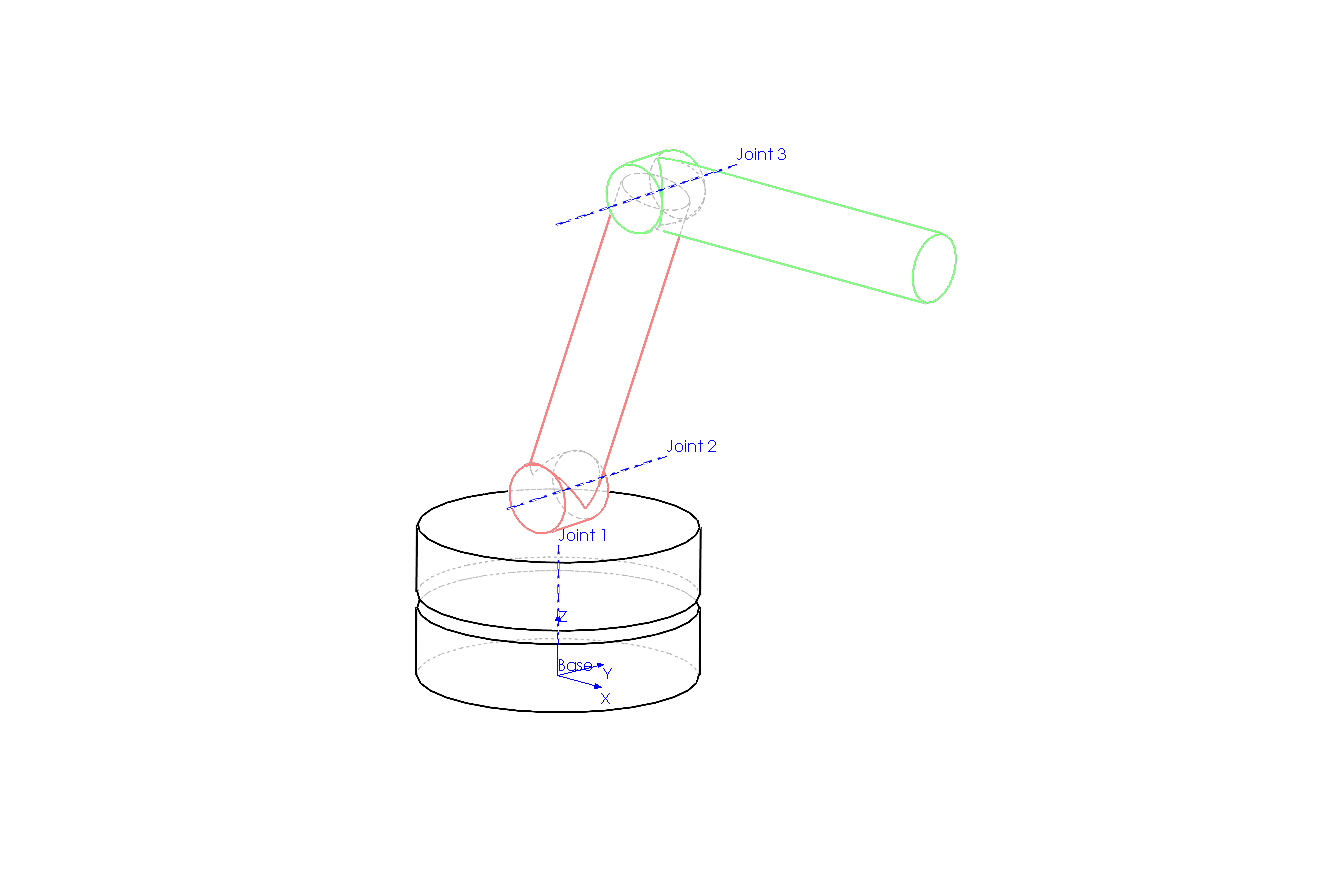
Kinematic diagram of the zyy robot arm model.¶
The bodies are as follows:
name |
color |
notes |
|---|---|---|
fixed |
blue |
base object fixed to the ground |
base |
blue |
upper base element rotating around the Z axis |
link1 |
red |
proximal link, attaches to base at ‘shoulder’ |
link2 |
green |
the distal link, attaches to link1 at ‘elbow’ |
The joints are as follows:
name |
parent |
child |
notes |
|---|---|---|---|
joint1 |
fixed |
base |
the base pivot, includes motor1 |
joint2 |
base |
link1 |
the ‘shoulder’, includes motor2 |
joint3 |
link1 |
link2 |
the ‘elbow’, includes motor3 |
The joint limits are as follows:
name |
min deg |
max deg |
description |
|---|---|---|---|
joint1 |
-120 |
120 |
symmetric pivot around vertical axis |
joint2 |
-5 |
90 |
from slight reverse down to link1 horizontal |
joint3 |
-5 |
120 |
from slight reverse down to an acute retraction |
The axes are as follows:
name |
direction |
notes |
|---|---|---|
joint1 |
along Z |
located above the origin |
joint2 |
along Y |
located above the origin |
joint3 |
along Y |
located at the end of link1 |
The motors and sensors are named as follows:
name |
notes |
|---|---|
motor1 |
RotationalMotor on joint1 |
motor2 |
RotationalMotor on joint2 |
motor3 |
RotationalMotor on joint3 |
joint1 |
PositionSensor on joint1 |
joint2 |
PositionSensor on joint2 |
joint3 |
PositionSensor on joint3 |
endRangeSensor |
DistanceSensor at end of link2 |
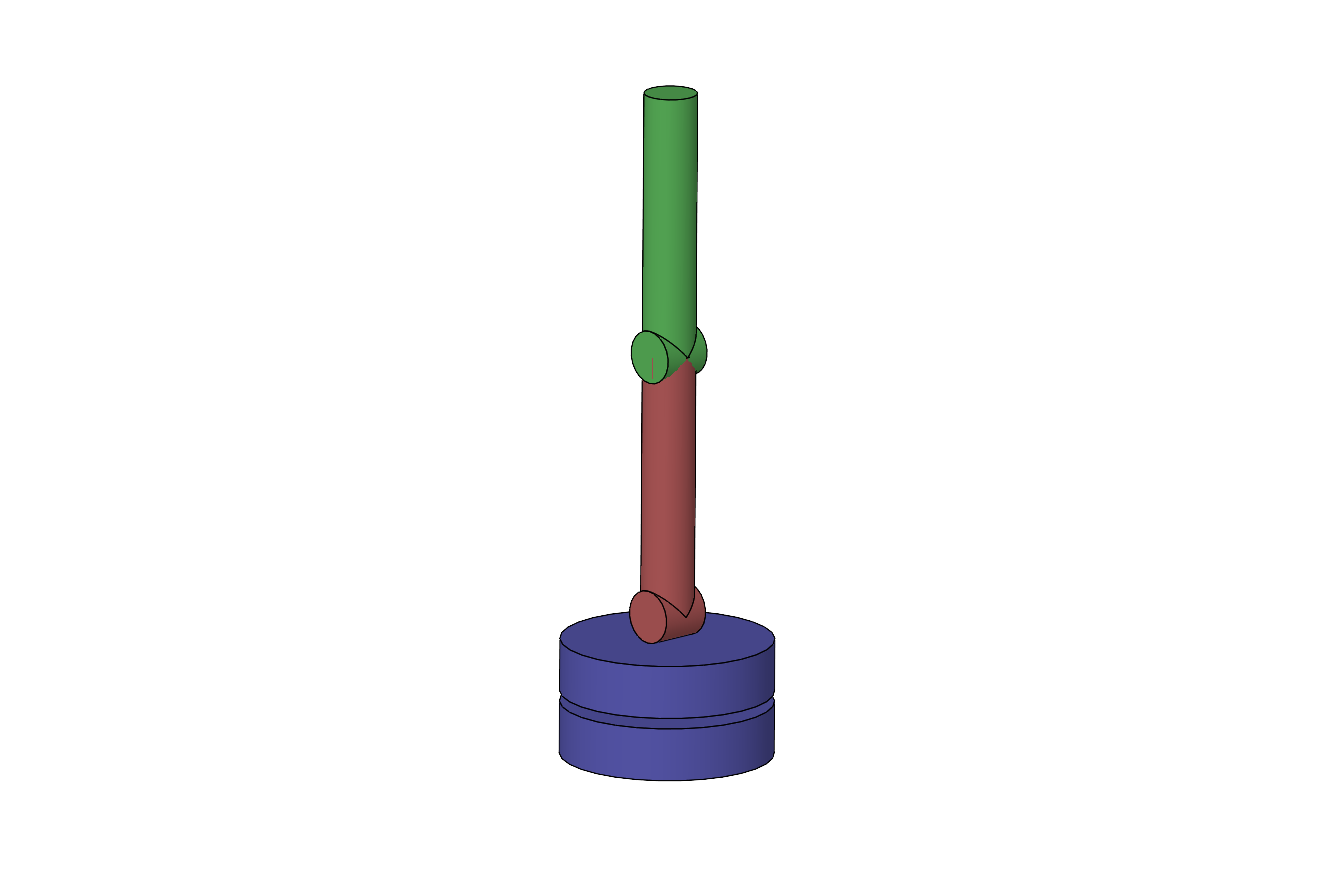
Reference pose of the zyy robot arm model: all joints are zero when the arm is pointing straight up.¶
zyy.proto¶
The robot model has been encapsulated in a .proto file for easy reuse. The model includes user-accessible link length parameters to demonstrate procedural scaling.
1#VRML_SIM R2023b utf8
2#
3# Two-link actuated arm featuring three degreees of freedom. The first axis is
4# a base rotation around Z, followed by two arm joints rotating around Y. The
5# graphics use only cylinder and cone primitives. The base has NULL physics so
6# it will be fixed in place. The two link lengths are adjustable parameters to
7# demonstrate using procedural elements in the prototype. The link physics
8# properties are specified using density so the dynamics will also scale, but
9# the motor parameters are constant. The end includes a distance sensor pointed
10# along the second link axis.
11#
12# documentation url: https://courses.ideate.cmu.edu/16-375
13# license: No copyright, 2020-2024 Garth Zeglin. This file is explicitly placed in the public domain.
14
15PROTO zyy [
16 field SFVec3f translation 0 0 0
17 field SFRotation rotation 0 1 0 0
18 field SFFloat link1Length 0.5
19 field SFFloat link2Length 0.5
20 field SFString controller "zyy"
21 field SFString name ""
22 field SFString customData ""
23]
24{
25 Robot {
26 # connect properties to user-visible data fields
27 translation IS translation
28 rotation IS rotation
29 controller IS controller
30 name IS name
31 customData IS customData
32
33 # calculate derived parameters
34 %{
35 local halfLink1Len = fields.link1Length.value / 2
36 local halfLink2Len = fields.link2Length.value / 2
37 }%
38
39 # define the kinematic tree
40 children [
41 # add a default radio receiver and transmitter
42 Receiver {
43 channel 1
44 }
45 Emitter {
46 channel 1
47 }
48
49 # the cylindrical base shape is wrapped in a Pose
50 # to position it within the robot body coordinates
51 DEF fixedBaseShape Pose {
52 translation 0 0 0.05
53 children [
54 Shape {
55 appearance DEF blueAppearance PBRAppearance {
56 baseColor 0.21529 0.543008 0.99855
57 metalness 0.5
58 roughness 0.5
59 }
60 geometry Cylinder {
61 height 0.1
62 radius 0.2
63 }
64 }
65 ]
66 }
67
68 # define the base Z-axis pivot connecting the fixed base and the rotating base
69 HingeJoint {
70 jointParameters HingeJointParameters {
71 axis 0 0 1
72 # limit travel to (-120, 120) degrees
73 minStop -2.0943951023931953
74 maxStop 2.0943951023931953
75 }
76 device [
77 PositionSensor {
78 name "joint1"
79 }
80 RotationalMotor {
81 name "motor1"
82 acceleration 2
83 maxVelocity 3.14
84 maxTorque 20
85 }
86 ]
87 # define rotating base element
88 endPoint Solid {
89 translation 0 0 0.120
90 name "base"
91 children [
92 DEF rotatingBaseShape Pose {
93 translation 0 0 0.050
94 children [
95 # rotating base geometry
96 Shape {
97 appearance USE blueAppearance
98 geometry Cylinder {
99 height 0.100
100 radius 0.200
101 subdivision 6
102 }
103 }
104 ]
105 }
106 # define the j2 Y axis pivot connecting the rotating base and the first arm link
107 HingeJoint {
108 jointParameters HingeJointParameters {
109 axis 0 1 0
110 anchor 0 0 0.170
111 # limit travel to (-5, 90) degrees
112 minStop -0.08726646259971647
113 maxStop 1.5707963267948966
114 }
115 device [
116 PositionSensor {
117 name "joint2"
118 }
119 RotationalMotor {
120 name "motor2"
121 acceleration 2
122 maxVelocity 3.14
123 maxTorque 20
124 }
125 ]
126 # start definition of the first link
127 endPoint Solid {
128 # place the shape origin halfway along the first link;
129 # this vector is in base coordinates, Z points along
130 # the link in the neutral pose
131 translation 0 0 %{=halfLink1Len+0.17}%
132
133 children [
134 # define the j3 Y-axis 'elbow' pivot connecting the links
135 HingeJoint {
136 jointParameters HingeJointParameters {
137 axis 0 1 0
138 # place the elbow joint axis at the end of the first
139 # link; position is relative to link1 origin
140 anchor 0 0 %{= halfLink1Len }%
141 dampingConstant 0.1
142 # limit travel to (-5, 120) degrees
143 minStop -0.08726646259971647
144 maxStop 2.0943951023931953
145 }
146 device [
147 PositionSensor {
148 name "joint3"
149 }
150 RotationalMotor {
151 name "motor3"
152 acceleration 2
153 maxVelocity 6.28
154 maxTorque 15
155 }
156 ]
157 # define the second link
158 endPoint Solid {
159 # place the link2 origin halfway along the second link
160 translation 0 0 %{= halfLink1Len+halfLink2Len}%
161 children [
162 # the cylindrical link shape is wrapped in a Pose
163 # to position it within the link2 coordinates
164 DEF link2Shape Pose {
165 # the Cylinder shape coordinates use Z as the
166 # long axis; this 90 deg rotation around Y
167 # places the lengthwise Z axis along the link.
168 children [
169 Shape {
170 appearance DEF greenAppearance PBRAppearance {
171 baseColor 0.413001 1 0.33489
172 metalness 0.5
173 roughness 0.5
174 }
175 geometry Cylinder {
176 height IS link2Length
177 radius 0.05
178 }
179 }
180 ]
181 } # end link2 Shape
182 # add a visual hub to the base of link2, not part of the bounding object
183 Pose {
184 rotation 1 0 0 1.5708
185 translation 0 0 %{= -halfLink2Len}%
186 children [
187 Shape {
188 appearance USE greenAppearance
189 geometry Cylinder {
190 height 0.1
191 radius 0.05
192 }
193 }
194 ]
195 } # end Pose around link2 base hub
196 # define a DistanceSensor attached to the second link Solid node
197 DistanceSensor {
198 translation 0 0 %{= halfLink2Len}%
199 name "endRangeSensor"
200
201 # the sensor lookup table implicitly defines the maximum range and the units, each
202 # entry is [distance, value, noise]
203 lookupTable [
204 0 0 0
205 0.9 0.9 0 # 0.9 meters reads as 0.9 meters
206 ]
207 resolution 0.001 # assume millimeter resolution
208 numberOfRays 5
209 aperture 0.1
210 children [
211 Pose {
212 # flip the cone representing the sensor so the base is up
213 rotation 0 1 0 3.14159
214 children [
215 Shape {
216 appearance PBRAppearance {
217 baseColor 1 0.99028 0.0584421
218 roughness 0.5
219 metalness 0.5
220 emissiveColor 1 0.99028 0.0584421
221 emissiveIntensity 0.2
222 }
223 geometry Cone {
224 bottomRadius 0.02
225 height 0.1
226 }
227 }
228 ]
229 }
230 ]
231 } # end DistanceSensor
232 ] # end link2 Solid children
233 # top-level properties of link2
234 name "link2"
235 boundingObject USE link2Shape
236 physics Physics {
237 # Assume the link is a thin-walled aluminum tube with 50 mm
238 # radius and 2 mm wall thickness. Aluminum has a density of
239 # 2700 kg/m^3, but this will be scaled by the ratio of the
240 # tube cross-section to the solid cylinder cross-section
241 # assumed by the simulator. Note that the moment of inertia
242 # around the long axis will be underestimated.
243 # density = 2700 * (R_outer**2 - R_inner**2) / R_outer**2
244 density 211.7
245 mass -1
246 }
247 }
248 }
249 # finish the definition of link1 with a shape
250 # node in the 'children' list
251 DEF link1Shape Pose {
252 children [
253 Shape {
254 appearance DEF redAppearance PBRAppearance {
255 baseColor 00.990494 0.516915 0.468254
256 metalness 0.5
257 roughness 0.5
258 }
259 geometry Cylinder {
260 height IS link1Length
261 radius 0.05
262 }
263 }
264 ]
265 }
266 # add a visual hub to the base of link1, not part of the bounding object
267 Pose {
268 rotation 1 0 0 1.5708
269 translation 0 0 %{= -halfLink1Len}%
270 children [
271 Shape {
272 appearance USE redAppearance
273 geometry Cylinder {
274 height 0.1
275 radius 0.05
276 }
277 }
278 ]
279 } # end Pose around link1 base hub
280 ] # close the children list of the link1 node
281 # top-level properties of link1
282 name "link1"
283 boundingObject USE link1Shape
284 physics Physics {
285 # See notes for link2 density; this assumes the same geometry.
286 density 211.7
287 mass -1
288 } # close the Physics for the first arm link
289 } # close the Solid in the HingeJoint endpoint
290 } # close the HingeJoint between the base and the first arm link
291 ] # close the children of the rotating base
292 # the rotating robot base participates in collisions
293 boundingObject USE rotatingBaseShape
294 # the rotating robot base has some mass and physics
295 physics Physics {
296 mass 2.0
297 density -1
298 }
299 } # close the Solid in the base axis HingeJoint endpoint
300 } # close the HingeJoint between the fixed and rotating base
301 ] # close the children list of the base Robot node
302
303 # the fixed robot base participates in collision
304 boundingObject USE fixedBaseShape
305
306 # the base of the robot itself has NULL physics to simulate being fixed to the ground
307
308 } # close the Robot definition
309}
Sample Control Code¶
1# zyy.py
2#
3# Sample Webots controller file for driving a two-link arm with three driven
4# joints. This example provides inverse kinematics for performing
5# position-controlled trajectories.
6
7# No copyright, 2020-2024, Garth Zeglin. This file is
8# explicitly placed in the public domain.
9
10print("zyy.py waking up.")
11
12# Import the Webots simulator API.
13from controller import Robot
14
15# Import the standard Python math library.
16import math, random, time
17
18# Import the bezier module from the same directory. Note: this requires numpy.
19import bezier
20
21# Import the third-party numpy library for matrix calculations.
22# Note: this can be installed using 'pip3 install numpy' or 'pip3 install scipy'.
23import numpy as np
24
25# Define the time step in milliseconds between controller updates.
26EVENT_LOOP_DT = 20
27
28################################################################
29class ZYY(Robot):
30 def __init__(self):
31
32 super(ZYY, self).__init__()
33 self.robot_name = self.getName()
34 print("%s: controller connected." % (self.robot_name))
35
36 # Attempt to randomize the random library sequence.
37 random.seed(time.time())
38
39 # Initialize geometric constants. These should match
40 # the current geometry of the robot.
41 self.base_z = 0.29 # joint2 axis height: 0.12 fixed base height + 0.17 j2 z offset
42 self.link1 = 0.5 # link1 length, i.e. distance between j2 and j3
43 self.link2 = 0.5 # link2 length, i.e. distance between j3 and end
44
45 # Fetch handles for the joint motors.
46 self.motor1 = self.getDevice('motor1')
47 self.motor2 = self.getDevice('motor2')
48 self.motor3 = self.getDevice('motor3')
49
50 # Adjust the motor controller properties.
51 self.motor1.setAvailableTorque(20.0)
52 self.motor2.setAvailableTorque(15.0)
53 self.motor3.setAvailableTorque(10.0)
54
55 # Adjust the low-level controller gains.
56 print("%s: setting PID gains." % (self.robot_name))
57 self.motor1.setControlPID(100.0, 0.0, 25.0)
58 self.motor2.setControlPID( 50.0, 0.0, 15.0)
59 self.motor3.setControlPID( 50.0, 0.0, 15.0)
60
61 # Fetch handles for the joint sensors.
62 self.joint1 = self.getDevice('joint1')
63 self.joint2 = self.getDevice('joint2')
64 self.joint3 = self.getDevice('joint3')
65
66 # Specify the sampling rate for the joint sensors.
67 self.joint1.enable(EVENT_LOOP_DT)
68 self.joint2.enable(EVENT_LOOP_DT)
69 self.joint3.enable(EVENT_LOOP_DT)
70
71 # Connect to the end sensor.
72 self.end_sensor = self.getDevice("endRangeSensor")
73 self.end_sensor.enable(EVENT_LOOP_DT) # set sampling period in milliseconds
74 self.end_sensor_interval = 1000
75 self.end_sensor_timer = 1000
76
77 # Initialize behavior state machines.
78 self.state_timer = 2*EVENT_LOOP_DT
79 self.state_index = 0
80 self._init_spline()
81 return
82
83 #================================================================
84 def endpoint_forward_kinematics(self, q):
85 """Compute the forward kinematics for the end point. Returns the
86 body-coordinate XYZ Cartesian position of the end point for a given joint
87 angle vector.
88 :param q: three-element list with [q1, q2, q3] joint angles in radians
89 :return: three-element list with endpoint [x,y,z] location
90
91 """
92 j1 = q[0]
93 j2 = q[1]
94 j3 = q[2]
95
96 return [(self.link1*math.sin(j2) + self.link2*math.sin(j2 + j3))*math.cos(j1),
97 (self.link1*math.sin(j2) + self.link2*math.sin(j2 + j3))*math.sin(j1),
98 self.base_z + self.link1*math.cos(j2) + self.link2*math.cos(j2 + j3)]
99
100 #================================================================
101 def endpoint_inverse_kinematics(self, target):
102 """Compute the joint angles for a target end position. The target is a
103 XYZ Cartesian position vector in body coordinates, and the result vector
104 is a joint angles as list [j1, j2, j3]. If the target is out of reach,
105 returns the closest pose. With j1 between -pi and pi, and j2 and j3
106 limited to positive rotations, the solution is always unique.
107 """
108
109 x = target[0]
110 y = target[1]
111 z = target[2]
112
113 # the joint1 base Z rotation depends only upon x and y
114 j1 = math.atan2(y, x)
115
116 # distance within the XY plane from the origin to the endpoint projection
117 xy_radial = math.sqrt(x*x + y*y)
118
119 # find the Z offset from the J2 horizontal plane to the end point
120 end_z = z - self.base_z
121
122 # angle between the J2 horizonta plane and the endpoint
123 theta = math.atan2(end_z, xy_radial)
124
125 # radial distance from the J2 axis to the endpoint
126 radius = math.sqrt(x*x + y*y + end_z*end_z)
127
128 # use the law of cosines to compute the elbow angle solely as a function of the
129 # link lengths and the radial distance from j2 to end
130 # R**2 = l1**2 + l2**2 - 2*l1*l2*cos(pi - elbow)
131 acosarg = (radius*radius - self.link1**2 - self.link2**2) / (-2 * self.link1 * self.link2)
132 if acosarg < -1.0: elbow_supplement = math.pi
133 elif acosarg > 1.0: elbow_supplement = 0.0
134 else: elbow_supplement = math.acos(acosarg)
135
136 print("theta:", theta, "radius:", radius, "acosarg:", acosarg)
137
138 # use the law of sines to find the angle at the bottom vertex of the triangle defined by the links
139 # radius / sin(elbow_supplement) = l2 / sin(alpha)
140 if radius > 0.0:
141 alpha = math.asin(self.link2 * math.sin(elbow_supplement) / radius)
142 else:
143 alpha = 0.0
144
145 # calculate the joint angles
146 return [j1, math.pi/2 - theta - alpha, math.pi - elbow_supplement]
147
148
149 #================================================================
150 # motion primitives
151
152 def go_joints(self, target):
153 """Issue a position command to move to the given endpoint position expressed in joint angles."""
154
155 self.motor1.setPosition(target[0])
156 self.motor2.setPosition(target[1])
157 self.motor3.setPosition(target[2])
158 # print("%s: moving to (%f, %f, %f)" % (self.robot_name, target[0], target[1], target[2]));
159
160
161 #================================================================
162 # Polling function to process sensor input at different timescales.
163 def poll_sensors(self):
164 self.end_sensor_timer -= EVENT_LOOP_DT
165 if self.end_sensor_timer < 0:
166 self.end_sensor_timer += self.end_sensor_interval
167
168 # read the distance sensor
169 distance = self.end_sensor.getValue()
170
171 if distance < 0.9:
172 # print("%s: range sensor detected obstacle at %f." % (self.robot_name, distance))
173 pass
174
175 #================================================================
176
177 # Define a joint-space movement sequence as a Bezier cubic spline trajectory
178 # specified in degrees. This should have three rows per spline segment.
179
180 _path = np.array([ # the first waypoint is implicitly zero
181 [ 0, 0, 0],
182 [ 5, 30, 30],
183 [ 5, 30, 30], # waypoint
184 [ 5, 30, 30],
185 [ 5, 30, 30],
186 [ 5, 30, 90], # waypoint
187 [ 5, 30, 30],
188 [ 5, 30, 30],
189 [ 5, 30, 30], # waypoint
190 [ 5, 30, 30],
191 [ 0, 0, 0],
192 [ 0, 0, 0], # waypoint
193 [ 0, 0, 0],
194 [ 45, 30, 30],
195 [ 45, 30, 30], # waypoint
196 [ 45, 30, 30],
197 [ 45, 30, 30],
198 [ 45, 30, 90], # waypoint
199 [ 45, 30, 30],
200 [ 45, 30, 30],
201 [ 45, 30, 30], # waypoint
202 [ 45, 30, 30],
203 [ 0, 0, 0],
204 [ 0, 0, 0], # waypoint (should be zero for continuity)
205 ])
206
207 def _init_spline(self):
208 self.interpolator = bezier.PathSpline(axes=3)
209 self.interpolator.set_tempo(30.0)
210 self.interpolator.add_spline(self._path)
211 self._last_segment_count = self.interpolator.segments()
212
213 def poll_spline_path(self):
214 """Update function to loop a cubic spline trajectory."""
215 degrees = self.interpolator.update(dt=EVENT_LOOP_DT*0.001)
216 radians = [math.radians(theta) for theta in degrees]
217
218 # mirror the base rotation of the right robot for symmetric motion
219 if 'right' in self.robot_name:
220 radians[0] *= -1
221
222 self.go_joints(radians)
223 # print("u: ", self.interpolator.u, "knots:", self.interpolator.knots.shape[0])
224
225 segment_count = self.interpolator.segments()
226 if segment_count != self._last_segment_count:
227 self._last_segment_count = segment_count
228 print("Starting next spline segment.")
229
230 if self.interpolator.is_done():
231 print("Restarting the spline path.")
232 self.interpolator.add_spline(self._path)
233
234 #================================================================
235 # Define joint-space movement sequences. For convenience the joint angles
236 # are specified in degrees, then converted to radians for the controllers.
237 _right_poses = [[0, 0, 0],
238 [-45, 0, 60],
239 [45, 60, 60],
240 [0, 60, 0],
241 ]
242
243 _left_poses = [[0, 0, 0],
244 [45, 0, 60],
245 [-45, 60, 60],
246 [0, 60, 0],
247 ]
248
249 #================================================================
250 def poll_sequence_activity(self):
251 """State machine update function to walk through a series of poses at regular intervals."""
252
253 # Update the state timer
254 self.state_timer -= EVENT_LOOP_DT
255
256 # If the timer has elapsed, reset the timer and update the outputs.
257 if self.state_timer < 0:
258 self.state_timer += 2000
259
260 # Look up the next pose.
261 if 'left' in self.robot_name:
262 next_pose = self._left_poses[self.state_index]
263 self.state_index = (self.state_index + 1) % len(self._left_poses)
264 else:
265 next_pose = self._right_poses[self.state_index]
266 self.state_index = (self.state_index + 1) % len(self._right_poses)
267
268 # Convert the pose to radians and issue to the motor controllers.
269 angles = [math.radians(next_pose[0]), math.radians(next_pose[1]), math.radians(next_pose[2])]
270 self.go_joints(angles)
271
272
273 #================================================================
274 def run(self):
275 # Run loop to execute a periodic script until the simulation quits.
276 # If the controller returns -1, the simulator is quitting.
277 while self.step(EVENT_LOOP_DT) != -1:
278 # Read simulator clock time.
279 self.sim_time = self.getTime()
280
281 # Read sensor values.
282 self.poll_sensors()
283
284 # Update the activity state machine.
285 # self.poll_sequence_activity()
286
287 # Update the spline trajectory generator.
288 self.poll_spline_path()
289
290
291################################################################
292# Start the script.
293robot = ZYY()
294robot.run()