OVERVIEW
LaserCut provides a Universal Platform in which Users may import CAD Geometry, and prepare the File for Laser Processing. Users must have experience with any CAD Platform (or a Vector Based Graphics Program, i.e. Adobe Illustrator, CorelDraw etc.), to successfully operate within the LaserCut Software Environment. Users should also have completed Fire Extinguisher Training, and Policy/Procedure Training to successfully operate the Laser Equipment.
LASERCUT
![]() Find the LaserCut Application Icon on the Computer Desktop, and open the Application.
Find the LaserCut Application Icon on the Computer Desktop, and open the Application.
FILE > IMPORT
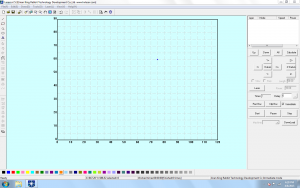
The LaserCut Interface, features various Drop-Down Menus from the Top of the screen; Command-Icon Buttons along the top and left side; a color-bar along the bottom, and Equipment Control/Layer Manager on the right side. The majority of the interface is a window, with a grid-layout. This is a TOP View of the Laser Equipment Cutting Table.
Begin, by importing a previously prepared CAD File. Adobe Illustrator (.ai) and AutoCad Drawing Exchange (.dxf) File Formats will work best for Laser CUTTING/SCORING/ENGRAVING; whereas Image formats (i.e. [.jpeg]) will work only for ENGRAVING. To import a file, browse to the ‘FILE’ Menu, and find the ‘IMPORT’ Option. Find and select your file location from the Import Window.
TOOLS > UNITE LINES
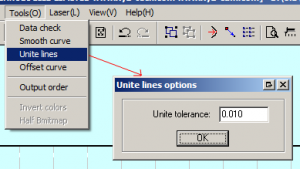
Your CAD Geometry, will be placed on the Grid. All Geometry should appear as the same color. During the import, all Joined Curve Geometry is separated/exploded into single segments- separated by their Start and End Points. Fix this issue, by selecting ALL of your Geometry (CTRL+A), then, find the ‘TOOLS’ Drop-Down Menu, and select ‘UNITE LINES’ from the list of options. A new window will appear, prompting your input for a Tolerance Value- the default setting is sufficient, Select ‘OK’ and your Geometry will be re-joined. This will create a more efficient Laser process.
BACK TO TOP
LAYERS
 Within the LaserCut Application, a User can control the order in which Geometry is Processed; and the Mode in which Geometry is Processed. To control any of these parameters, your geometry must be separated onto Layers. Your Layer Menu is located in the top-right of the LaserCut Interface. To place geometry on a Layer, or Create a New Layer, select ALL Geometry you would like to separate onto an individual Layer; then, Select a Color that suits your taste from the Color Bar at the bottom of the LaserCut Interface. Within your Layer Menu, you will find the new color listed under the Layer Column.
Within the LaserCut Application, a User can control the order in which Geometry is Processed; and the Mode in which Geometry is Processed. To control any of these parameters, your geometry must be separated onto Layers. Your Layer Menu is located in the top-right of the LaserCut Interface. To place geometry on a Layer, or Create a New Layer, select ALL Geometry you would like to separate onto an individual Layer; then, Select a Color that suits your taste from the Color Bar at the bottom of the LaserCut Interface. Within your Layer Menu, you will find the new color listed under the Layer Column.
LAYERS > CUT ORDER
To control Cut Order, simply select a Layer, and drag it downward or upward in the Layer Menu. The Topmost Layer will cut first, and the Laser Equipment will continue to process geometry from the topmost layer- down. Cut Order, may or may not be important- depending on your File, Geometry, and Material. It is common practice, however, to cut out smaller areas first, and larger areas second. Certain Materials can bend or warp when heat is applied, so it may be necessary to cut internal structures before cutting outer/surrounding/external geometry.
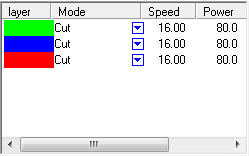
The image above, indicates that all Geometry appearing in GREEN, will be processed first. BLUE Geometry, will be second- and RED Geometry will process last in the Cut Order. Note, that smaller internal geometry is cut first, and external surrounding geometry is cut last.
LAYERS > CUT MODE

Laser Modes, indicate how the Geometry should be processed. If you select the arrow, within any of your Layer’s Mode Columns, it will create a drop-down menu; allowing you to change how Geometry on each layer is processed:
‘CUT’ Mode, indicates that your geometry will be processed as Cut Lines, this Mode is most often used- and will cut through your material completely, as long as you’ve indicated the correct settings for Speed and Power.
‘ENGRAVE’ Mode, indicates that your geometry will be processed as Engraving Areas. To Engrave, you must have completely closed geometry (i.e. the Curve Start Point, and End Point exist in the same location) Alternately, you can import an image, and process as an Engraving File.
‘GRADE ENGRAVE’, indicates that your geometry will be processed as Gradated Engraving Areas. This is similar to ENGRAVE Mode, but different in that the engraving will adjust from a lighter engraving power near the edge areas, and a deeper engraving power near the center of you Engrave Areas. To Engrave, you must have completely closed geometry (i.e. the Curve Start Point, and End Point exist in the same location) Alternately, you can import an image, and process as an Engraving File.
‘HOLES’ Mode, is specifically for Circle Geometry, and useful for precise operations and parts. This Mode will control the Start and End Point Power for Circle Geometry, reducing fire hazards, and providing the User with less warping.
In the image above, ALL of our Geometry is listed as ‘CUT’ Mode. All Geometry will be cut completely through, in the order of the Layer List.
MODE SETTINGS
Each Mode, requires User Input settings, that will typically control Laser Speed, and Power. These settings, are dependent on Material Selection, Material Thickness, and the Laser Processing Mode. Users are responsible for knowing these values. It is difficult to remember every setting, for each combination of Material, Thickness, and Mode, so we’ve created a web-based form, that will assist you with these settings. Visit the [RABBIT] Laser Settings Page, and fill out the necessary information in the form-fields. Select the search button, and a new window will appear, with various tested-and-approved settings for your specific Laser Operation. To change your Mode’s Settings, Double-Click on the Layer you wish to edit, and a new window will appear with various parameters. Take the information from the [RABBIT] Laser Settings Results Page, and input them accordingly into the available fields.
Frequently, you may have a material that IDeATe@Hunt has yet to record settings for. In the event you cannot find settings for your operation/material- you may have to do some testing before-hand. Figuring out the correct settings, may take some time- but once you’ve figured them out, providing the information to an IDeATe@Hunt Staff Member, will ensure the successful future operation of similar Laser Processes. While testing, it is important that you recognize how SPEED and POWER can affect your outcome:
SPEED: Too much speed, won’t allow the Laser to pass through your Material. Faster Speeds (50%-100%), are useful for thinner and/or less dense materials- such as cardboard, matte board, illustration board, or paper. Slower speeds (1%-49%), are useful for thicker and/or dense materials- such as acrylic, MDF, and Plywood.
POWER: Too much Power, will cause a fire-hazard, and possible warping of your material. Higher Power (50%-100%), is useful for thicker and/or dense materials- such as acrylic, MDF, and Plywood. Lower Power (1%-49%), is useful for thinner and/or less dense materials- such as cardboard, matte board, illustration board, or paper.
You must find a safe, starting combination of these two values, before performing any test cuts. When in doubt, always use a lower power- this will eliminate additional, unnecessary fire-hazards. For instance, we could begin testing CUT settings for 1/8″ (3mm) thick Cardboard. If we use 50% Speed, and 100% Power, it will certainly CUT all the way through. However, the Power Setting is TOO HIGH for this material. Instead, start with 50% Speed, and 40% Power- if it doesn’t cut through, lower your Speed by 5%, and raise the Power 5%. Repeat this process until you’ve found reliable and consistent settings.
DOWNLOAD
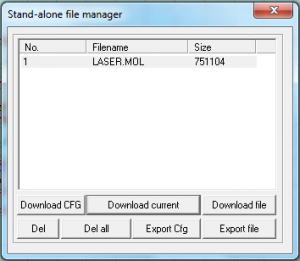
After you’ve imported your file, completed the UNITE LINES Command, organized your geometry onto layers, adjusted your Cut Order + Cut Mode, and input Laser Mode Settings- you must DOWNLOAD your file to the Laser Equipment. In the Equipment Control/Layer Menu, on the right-side of your LaserCut Interface; you will find a button near the bottom, labeled : ‘DownLoad’ Find and Select this button- and a new window will appear. This window will list any files that are currently downloaded and stored on the Equipment’s Flash Memory. Begin, by selecting the ‘Del all’ Button, to clear all existing files from the Equipment’s Memory. Next, find and select the ‘Download current’ Button, to download your current file into the Equipment’s Memory. Your file will be sent to the Laser Equipment, and you may begin Equipment and Material Preparation.
EQUIPMENT PREPARATION
Your file has been downloaded into the Equipment’s Memory, and it is ready to be processed- however, there is a specific set of tasks that must be completed before your file may be processed. Follow the Equipment’s Procedural Steps before beginning your Laser Job.
