Ultrasonic Ranger Examples - Raspberry Pi Pico¶
The following short Python programs will demonstrate essential operation of the
Raspberry Pi Pico board. These assume one or more binary input or output circuits are
externally attached. Each can be run by copying the program into code.py on
the CIRCUITPY drive offered by the board. The text can be pasted directly from
this page, or each file can be downloaded from the CircuitPython sample code
folder on this site.
Related Pages
Sample Ultrasonic Ranger Circuit¶
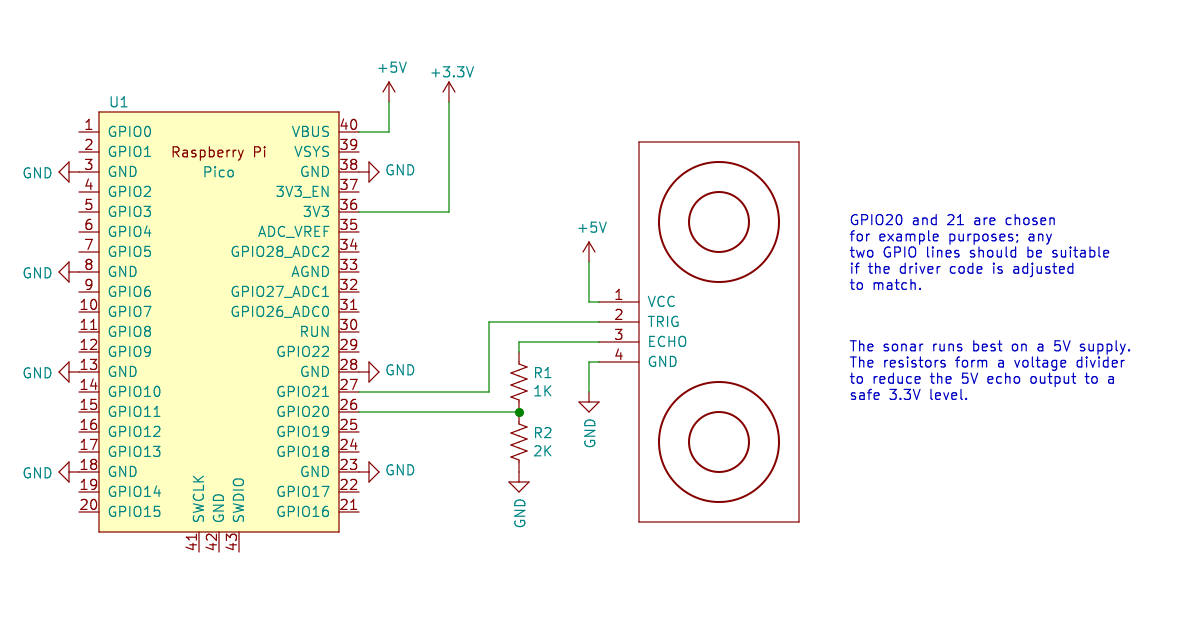
Sample sonar driver circuit using an HC-04 module. Any two GPIO pins may be used to control the driver. Please note the voltage divider to reduce the ECHO pin voltages to 3.3V logic levels.¶
Sonar Demo¶
Direct download: sonar_demo.py.
1# sonar_demo.py
2#
3# Raspberry Pi Pico - HC-04 sonar module demo
4
5# This module provides a class for measuring distance using an HC-04 ultrasonic
6# ranger.
7
8# The device requires one digital trigger output and one digital echo input.
9# It is a 5V device, so echo needs to be level-shifted to 3.3V logic levels. One option
10# is a pair of resistors as a voltage divider.
11
12# This implementation uses bit-banged digital I/O to measure the echo pulse
13# width. But the timing precision is limited by CircuitPython execution and
14# clock resolution, so the result is only good for rough proximity detection.
15
16# Likely a better long-term solution will be to use the RP2040 programmable IO
17# peripheral (PIO) to precisely measure the echo duration.
18
19################################################################
20# CircuitPython module documentation:
21# time https://circuitpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/shared-bindings/time/index.html
22# board https://circuitpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/shared-bindings/board/index.html
23# digitalio https://circuitpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/shared-bindings/digitalio/index.html
24#
25# Driver lifecycle documentation:
26# https://circuitpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/docs/design_guide.html#lifetime-and-contextmanagers
27#
28################################################################################
29# load standard Python modules
30import time
31
32# load the CircuitPython hardware definition module for pin definitions
33import board
34
35# load the CircuitPython GPIO support
36import digitalio
37
38#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
39class Sonar:
40 def __init__(self, ECHO=board.GP20, TRIG=board.GP21):
41 """This class represents an HC-04 ultraonic ranger module. It uses one output
42 pin for trigger and one input pin for echo pulse measurement. N.B. the
43 device is 5V so the ECHO pin will need level-shifting to 3.3V logic
44 levels."""
45
46 self._trig = digitalio.DigitalInOut(TRIG)
47 self._trig.direction = digitalio.Direction.OUTPUT
48 self._trig.value = False
49
50 self._echo = digitalio.DigitalInOut(ECHO)
51 self._echo.direction = digitalio.Direction.INPUT
52
53 def ping_sync(self):
54 """Measure the round-trip echo time, returning either a value in seconds or None
55 if the measurement times out. N.B. this function will not return until
56 the cycle is done, so it is not compatible with asynchronous event
57 loops.
58 """
59
60 # trigger the ultrasonic pulse
61 self._trig.value = True
62 time.sleep(1e-5)
63 self._trig.value = False
64
65 start = time.monotonic_ns()
66 timeout = start + int(0.1 * 1e9)
67
68 # wait for echo to go high
69 while self._echo.value is False:
70 now = time.monotonic_ns()
71 if now > timeout:
72 # print("Error: ECHO never went high.")
73 return None
74
75 # wait for echo to go low
76 while True:
77 now = time.monotonic_ns()
78
79 if self._echo.value is False:
80 return 1e-9 * (now - start)
81
82 if now >= timeout:
83 return None
84
85 def deinit(self):
86 """Manage resource release as part of object lifecycle."""
87 self._trig.deinit()
88 self._echo.deinit()
89 self._trig = None
90 self._echo = None
91
92 def __enter__(self):
93 return self
94
95 def __exit__(self):
96 # Automatically deinitializes the hardware when exiting a context.
97 self.deinit()
98
99#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
100# Ultrasonic ranger demonstration.
101
102sonar = Sonar()
103print("Starting sonar test.")
104
105while True:
106 range = sonar.ping_sync()
107 print(f"Range: {range} seconds round-trip time.")
108 time.sleep(0.1)
Sonar PulseIO Demo¶
An alternate implementation using the pulseio library. So far, this actually appears to perform worse than bit-banging on the Pico.
Direct download: sonar_pulseio_demo.py.
1# sonar_demo.py
2#
3# Raspberry Pi Pico - HC-04 sonar module demo
4
5# This module provides a class for measuring distance using an HC-04 ultrasonic
6# ranger.
7
8# The device requires one digital trigger output and one digital echo input.
9# It is a 5V device, so echo needs to be level-shifted to 3.3V logic levels. One option
10# is a pair of resistors as a voltage divider.
11
12# This implementation uses the pulseio module to measure the echo pulse width.
13# But the precision appears to be low, so the result is only suitable for binary
14# proximity detection.
15
16# Likely a better long-term solution will be to use the RP2040 programmable IO
17# peripheral (PIO) to precisely measure the echo duration.
18
19################################################################
20# CircuitPython module documentation:
21# time https://circuitpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/shared-bindings/time/index.html
22# board https://circuitpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/shared-bindings/board/index.html
23# digitalio https://circuitpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/shared-bindings/digitalio/index.html
24# pulseio https://circuitpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/shared-bindings/pulseio/index.html
25#
26# Driver lifecycle documentation:
27# https://circuitpython.readthedocs.io/en/latest/docs/design_guide.html#lifetime-and-contextmanagers
28#
29################################################################################
30# load standard Python modules
31import time
32
33# load the CircuitPython hardware definition module for pin definitions
34import board
35
36# load the CircuitPython GPIO support
37import digitalio
38
39# load the CircuitPython pulse measurement support
40import pulseio
41
42#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
43class Sonar:
44 def __init__(self, ECHO=board.GP20, TRIG=board.GP21):
45 """This class represents an HC-04 ultraonic ranger module. It uses one output
46 pin for trigger and one input pin for echo pulse measurement. N.B. the
47 device is 5V so the ECHO pin will need level-shifting to 3.3V logic
48 levels."""
49
50 self._trig = digitalio.DigitalInOut(TRIG)
51 self._trig.direction = digitalio.Direction.OUTPUT
52 self._trig.value = False
53
54 self._echo = pulseio.PulseIn(ECHO)
55 self._echo.pause()
56
57 def ping_sync(self):
58 """Measure the round-trip echo time, returning either a value in seconds or None
59 if the measurement times out. N.B. this function will not return until
60 the cycle is done, so it is not compatible with asynchronous event
61 loops.
62 """
63
64 self._echo.clear()
65
66 # trigger the ultrasonic pulse
67 self._trig.value = True
68 time.sleep(1e-5)
69 self._trig.value = False
70
71 self._echo.resume()
72 start = time.monotonic_ns()
73 timeout = start + int(0.5 * 1e9)
74
75 # wait for the measurement to complete or time out
76 while len(self._echo) < 1:
77 now = time.monotonic_ns()
78 if now > timeout:
79 self._echo.pause()
80 return None
81
82 self._echo.pause()
83 return self._echo[0] * 1e-6
84
85 def deinit(self):
86 """Manage resource release as part of object lifecycle."""
87 self._trig.deinit()
88 self._echo.deinit()
89 self._trig = None
90 self._echo = None
91
92 def __enter__(self):
93 return self
94
95 def __exit__(self):
96 # Automatically deinitializes the hardware when exiting a context.
97 self.deinit()
98
99#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
100# Ultrasonic ranger demonstration.
101
102sonar = Sonar()
103print("Starting sonar test.")
104
105while True:
106 range = sonar.ping_sync()
107 print(f"Range: {range} seconds round-trip time.")
108 time.sleep(0.1)