Month: September 2020
Interactive Wall
Premise:
Even though the physical interaction between intelligent system and humans is advanced in the movie Blade Runner 2049, I did not like the austere apartment the protagonist lives in. It displays little interest in the comfort of the occupant with simple furniture and grey, industrial walls. The only meaningful interaction that occurs comes from JOI, the holographic artificial intelligent. This makes me wonder what things in our private space can bring comfort if interaction is introduced.
Nowadays people in the city live in dorms and apartments where physical space can be quite limited. Walls define the boundaries of our private space, but walls are never used as space themselves. It is used as a surface to hang or mount things. Therefore, I want to envision an interactive wall that can expand beyond physical space.
Hardware Setup:
Depth is necessary to make use of the walls as space. “Holographic display” is still a developing technology but it will give walls the needed depth to create a visual space. Such walls can be used to change the environment of the space. For example, having bamboo around the room when having breakfast. And with a touch screen, such walls can also be used in many applications such as displaying and assembling 3D objects.
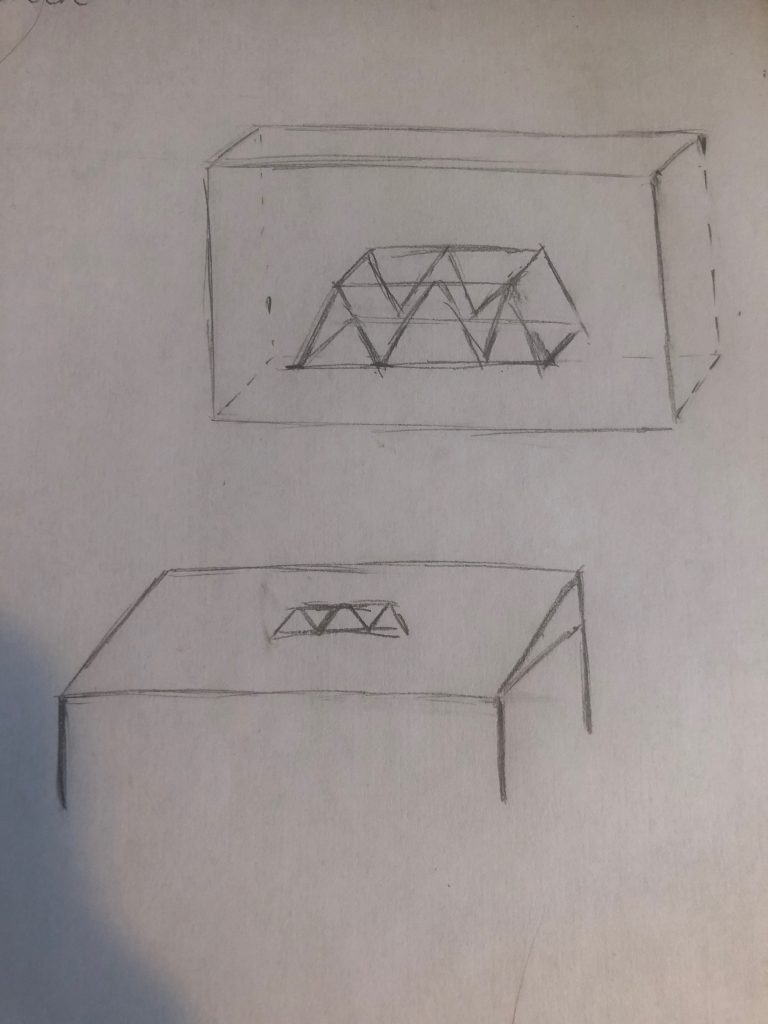
Lights and speakers can be incorporated into the wall to make it more interactive. As shown in the picture below, there are two speakers on the left and lighting on the wall. Together they can create a corner or a space of cinematic experience.
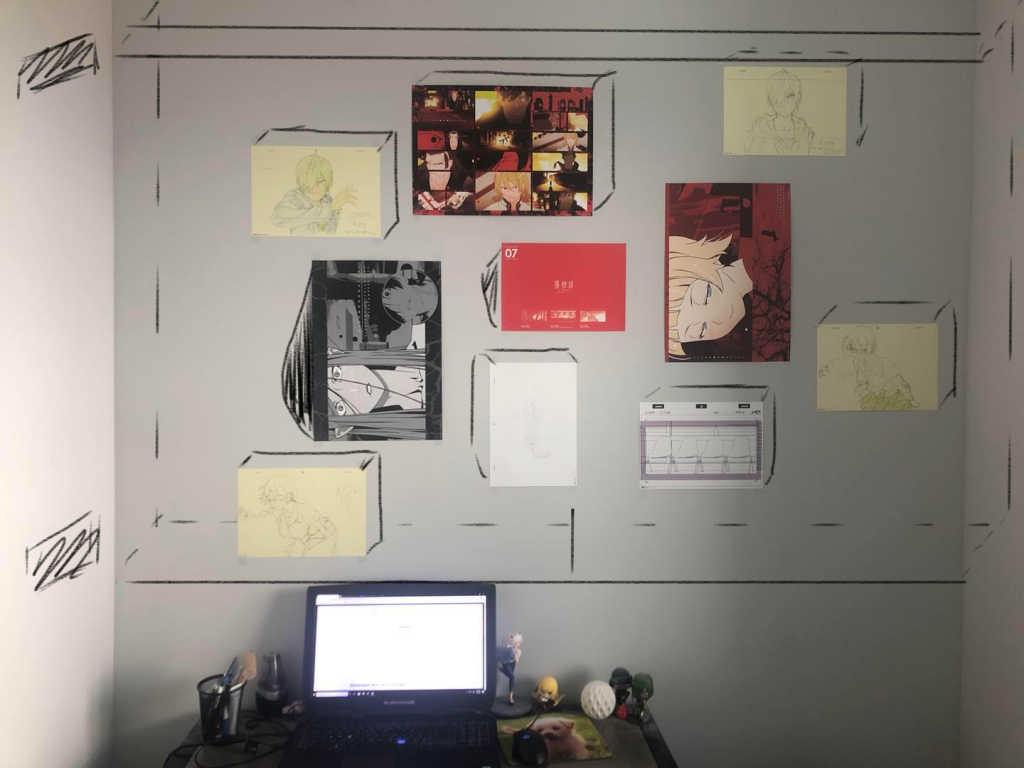

Interaction:
The wall can collect data on what the user like to display at different time of the day and week. Then like a smart “wallpaper engine”, it can change the environment of the room to fit the activity of the occupant. For example, once it “learns” that I like to look at bamboo and listen to birds’ tweets during breakfast, it shows a waterfall at the breakfast time the next day.
The wall can also be more engaged in the occupant’s living habit. I, for example, am often energetic during the night and I sometimes stay up until I realize there is not enough time to sleep. Or sometimes I did not realize that it is better to rest because my body is tired. With the active change of the range of light according to time in night, the wall is able to remind and urge me to rest. In similar way, the interactive wall can create a space that “synchronizes” with the occupant.



A Truly Smart Doorbell
Problem:
Smart Doorbell’s have been around since 2013 and have improved in features over the years, but don’t utilize the range of technological advancements that we have today. Smart Doorbells have the ability to notify the owner and show video of who is at the door when the bell is rung and when motion is detected as well as store recordings to the cloud; many have two-way audio communication wherein the owner and the visitor can speak to each other; and some allow the owner to unlock the door. None of these features take much advantage of automatic responses.
Proposed Solution:
A true Smart Doorbell would be able to do all of the above features and be much more customizable. It would be able to do different actions based on both who is at the door and who is home. Given a set of pictures of approved people, such as family members and really close friends, the Smart Doorbell would be able to automatically unlock the door for them and others who are only allowed automatic entry if certain people are at home and during a certain time frame. It would also be able to recognize delivery people and solicitors and perform certain tasks based on what was chosen in the app. For example, different recordings can be automatically played to tell a delivery person where to leave the package and a solicitor to go away. Another option would be to mute the doorbell for certain types of solicitors. A truly Smart Doorbell would be fully customizable with the ability to have numerous preset responses to make the owners life more convenient.
Smart Doorbell (Catherine)
One thing that frustrates me when I ring someone else’s doorbell is that I don’t know if people inside the house has heard me ringing the doorbell. Another thing that frustrates me when someone else’s rings my doorbell is that as I’m getting the door, whoever rang the doorbell does not know that I’m coming and keeps ringing the doorbell.
Given the above two scenarios, a smart doorbell that can detect whether people inside the house are ‘on their way’ to get the door and notify the people ringing the doorbell would be helpful for both parties.
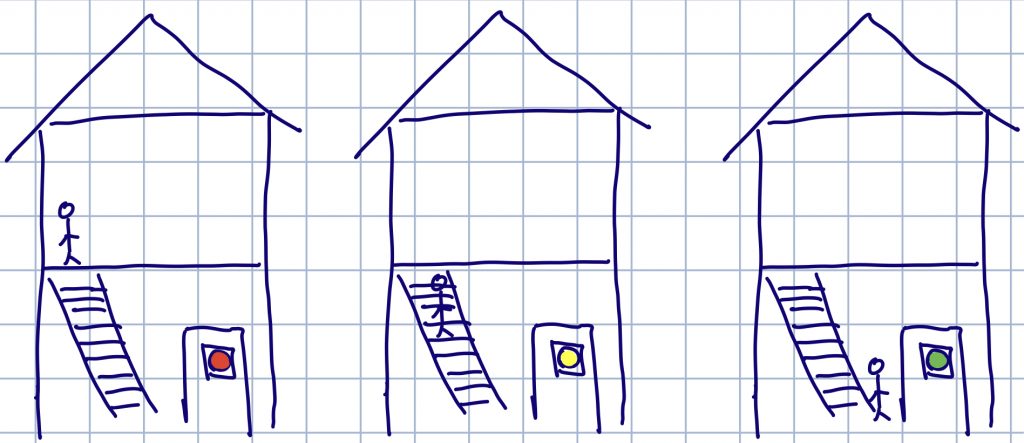 In the sketch above, we are looking at this house that has two floors and the person inside is on the second floor. After the doorbell rings, if the person does not move to get the door, the doorbell is red and the person outside should keep ringing the bell. If the person inside is on his/her way to the door, the doorbell turns yellow so the person outside is ensured that he/she has gotten the insider person’s attention. It’s likely that the person inside gets distracted and forget about the door, so if doorbell stays yellow for too long, the person outside could ring the bell again. And finally, if the person inside is near the door already, then the doorbell turns green and the person outside can be prepared to see the door open.
In the sketch above, we are looking at this house that has two floors and the person inside is on the second floor. After the doorbell rings, if the person does not move to get the door, the doorbell is red and the person outside should keep ringing the bell. If the person inside is on his/her way to the door, the doorbell turns yellow so the person outside is ensured that he/she has gotten the insider person’s attention. It’s likely that the person inside gets distracted and forget about the door, so if doorbell stays yellow for too long, the person outside could ring the bell again. And finally, if the person inside is near the door already, then the doorbell turns green and the person outside can be prepared to see the door open.
Class 2 notes, 3 Sep, 2020
Introductions and Admin
Introduce ourselves and describe what we want out of the class
Class blog — I have to “promote” you after you sign on for the first time.
A10 cannot be used outside of class time. I’ll see if I can create a “class time” for MTI
kits are available: https://bookstore.web.cmu.edu/SiteText?id=73598
How do we handle the end of the semester?
Pick My Office Hours
Discuss
revisit tigoe’s page — what was physical interaction and what was reaction? Do you see any themes in projects that aren’t allowed? is there something you’re tired of seeing?
reading assignment — what makes something interactive?
does interaction require emotion or just the appearance of emotion? When do we go from “robot” to “uncanny valley” to “human”?
Musicians and DJs working a crowd — who is interacting and who is driving the interaction?
so what is physical interaction? When/where did it start?
Physical Interaction History
Beekeepers – explain the complexity of a hive and how we’re only just now (past 20 years) discovering how bees vote to make hive-wide decisions. “Honeybee Democracy” is a great introduction to how science works and how to write about science: https://amzn.to/2Z6Y9yL
Alchemists – trying to make things happen with substances they don’t understand. If you don’t know about elements and that lead and gold are elements, what decisions are making to interact with substances? People knew that honey bee “propolis” helped prevent infection thousands of years before we discovered bacteria. Sometimes working in ignorance still leads to progress.
New music and dance styles based on sampling and analog synths: Moog, ARP 2600, hip-hop. Early hip-hop was limited to record players and mics; early synths were insanely expensive and shared at fancy studios. Grand Wizard Theodore *invented* scratching: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eHCOIK_fICU
Console games with physical feedback, Rez Trance Vibrator: https://www.theverge.com/2016/9/25/13046770/rez-trance-vibrator-ps2
Dance Dance Revolution from arcades to console games
Driving assistance with vehicles: AI? Interaction? What if the car won’t let me turn, start, or stop? How can I disable safety features?
Flight assistance software in commercial aircraft. Is autopilot interactive?
Flight assistance for military aircraft: self-guiding drones, incoming missile warnings for helicopter pilots. Interaction or reaction?
Near-future Interaction
the focus of this class – we’re prototyping for five years out
interacting with intelligent systems that we don’t completely understand and that can make decisions against our will or with results we don’t appreciate
- car that thinks you’re too intoxicated, sleepy, or incompetent to drive, so it refuses to move
- home automation system that won’t open the doors and let you leave because the particulate count in the air is hazardous and you’re not wearing a mask
- police equipment that won’t let you fire at unarmed civilians — pistol trapped in a holster, safety wont go off.
- fire engines that won’t engage fires that cannot be contained
- entertainment systems that can filter content as part of mental-health
We’re giving “agency” to interactive devices: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Agency_(philosophy)
“Near-future” is a popular base of pop-culture: MCU set a few years from now
Blade Runner 2049 is a bit farther in the future.
practical effects used as input devices to imagined systems of the future
Adam Savage gets a no-spoilers tour of the Blade Runner 2049 prop shop.
show Adam Savage with prop manager, start around 4:12, skip to 14:30, skip to 18:30
This is not new, in the past we talked about the future and technology. “Design for Dreaming”, released in 1956, is all about the future. It’s also all about the sexism in the 1950s, so you can skip to these points, to get the important points: start at 3:30; skip to 6; skip to 8
Good drama is about storytelling — what if interactive devices are characters in the story?
- Colossus: The Forbin Project (1970) — our super computer meets the Soviet supercomputer and they plan our future
- 2001 — HAL 9000, the ship’s computer that decides it does not want to follow the plan laid out by humans
- War Games (1983) — A computer controls all of America’s nuclear weapons. Would you like to play a game? the only way to win is to not play the game.
- Alien — MOTHER, a semi-intelligent computer that controls spacecraft while humans are in cryosleep.
- ST:TNG’s Data — a walking mobile phone smarter than spacecraft computers?
- (Terminator movies don’t count — killing spree robots, not interaction)
- Farscape — Moya is semi-intelligent spacecraft used by the main characters, and can refuse orders or do things because of her own desire, not that of her passengers.
Assignment 2, due at 11:59 the day before class, so these are due Monday, 7 September
First, order your kit https://bookstore.web.cmu.edu/SiteText?id=73598
This is a pen-and-paper assignment to go over posting to the class blog and what a good submission looks like. If you want to make something with hardware, that’s fine, but it’s not required. Science fiction is ok, fantasy is not. ever. NO UNICORNS.
1.) A smart doorbell, similar to the smart thermostat I talked about on Tuesday, or
2.) Make a useful practical effect by giving interaction to a thing that doesn’t currently interact with humans. For inspiration, watch Blade Runner 2049. Yes, it’s 3 hours long but OMFG. Look at the physical interfaces between intelligent systems, replicants, humans, AI, and agency for androids.
Prepare the presentation as you would for a crit. Look at previous classes for inspiration
https://courses.ideate.cmu.edu/48-339/f2019/
https://courses.ideate.cmu.edu/48-339/s2018/
Descendant short story thoughts
To me this was an intriguing but somewhat confusing story in that not much was explained fully. I wish that there were more details on the suit and what it was originally capable of, where the man is and why he went to that planet, other technology that they had on the orbital, how life was like before the war, and why they even got into the war. I understand that it is a short story for a reason, but I like having more questions answered than left in the air after reading a story. The idea of a smart suit seems like a great invention for company and help, but I wonder why there aren’t built in communication, warning, and emergency systems to automatically alert the orbital or others at war that something has gone wrong if they have something as advanced as a suit that is alive.
Skills bringing to the class (Assignment 1)
As a mechE, I have a lot of experience in fabricating things. With the remote setting and the resources I have, this won’t necessarily allow me to build amazing physical contraptions; however, I think that my experience and creativity will help me to make things that are still pretty cool even with household items. I have used Arduino quite a bit and know Python, so I have a good foundation for coding my projects. I also have used a wide variety of sensors and actuators before, so am excited to keep expanding with new things this semester and to build more complicated contraptions.
Tom Igoe’s “Physical Computing’s Greatest Hits (or misses?)”
Found a PDF version of his blog entry: igoe_sketching2012
Class 1 notes, 1 Sep 2020
Remote Learning
No need to leave video on unless we’re having a group discussion so we can raise hands.
Most lectures (starting next week) will be recorded and take roughly half of the class time.
Classroom discussions will not be recorded.
Take-home kits will be available sometime next week. We’ll let you know when they can be ordered, please don’t call the bookstore.
Projects will be turned in on the blog and demoed via Zoom. Live or pre-recorded demos?
Office hours as needed — email me if you’re stuck and want to have a 1:1 Skype
How do you feel about Canvas?
Undergraduate Requirements
Undergrads have a pre-req of Intro to Physical Computing. If you haven’t taken the pre-req but think you know enough to keep up with MTI assignments, stay for this intro then talk to me after class.
Graduate students
Comfortable working with Arduino, equivalent knowledge of Intro to Phys Comp.
Skills needed by all students
Arduino
- Arduino IDE in C++ or CircuitPython. VSC is also an option if you prefer.
- for() vs. while() loops
- arrays (C++)
- switch/case
- analog vs digital voltages
- dictionaries (Python)
- integer vs. float (C++)
- interrupts
- Understand how/why to use state machines
Physical Computing skills
- Analog vs. digital electronics
- External power — wall outlets and batteries and power supplies
- The difference between servo motors, regular motor, solenoids
- Can do more than cut-and-paste a sketch and change a few variable names
- Can read/create basic sketches in Fritzing
Other Useful Skills
p5.js (javascript) can be used in this class
Python on Arduino is allowable as a substitute for C++, but I can’t help you debug
BeagleBone Black and Raspberry Pi may be used as a substitute for Arduino, again I can’t help you debug
If you want to learn this sort of technology but can’t take this class, feel free to email me for some pointers on how to get started on your own time. There are some “Arduino 101” kits that you could do over winter break that I would count for PhysComp in the future.
Introduction to the Class / go over Administration document
We’ll do real introductions on Thursday
Originally a required class for a MTID degree, that program has ended but SoA and IDeATe like this class.
What we’re doing differently in a remote class with additional readings and responses/projects.
Syllabus and grading: weekly assignments, three crits, final crit, class participation
Note taking vs. the class blog — will post my notes to the blog after class
Class Theme – “Accessiblity”
Improving the human condition by improving living spaces with tangible interaction design.
Tweaking Nathan Shedroff’s list:
- Assist
- Enhance
- Improve
- Qualify
- Sense
Class Theme – Quarantine Quitchen
A few months ago, TV personality Alton Brown and his wife, Elizabeth Ingram, started doing a youtube series called “Quarantine Quitchen”. He’s a famous chef, filmmaker, and host of competition cooking shows, she’s an interior designer who does restaurants. Every Tuesday evening (during our class), they make dinner based on whatever they can find in the fridge, freezer, or pantry. And drink some alcohol. I’m lifting their idea of “living in a quarantine” and changing class assignments to reflect being stuck at home, having limited access to physical social events, and social distancing. https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLSL8Njz6ML7Bf5VyF9b0oQ3hiBs_3j-sz
Introduction to Tangible Interaction
Reaction vs. Interaction
Classic thermostat (temperature sensor and on/off switch) vs. smart thermostat (PID controller https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PID_controller or AI google hive mind)
Tangent: explain how PID is different from a sensor + relay
Explain how machine learning (open ended system) is different from PID (a closed loop system)
Questions
What if we had a smart (AI) thermostat? NEST is on the edge of this.
- change heating/cooling controls based on history of changes made by people
- change temperature related to outside environment: tomorrow is hot, turn the AC on earlier
- react to weather changes: storm front rolls through from the north, temp drops almost 10C
- modulate temp based on who is in the house: I like it warm, spouse likes it cold
- modulate temp based on predicted activities: “they always stay up late on Friday”
- error control: “never let the house go below 50F” to prevent pipes from freezing
What if we had a smart door bell? What would it do? This will be an assignment on Thursday.
Short History of Physical Computing and Interaction Design
Physical computing and tangible interaction design are recently created fields but there is a history of how we got here. The key point is the size (scale) of computing hardware.
-
- water powered tools and windmills, literally physical computing
- beginning of the PID idea, centrifuges to maintain speed in grain mills
- water mills that stop pumping water when the reservoir is full
- industrial revolution
- early punch-card computing to control looms in 1725
- Korsakov proposes using punched cards to store data in 1832
- steam engines that can react to malfunctions (more physical computing)
- sophisticated PID in factories to run mills and lathes
- (skipping mainframes that only crunched numbers)
- transistors as second industrial revolution
- the first computers that didn’t fill buildings
- 1976: first use of “human-computer interaction” in a published paper https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Evaluating-the-impact-of-office-automation-on-top-Carlisle/7a864fc9cfbb01306cb2a75ceef1ed246727f1f0
- 1983: The Psychology of Human-Computer Interaction brings the concept to the general computing community https://amzn.to/3jDDVEu
- Early arcade games introduced haptic output or feedback: helicopter arcade game that shakes when you are shot (early 1980s)
- haptic technology: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Haptic_technology
- tactor: hardware that conveys a feeling of touch, pressure, or vibration
- Modems broadband access over the phone
- Interaction moves from an isolated software package to a network of software packages
- People can interact with other people at distant locations via BBS or USENET or email
- People can interact with systems, first online games and dating services
- Still no physical interaction
- Mobile phones — getting closer!
- contains sensors, CPU, network access
- has output in the form of image, sound, and vibration
- Arduino, 2005
- first affordable, usable, embedded controller
- opened up a market of input/output hardware
- set the space for Rpi, BBB, etc
- Five years from now
- where we’re thinking in this class
- experimental projects that show new interactions
- reading assignment is showing us a few more years ahead
- water powered tools and windmills, literally physical computing
What can we do in this class?
Study physical computing and interaction
Look at near future concepts
Design, build, and demonstrate physically interactive devices and systems