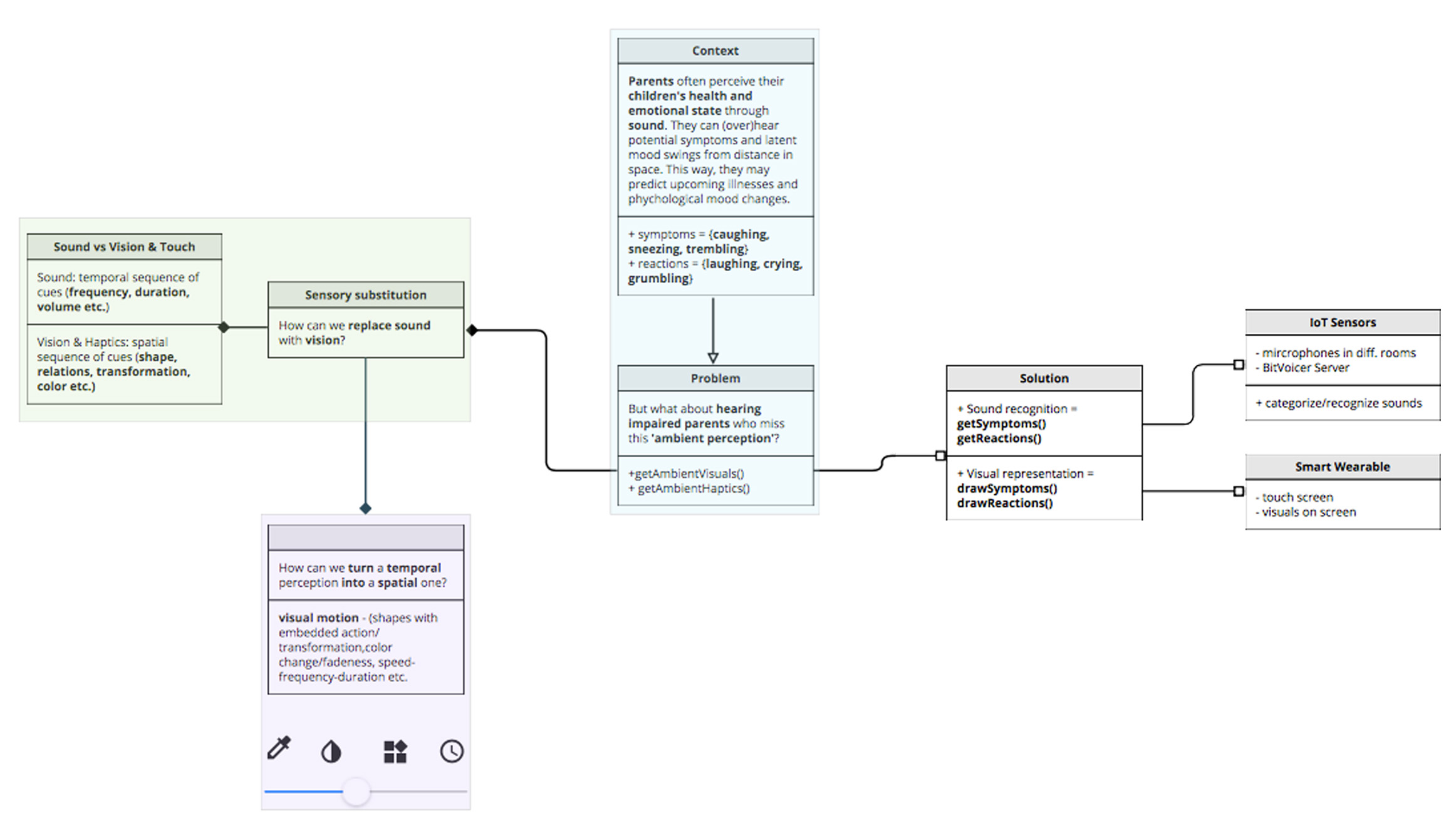
Problem-solving diagram – Train of thinking
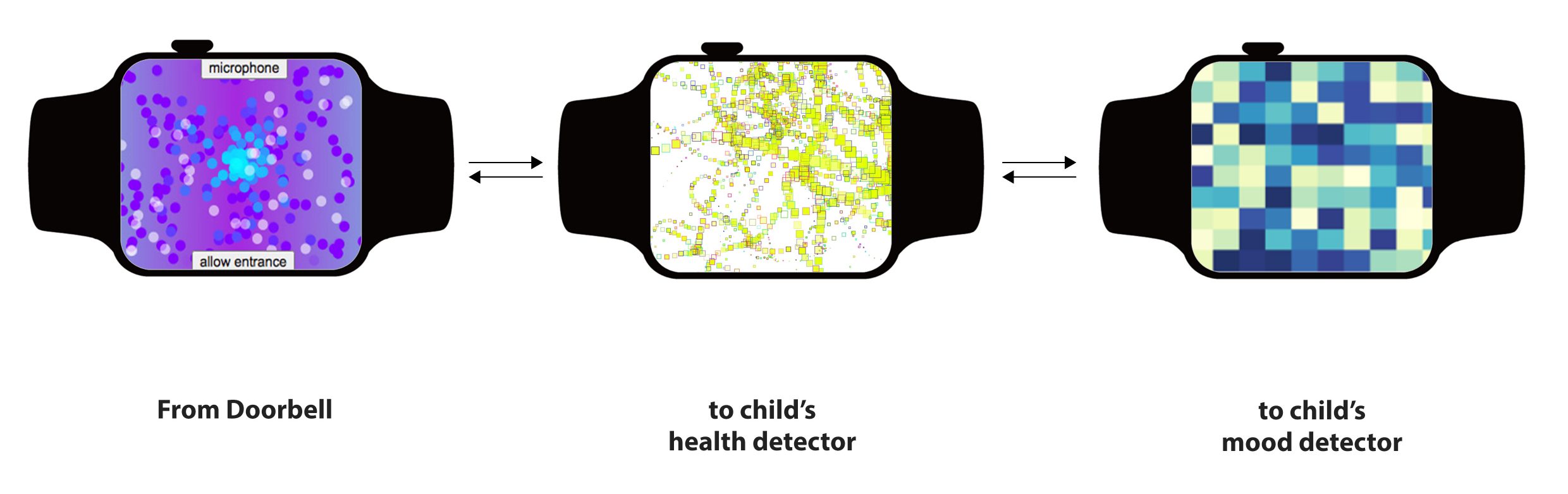
Multi-purpose wearable with multiple screens
Computational design logic
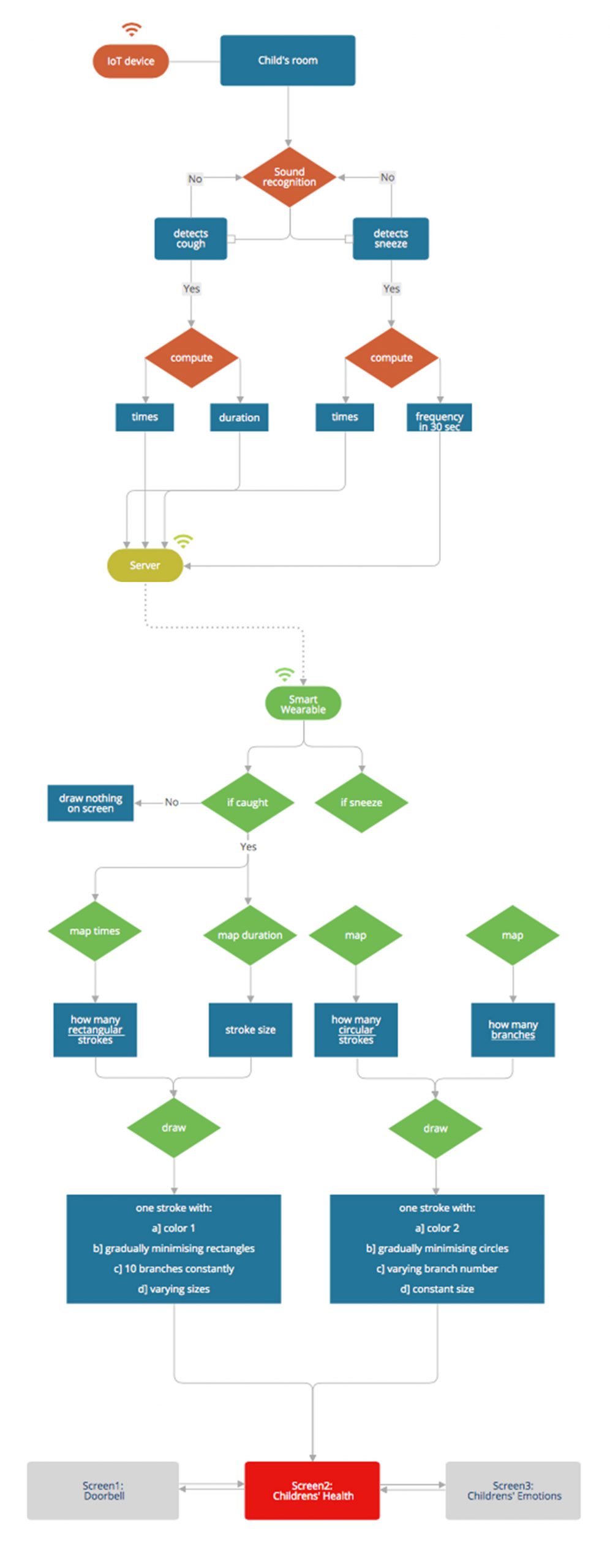
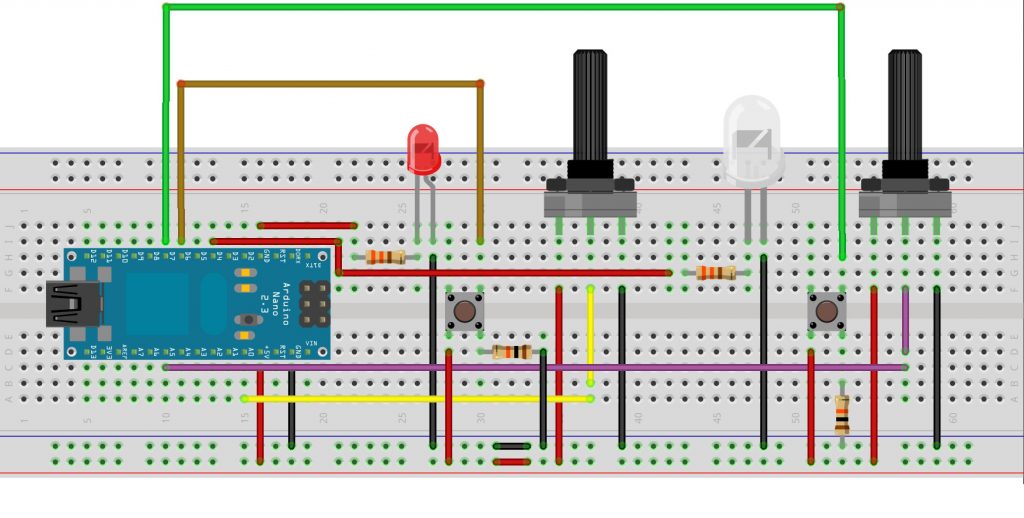
During this current stage, two pushbuttons and two potentiometers were chosen to represent the sound recognition. Button_1 represents ‘coughing’, button_2 ‘sneezing’, potentiometer_1 the strength of coughing and potentiometer_2 the continuity of sneezing. The inputs were sent through serialPort to the p5.js library of javascript to draw visuals outputs.
I/O notational system
Just some little practise..
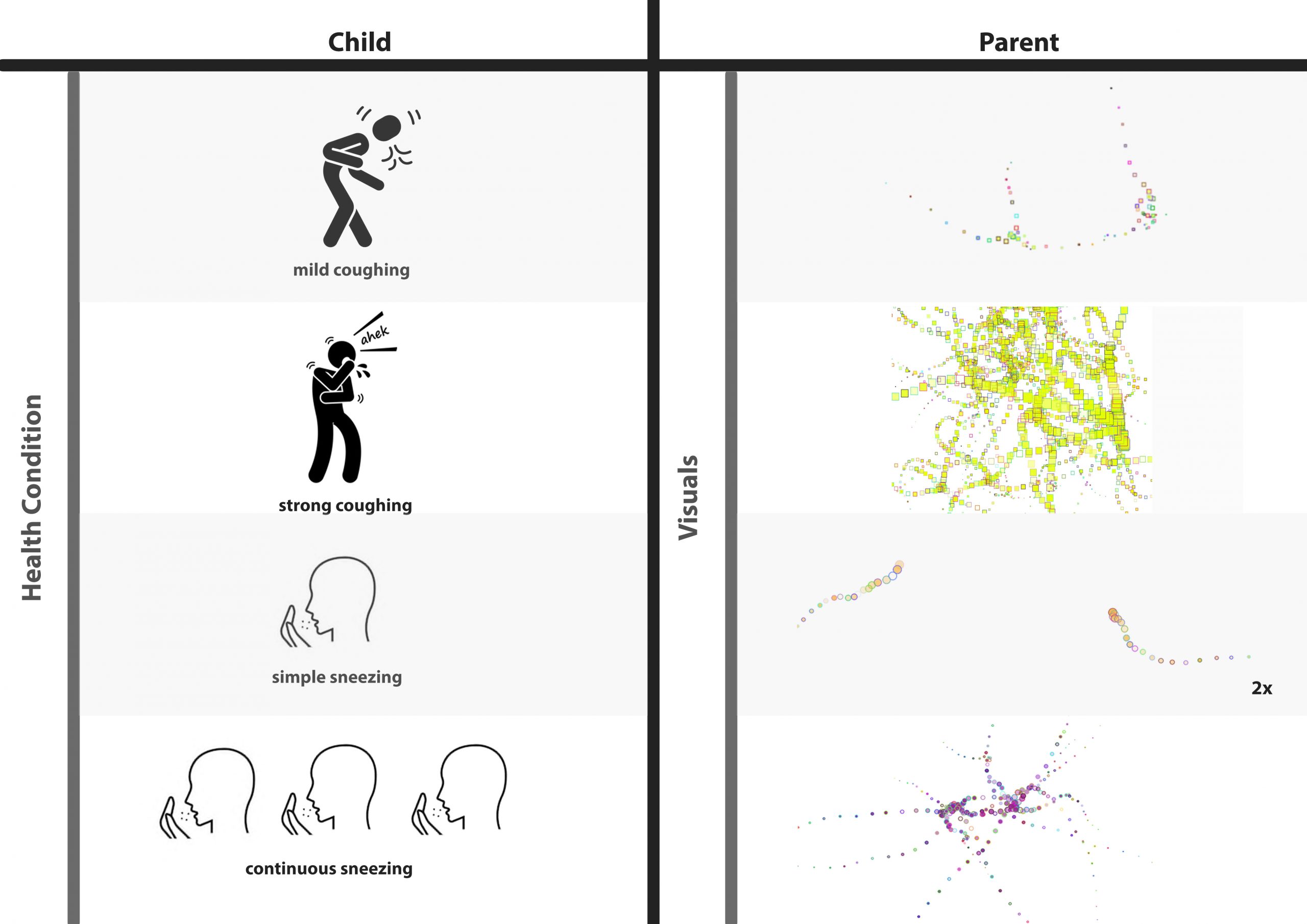
What is the child’s condition according to the graphs (1),(2) and (3)?
(1)
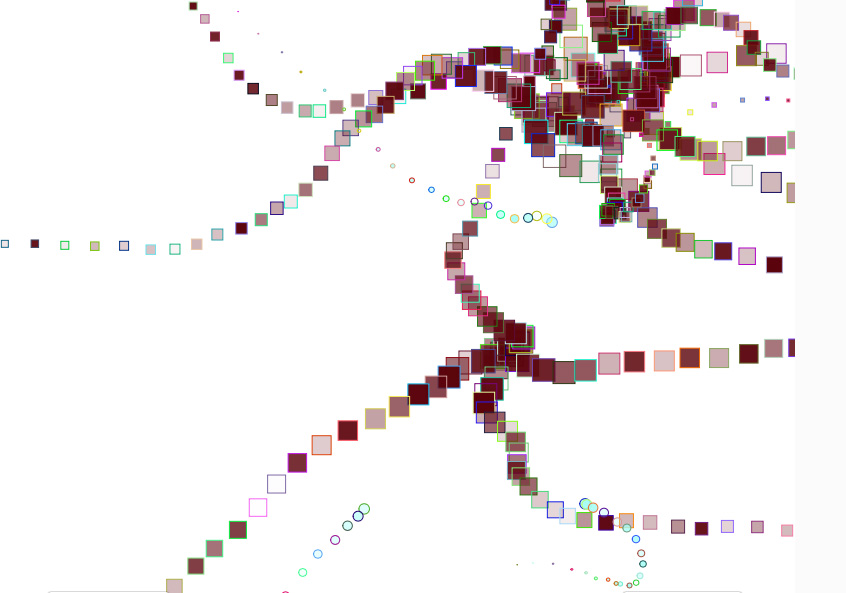
Intense coughing. Very mild sneezing. It may be about a flu that starts from the throat/lungs and not the nose.
(2)
The child is pretty much healthy today.
(3)
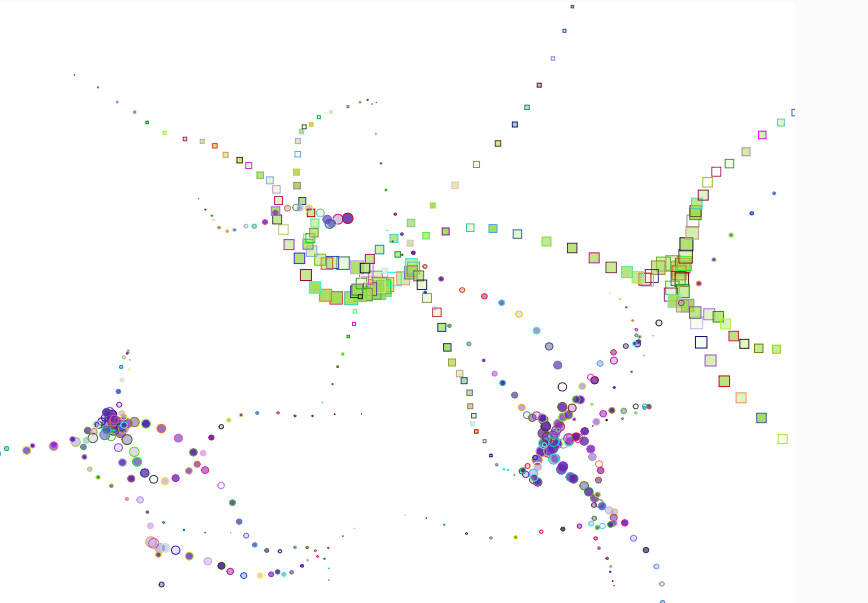
The child sneezes multiple times in a row. There is a mild coughing, too. It is either about an environmental allergy or a mild flu starting from the nose.
Code – Serial Communication between different platforms.
The following convention was made. As the goal for the current project was the visual representation of coughing/sneezing and not their auditory recognition using sensors and deep learning, the latter ones were replaced by simple methods and electronic components. The user himself/herself manipulates two push buttons and two analog potentiometers to keep track of the times he/she coughed or sneezed(buttons) and their intensity/duration (potentiometers). The values are sent serially to the platform p5.js through the p5.serial control. After the sensor values are read and proccessed in p5.js, the graphics on the parents’ smart watch are activated.
Demo: https://youtu.be/TGh9t0Zz7Tc
Circuit design:
Arduino Code:
/* --------------------------------------------------------------- */
// Two leds. Each turns on, when the corresponding switch is pushed down.
const int redPin = 2;
const int whitePin = 5;
// Analogy: One button pushed down when the person coughs, and the other when the person sneezes.
const int button1 = 7;
const int button2 = 8;
int button_1; int button_2;
char cough; char sneeze;
// Analogy: One potentiometer represents the intensity of coughing and the other the intesity of sneezing.
const int potPin1 = A0; const int potPin2 = A5;
unsigned int potVal1; unsigned int potVal2;
/* --------------------------------------------------------------- */
void setup() {
pinMode(redPin, OUTPUT); pinMode(whitePin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(button1, INPUT); pinMode(button2, INPUT);
pinMode(potPin1, INPUT); pinMode(potPin2, INPUT);
// We need serial port to send the values p5 serial port control
Serial.begin(9600);
}
/* --------------------------------------------------------------- */
void loop() {
/* --------------------------------------------------------------- */
// button_1 represents coughing. When button_1 == 1, the person just coughed (cough == 1)
button_1 = digitalRead(button1);
if (button_1) {
cough = 1;
} else {
cough = 0;
}
// When the persons coughs (cough == 1), we can adjust the tensity of coughing
while (cough == 1) {
potVal1 = analogRead(potPin1);
int mappedPot1 = map(potVal1, 0, 1023, 5, 30);
}
/* --------------------------------------------------------------- */
// button_2 represents sneezing. When button_2 == 1, the person just sneezed (sneeze == 1)
button_2 = digitalRead(button2);
if (button_2) {
sneeze = 1;
} else {
sneeze = 0;
}
// When the persons sneezes (sneeze == 1), we can adjust the tensty of sneezing
while (sneeze == 1) {
potVal2 = analogRead(potPin2);
int mappedPot1 = map(potVal1, 0, 1023, 5, 30); int mappedPot2 = map(potVal2, 0, 1023, 1, 9);
}
// that helps us see that the button are actually pushed.
leds();
/* --------------------------------------------------------------- */
// Now we print the values we want to communicate with p5.js
Serial.print(button_1);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(button_2);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.print(mappedPot1);
Serial.print(",");
Serial.println(mappedPot2);
//delay(500);
}
/* --------------------------------------------------------------- */
// different leds turn on when different buttons are pushed down.
void leds() {
if (button_1 == 1) {
digitalWrite(redPin, HIGH);
}
else {
digitalWrite(redPin, LOW);
}
if (button_2 == 1) {
digitalWrite(whitePin, HIGH);
}
else {
digitalWrite(whitePin, LOW);
}
}
5p.js code:
// VARIABLES ********************************************************
// variables for Serial communication
let serial;
let sensors = [];
let cough = false; // we start with 'no coughing detected'
let sneeze = false; // we start with 'no sneezing detected'
let howBadCaughing; // intensity of coughing measured by Arduino
let howLoadSneezing; // intensity of coughing measure by Arduino
let timeCough = true; // indicates when the program is ready to read the next coughing
let timeSneeze = true; // indicates when the program is ready to read the next sneezing
// variables for Particles
const startForce = 100;
const particle_maxVel = 30; // how far they spread around
const particle_maxAcc = 5; // how fast they spread around
let spawnNum; // number of particles produced by one click
let startSz;
let shrinkRate = 0.5; // how fast they shrink
const maxParticles = 20;
// variables for Particles' Color
let R1,G1,B1;
// SET UP ********************************************************
function setup() {
// canvas
createCanvas(800, 800);
background(255);
// Activate Serial communication
serial = new p5.SerialPort();
serial.list();
serial.open('COM4');
serial.on('connected', serverConnected);
serial.on('list', gotList);
serial.on('data', gotData);
serial.on('error', gotError);
serial.on('open', gotOpen);
serial.on('close', gotClose);
// create a universal system, in which we are going to create different particle spirals
system = new ParticleSystem();
// Color
R1 = random(255); G1 = random(255); B1 = random(255);
}
// DRAW ********************************************************
function draw() {
// Here, according to the reading values of the sensors, we draw parametric graphics each time the person sneezes or coughs
if (sensors[0] == 1 && timeCough){
timeCough = false;
pos = new p5.Vector(random(100, width-100),random(100,height-100));
system.addParticle(pos,"caugh");
}
if (sensors[1] == 1 && timeSneeze){
timeSneeze = false;
pos = new p5.Vector(random(100, width-100),random(100,height-100));
system.addParticle(pos,"sneeze");
}
// here we define the parameters of each graphic. According to how bad coughing and sneezing are, the particle spirals change parameters.
howBadCaughing = sensors[2];
howLoadSneezing = sensors[3];
startSz = howBadCaughing;
spawnNum = howLoadSneezing;
// we update/draw the system.
system.updateSystem();
}
// FUNCTIONS ********************************************************
// Serial: Here we collect the raw data sent from Arduino in the form of a string.We split the various values around ',' and save into a list named sensors
function serverConnected() {
print("Connected to Server");
}
function gotList(thelist) {
print("List of Serial Ports:");
for (let i = 0; i < thelist.length; i++) {
print(i + " " + thelist[i]);
}
}
function gotOpen() {
print("Serial Port is Open");
}
function gotClose(){
print("Serial Port is Closed");
let latestData = "Serial Port is Closed";
}
function gotError(theerror) {
print(theerror);
}
function gotData() {
let currentString = serial.readLine();
trim(currentString);
if (!currentString) return;
sensors = split(currentString,",");
//console.log(currentString);
latestData = currentString;
}
// by pressing the key 'a', the program becomes ready for the next coughing/sneezing reading
function keyTyped() {
if (key === 'a') {
timeCough = true;
timeSneeze = true;
}
}
// CLASSES ********************************************************
class Particle{
constructor(location,type){
this.loc = new p5.Vector(location.x, location.y);
this.vel = new p5.Vector(0, 0);
this.acc = new p5.Vector(0, 0);
this.angle = 0;
this.magnitude = 0;
this.type = type
if (this.type == "caugh"){
this.size = startSz;
}
else if (this.type == "sneeze") {
this.size = 13;
}
this.isDead = false;
} // constructor
update() {
// move in random direction with random speed
this.angle += random(0,2*PI);
this.magnitude = random(0,startForce);
// apply a force and limit its strength
this.acc.x += cos(this.angle)*this.magnitude;
this.acc.y += sin(this.angle)*this.magnitude;
this.acc.limit(particle_maxAcc);
// add to current velocity
this.vel.add(this.acc);
this.vel.limit(particle_maxVel);
// Apply result to current location
this.loc.add(this.vel);
// reduce size
this.size -= shrinkRate;
if (this.size<=0) {
this.isDead = true }
} // Particle update
display() {
push();
if (this.type == "caugh") {
rectMode(RADIUS);
rectMode(CENTER);
stroke(color(random(255),random(255),random(255)));
let c = color(R1,G1,B1,random(255));
fill(c);
rect(this.loc.x,this.loc.y,this.size,this.size);
}
else if (this.type == "sneeze") {
ellipseMode(RADIUS);
ellipseMode(CENTER);
stroke(color(random(255),random(255),random(255)));
let c = color(255-R1,255-G1,255-B1,random(255));
fill(c);
ellipse(this.loc.x,this.loc.y,this.size,this.size);
}
pop();
} // display
} // class Particle
class ParticleSystem {
constructor() {
this.loc2 = new p5.Vector(0,0);
this.particles = [];
this.type = ""
} // constructor
addParticle(newLoc,type) {
this.loc2.x = newLoc.x; this.loc2.y = newLoc.y;
this.type = type;
if (this.type == "caugh"){
this.spawnNum = 4;
}
else if (this.type == "sneeze") {
this.spawnNum = spawnNum;
}
if (this.particles.length + this.spawnNum < maxParticles) {
for (let i=0; i < this.spawnNum; i++) {
append(this.particles,new Particle(this.loc2,this.type));
}
}
} // addParticle
updateSystem(){
for (let i =0;i<this.particles.length;i++) {
let p = this.particles[i];
p.update();
if (p.isDead) {
this.particles.splice(i,1);
} else { p.display();
}
} // for
} // updateSystem
} // particleSystem class
/*! p5.serialport.js v0.0.1 2015-07-23 */
/**
* @module p5.serialport
* @submodule p5.serialport
* @for p5.serialport
* @main
*/
/**
* p5.serialport
* Shawn Van Every (Shawn.Van.Every@nyu.edu)
* ITP/NYU
* LGPL
*
* https://github.com/vanevery/p5.serialport
*
*/
(function(root, factory) {
if (typeof define === 'function' && define.amd)
define('p5.serialport', ['p5'], function(p5) {
(factory(p5));
});
else if (typeof exports === 'object')
factory(require('../p5'));
else
factory(root['p5']);
}(this, function(p5) {
// =============================================================================
// p5.SerialPort
// =============================================================================
/**
* Base class for a serial port. Creates an instance of the serial library and prints "hostname":"serverPort" in the console.
*
* @class p5.SerialPort
* @constructor
* @param {String} [hostname] Name of the host. Defaults to 'localhost'.
* @param {Number} [serverPort] Port number. Defaults to 8081.
* @example
* var portName = '/dev/cu.usbmodem1411'; //enter your portName
*
* function setup() {
* createCanvas(400, 300);
* serial = new p5.SerialPort()
* serial.open(portName);
* }
*/
p5.SerialPort = function(_hostname, _serverport) {
var self = this;
this.bufferSize = 1; // How much to buffer before sending data event
this.serialBuffer = [];
//this.maxBufferSize = 1024;
this.serialConnected = false;
this.serialport = null;
this.serialoptions = null;
this.emitQueue = [];
this.clientData = {};
this.serialportList = [];
if (typeof _hostname === 'string') {
this.hostname = _hostname;
} else {
this.hostname = "localhost";
}
if (typeof _serverport === 'number') {
this.serverport = _serverport;
} else {
this.serverport = 8081;
}
try {
this.socket = new WebSocket("ws://" + this.hostname + ":" + this.serverport);
console.log(("ws://" + this.hostname + ":" + this.serverport));
} catch (err) {
if (typeof self.errorCallback !== "undefined") {
self.errorCallback("Couldn't connect to the server, is it running?");
}
}
this.socket.onopen = function(event) {
console.log('opened socket');
serialConnected = true;
if (typeof self.connectedCallback !== "undefined") {
self.connectedCallback();
}
if (self.emitQueue.length > 0) {
for (var i = 0; i < self.emitQueue.length; i ++){
self.emit(self.emitQueue[i]);
}
self.emitQueue = [];
}
};
this.socket.onmessage = function(event) {
var messageObject = JSON.parse(event.data);
// MESSAGE ROUTING
if (typeof messageObject.method !== "undefined") {
if (messageObject.method == 'echo') {
} else if (messageObject.method === "openserial") {
if (typeof self.openCallback !== "undefined") {
self.openCallback();
}
} else if (messageObject.method === "data") {
// Add to buffer, assuming this comes in byte by byte
self.serialBuffer.push(messageObject.data);
if (typeof self.dataCallback !== "undefined") {
// Hand it to sketch
if (self.serialBuffer.length >= self.bufferSize) {
self.dataCallback();
}
}
if (typeof self.rawDataCallback !== "undefined") {
self.rawDataCallback(messageObject.data);
}
} else if (messageObject.method === 'list') {
self.serialportList = messageObject.data;
if (typeof self.listCallback !== "undefined") {
self.listCallback(messageObject.data);
}
} else if (messageObject.method === "close") {
if (typeof self.closeCallback !== "undefined") {
self.closeCallback();
}
} else if (messageObject.method === "write") {
// Success Callback?
} else if (messageObject.method === "error") {
//console.log(messageObject.data);
if (typeof self.errorCallback !== "undefined") {
self.errorCallback(messageObject.data);
}
} else {
// Got message from server without known method
console.log("Unknown Method: " + messageObject);
}
} else {
console.log("Method Undefined: " + messageObject);
}
};
this.socket.onclose = function(event) {
if (typeof self.closeCallback !== "undefined") {
self.closeCallback();
}
};
this.socket.onerror = function(event) {
if (typeof self.errorCallback !== "undefined") {
self.errorCallback();
}
};
};
/**
*
* @method emit
* @private
* @return
* @example
*
*/
p5.SerialPort.prototype.emit = function(data) {
if (this.socket.readyState == WebSocket.OPEN) {
this.socket.send(JSON.stringify(data));
} else {
this.emitQueue.push(data);
}
};
/**
* Tells you whether p5 is connected to the serial port.
*
* @method isConnected
* @return {Boolean} true or false
* @example
* var serial; // variable to hold an instance of the serialport library
* var portName = '/dev/cu.usbmodem1411';
*
* function setup() {
* createCanvas(400, 300);
* serial = new p5.SerialPort();
* serial.open(portName);
* println(serial.isConnected());
* }
*/
p5.SerialPort.prototype.isConnected = function() {
if (self.serialConnected) { return true; }
else { return false; }
};
/**
* Lists serial ports available to the server.
* Synchronously returns cached list, asynchronously returns updated list via callback.
* Must be called within the p5 setup() function.
* Doesn't work with the p5 editor's "Run in Browser" mode.
*
* @method list
* @return {Array} array of available serial ports
* @example
* function setup() {
* createCanvas(windowWidth, windowHeight);
* serial = new p5.SerialPort();
* serial.list();
* serial.open("/dev/cu.usbmodem1411");
* }
*
* For full example: <a href="https://itp.nyu.edu/physcomp/labs/labs-serial-communication/two-way-duplex-serial-communication-using-p5js/">Link</a>
* @example
* function printList(portList) {
* // portList is an array of serial port names
* for (var i = 0; i < portList.length; i++) {
* // Display the list the console:
* println(i + " " + portList[i]);
* }
* }
*/
p5.SerialPort.prototype.list = function(cb) {
if (typeof cb === 'function') {
this.listCallback = cb;
}
this.emit({
method: 'list',
data: {}
});
return this.serialportList;
};
/**
* Opens the serial port to enable data flow.
* Use the {[serialOptions]} parameter to set the baudrate if it's different from the p5 default, 9600.
*
* @method open
* @param {String} serialPort Name of the serial port, something like '/dev/cu.usbmodem1411'
* @param {Object} [serialOptions] Object with optional options as {key: value} pairs.
* Options include 'baudrate'.
* @param {Function} [serialCallback] Callback function when open completes
* @example
* // Change this to the name of your arduino's serial port
* serial.open("/dev/cu.usbmodem1411");
*
* @example
* // All of the following are valid:
* serial.open(portName);
* serial.open(portName, {}, onOpen);
* serial.open(portName, {baudrate: 9600}, onOpen)
*
* function onOpen() {
* print('opened the serial port!');
* }
*/
p5.SerialPort.prototype.open = function(_serialport, _serialoptions, cb) {
if (typeof cb === 'function') {
this.openCallback = cb;
}
this.serialport = _serialport;
if (typeof _serialoptions === 'object') {
this.serialoptions = _serialoptions;
} else {
//console.log("typeof _serialoptions " + typeof _serialoptions + " setting to {}");
this.serialoptions = {};
}
// If our socket is connected, we'll do this now,
// otherwise it will happen in the socket.onopen callback
this.emit({
method: 'openserial',
data: {
serialport: this.serialport,
serialoptions: this.serialoptions
}
});
};
/**
* Sends a byte to a webSocket server which sends the same byte out through a serial port.
* @method write
* @param {String, Number, Array} Data Writes bytes, chars, ints, bytes[], and strings to the serial port.
* @example
* You can use this with the included Arduino example called PhysicalPixel.
* Works with P5 editor as the socket/serial server, version 0.5.5 or later.
* Written 2 Oct 2015 by Tom Igoe. For full example: <a href="https://github.com/vanevery/p5.serialport/tree/master/examples/writeExample">Link</a>
*
* function mouseReleased() {
* serial.write(outMessage);
* if (outMessage === 'H') {
* outMessage = 'L';
* } else {
* outMessage = 'H';
* }
* }
*
* For full example: <a href="https://itp.nyu.edu/physcomp/labs/labs-serial-communication/lab-serial-output-from-p5-js/">Link</a>
* @example
* function mouseDragged() {
* // map the mouseY to a range from 0 to 255:
* outByte = int(map(mouseY, 0, height, 0, 255));
* // send it out the serial port:
* serial.write(outByte);
* }
*/
p5.SerialPort.prototype.write = function(data) {
//Writes bytes, chars, ints, bytes[], Strings to the serial port
var toWrite = null;
if (typeof data == "number") {
// This is the only one I am treating differently, the rest of the clauses are meaningless
toWrite = [data];
} else if (typeof data == "string") {
toWrite = data;
} else if (Array.isArray(data)) {
toWrite = data;
} else {
toWrite = data;
}
this.emit({
method: 'write',
data: toWrite
});
};
/**
* Returns a number between 0 and 255 for the next byte that's waiting in the buffer.
* Returns -1 if there is no byte, although this should be avoided by first checking available() to see if data is available.
*
* @method read
* @return {Number} Value of the byte waiting in the buffer. Returns -1 if there is no byte.
* @example
* function serialEvent() {
* inByte = int(serial.read());
* byteCount++;
* }
*
* @example
* function serialEvent() {
* // read a byte from the serial port:
* var inByte = serial.read();
* // store it in a global variable:
* inData = inByte;
* }
*/
p5.SerialPort.prototype.read = function() {
if (this.serialBuffer.length > 0) {
return this.serialBuffer.shift();
} else {
return -1;
}
};
/**
* Returns the next byte in the buffer as a char.
*
* @method readChar
* @return {String} Value of the Unicode-code unit character byte waiting in the buffer, converted from bytes. Returns -1 or 0xffff if there is no byte.
* @example
* var inData;
*
* function setup() {
* // callback for when new data arrives
* serial.on('data', serialEvent);
*
* function serialEvent() {
* // read a char from the serial port:
* inData = serial.readChar();
* }
*/
p5.SerialPort.prototype.readChar = function() {
if (this.serialBuffer.length > 0) {
/*var currentByte = this.serialBuffer.shift();
console.log("p5.serialport.js: " + currentByte);
var currentChar = String.fromCharCode(currentByte);
console.log("p5.serialport.js: " + currentChar);
return currentChar;
*/
return String.fromCharCode(this.serialBuffer.shift());
} else {
return -1;
}
};
/**
* Returns a number between 0 and 255 for the next byte that's waiting in the buffer, and then clears the buffer of data. Returns -1 if there is no byte, although this should be avoided by first checking available() to see if data is available.
* @method readBytes
* @return {Number} Value of the byte waiting in the buffer. Returns -1 if there is no byte.
* @example
* var inData;
*
* function setup() {
* // callback for when new data arrives
* serial.on('data', serialEvent);
*
* function serialEvent() {
* // read bytes from the serial port:
* inData = serial.readBytes();
* }
*/
p5.SerialPort.prototype.readBytes = function() {
if (this.serialBuffer.length > 0) {
var returnBuffer = this.serialBuffer.slice();
// Clear the array
this.serialBuffer.length = 0;
return returnBuffer;
} else {
return -1;
}
};
/**
* Returns all of the data available, up to and including a particular character.
* If the character isn't in the buffer, 'null' is returned.
* The version without the byteBuffer parameter returns a byte array of all data up to and including the interesting byte.
* This is not efficient, but is easy to use.
*
* The version with the byteBuffer parameter is more efficient in terms of time and memory.
* It grabs the data in the buffer and puts it into the byte array passed in and returns an integer value for the number of bytes read.
* If the byte buffer is not large enough, -1 is returned and an error is printed to the message area.
* If nothing is in the buffer, 0 is returned.
*
* @method readBytesUntil
* @param {[byteBuffer]}
* @return {[Number]} [Number of bytes read]
* @example
* // All of the following are valid:
* charToFind.charCodeAt();
* charToFind.charCodeAt(0);
* charToFind.charCodeAt(0, );
*/
p5.SerialPort.prototype.readBytesUntil = function(charToFind) {
console.log("Looking for: " + charToFind.charCodeAt(0));
var index = this.serialBuffer.indexOf(charToFind.charCodeAt(0));
if (index !== -1) {
// What to return
var returnBuffer = this.serialBuffer.slice(0, index + 1);
// Clear out what was returned
this.serialBuffer = this.serialBuffer.slice(index, this.serialBuffer.length + index);
return returnBuffer;
} else {
return -1;
}
};
/**
* Returns all the data from the buffer as a String.
* This method assumes the incoming characters are ASCII.
* If you want to transfer Unicode data: first, convert the String to a byte stream in the representation of your choice (i.e. UTF8 or two-byte Unicode data).
* Then, send it as a byte array.
*
* @method readString
* @return
* @example
*
*
*
*
*/
p5.SerialPort.prototype.readString = function() {
//var returnBuffer = this.serialBuffer;
var stringBuffer = [];
//console.log("serialBuffer Length: " + this.serialBuffer.length);
for (var i = 0; i < this.serialBuffer.length; i++) {
//console.log("push: " + String.fromCharCode(this.serialBuffer[i]));
stringBuffer.push(String.fromCharCode(this.serialBuffer[i]));
}
// Clear the buffer
this.serialBuffer.length = 0;
return stringBuffer.join("");
};
/**
* Returns all of the data available as an ASCII-encoded string.
*
* @method readStringUntil
* @param {String} stringToFind String to read until.
* @return {String} ASCII-encoded string until and not including the stringToFind.
* @example
*
* For full example: <a href="https://github.com/tigoe/p5.serialport/blob/master/examples/twoPortRead/sketch.js">Link</a>
*
* var serial1 = new p5.SerialPort();
* var serial2 = new p5.SerialPort();
* var input1 = '';
* var input2 = '';
*
* function serialEvent(){
* data = serial1.readStringUntil('\r\n');
* if (data.length > 0){
* input1 = data;
* }
* }
*
* function serial2Event() {
* var data = serial2.readStringUntil('\r\n');
* if (data.length > 0){
* input2 = data;
* }
* }
*/
p5.SerialPort.prototype.readStringUntil = function(stringToFind) {
var stringBuffer = [];
//console.log("serialBuffer Length: " + this.serialBuffer.length);
for (var i = 0; i < this.serialBuffer.length; i++) {
//console.log("push: " + String.fromCharCode(this.serialBuffer[i]));
stringBuffer.push(String.fromCharCode(this.serialBuffer[i]));
}
stringBuffer = stringBuffer.join("");
//console.log("stringBuffer: " + stringBuffer);
var returnString = "";
var foundIndex = stringBuffer.indexOf(stringToFind);
//console.log("found index: " + foundIndex);
if (foundIndex > -1) {
returnString = stringBuffer.substr(0, foundIndex);
this.serialBuffer = this.serialBuffer.slice(foundIndex + stringToFind.length);
}
//console.log("Sending: " + returnString);
return returnString;
};
/**
* Returns all of the data available as an ASCII-encoded string until a line break is encountered.
*
* @method readLine
* @return {String} ASCII-encoded string
* @example
*
* You can use this with the included Arduino example called AnalogReadSerial.
* Works with P5 editor as the socket/serial server, version 0.5.5 or later.
* Written 2 Oct 2015 by Tom Igoe. For full example: <a href="https://github.com/vanevery/p5.serialport/tree/master/examples/readAndAnimate">Link</a>
*
* function gotData() {
* var currentString = serial.readLine(); // read the incoming data
* trim(currentString); // trim off trailing whitespace
*
* if (!currentString) return; { // if the incoming string is empty, do no more
* console.log(currentString);
* }
*
* if (!isNaN(currentString)) { // make sure the string is a number (i.e. NOT Not a Number (NaN))
* textXpos = currentString; // save the currentString to use for the text position in draw()
* }
* }
*/
p5.SerialPort.prototype.readLine = function() {
return this.readStringUntil("\r\n");
};
/**
* Returns the number of bytes available.
*
* @method available
* @return {Number} The length of the serial buffer array, in terms of number of bytes in the buffer.
* @example
* function draw() {
* // black background, white text:
* background(0);
* fill(255);
* // display the incoming serial data as a string:
* var displayString = "inByte: " + inByte + "\t Byte count: " + byteCount;
* displayString += " available: " + serial.available();
* text(displayString, 30, 60);
* }
* */
p5.SerialPort.prototype.available = function() {
return this.serialBuffer.length;
};
/**
* Returns the last byte of data from the buffer.
*
* @method last
* @return {Number}
* @example
*
* */
p5.SerialPort.prototype.last = function() {
//Returns last byte received
var last = this.serialBuffer.pop();
this.serialBuffer.length = 0;
return last;
};
/**
* Returns the last byte of data from the buffer as a char.
*
* @method lastChar
* @example
*
* */
p5.SerialPort.prototype.lastChar = function() {
return String.fromCharCode(this.last());
};
/**
* Clears the underlying serial buffer.
*
* @method clear
* @example
*/
p5.SerialPort.prototype.clear = function() {
//Empty the buffer, removes all the data stored there.
this.serialBuffer.length = 0;
};
/**
* Stops data communication on this port.
* Use to shut the connection when you're finished with the Serial.
*
* @method stop
* @example
*
*/
p5.SerialPort.prototype.stop = function() {
};
/**
* Tell server to close the serial port. This functions the same way as serial.on('close', portClose).
*
* @method close
* @param {String} name of callback
* @example
*
* var inData;
*
* function setup() {
* serial.open(portOpen);
* serial.close(portClose);
* }
*
* function portOpen() {
* println('The serial port is open.');
* }
*
* function portClose() {
* println('The serial port closed.');
* }
*/
p5.SerialPort.prototype.close = function(cb) {
//
if (typeof cb === 'function') {
this.closeCallback = cb;
}
this.emit({
method: 'close',
data: {}
});
};
/**
* Register clients that connect to the serial server.
*
* This is for use with the p5 Serial Control application so the application
* can access and render the names of clients who have connected. Note that
* calling this method does not log the list of registered clients. To do that,
* you'd use:
* serial.on('registerClient', logClientData)
*
* The example demonstates the registerClient method, as well as how you'd log
* the list of clients.
*
* @method registerClient
* @example
*
* function setup() {
* // Create a new p5 Serial Port object
* serial = new p5.SerialPort();
* // List the available ports
* serial.list();
* // On port open, call the gotOpen callback
* serial.on('open', gotOpen);
* // Register the clients that have connected to the server
* serial.registerClient();
* // After registerClient method is done, call the logClientData callback
* serial.on('registerClient', logClientData)
* }
*
* // Callback to log the client data
* function logClientData(data) {
* console.log("Client data: ", data)
* }
*
* // Callback to log a message when the port is opened
* function gotOpen() {
* console.log("Serial port is open.")
* }
*/
// p5.SerialPort.prototype.registerClient = function(cb) {
// if (typeof cb === 'function') {
// this.registerCallback = cb;
// }
// this.emit({
// method: 'registerClient',
// data: {}
// });
// return this.clientData;
// };
/**
* // Register callback methods from sketch
*
*/
p5.SerialPort.prototype.onData = function(_callback) {
this.on('data',_callback);
};
p5.SerialPort.prototype.onOpen = function(_callback) {
this.on('open',_callback);
};
p5.SerialPort.prototype.onClose = function(_callback) {
this.on('close',_callback);
};
p5.SerialPort.prototype.onError = function(_callback) {
this.on('error',_callback);
};
p5.SerialPort.prototype.onList = function(_callback) {
this.on('list',_callback);
};
p5.SerialPort.prototype.onConnected = function(_callback) {
this.on('connected',_callback);
};
p5.SerialPort.prototype.onRawData = function(_callback) {
this.on('rawdata',_callback);
};
// Version 2
p5.SerialPort.prototype.on = function(_event, _callback) {
if (_event == 'open') {
this.openCallback = _callback;
} else if (_event == 'data') {
this.dataCallback = _callback;
} else if (_event == 'close') {
this.closeCallback = _callback;
} else if (_event == 'error') {
this.errorCallback = _callback;
} else if (_event == 'list') {
this.listCallback = _callback;
} else if (_event == 'connected') {
this.connectedCallback = _callback;
} else if (_event == 'rawdata') {
this.rawDataCallback = _callback;
}
};
}));
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/p5.js/1.1.9/p5.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/p5.js/1.1.9/addons/p5.sound.min.js"></script>
<script language="javascript" type="text/javascript" src="p5.serialport.js"></script>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="style.css">
<meta charset="utf-8" />
</head>
<body>
<script src="sketch.js"></script>
</body>
</html>