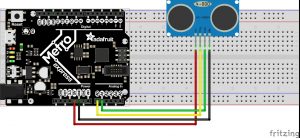
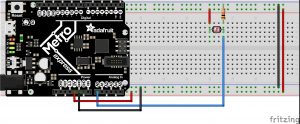
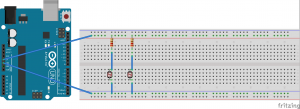
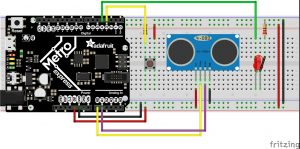
Hot/Cold
I wanted to build upon and improve the previous assignment. The goal is to balance at a certain distance in order to turn on the LED, but done through a classic game of hot or cold. While it’s rather trivial, it has helped me to better understand the ultrasonic sensor and its possibilities. refining the sensor data and perfecting the timing is something that I’d like to explore further down the road.
The states are used in order to guide you through the game. State one lets you now that the game is ready, state two sets a random number for you to find using the ultrasonic sensor, and in state three…you find the number. Prompted in the serial monitor if you are getting warmer or colder.
Code:
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#ifdef __AVR__
#include <avr/power.h>
#endif
static const int PIN = 40;
static const int NUMPIXELS = 1;
Adafruit_NeoPixel pixels = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUMPIXELS, PIN, NEO_GRBW + NEO_KHZ800);
//--------ULTRASONIC PINS--------
static const int trigPin = A0;
static const int echoPin = A1;
//--------LIGHTS--------
static const int ledPin = 4;
//--------SWITCH PIN--------
static const int switchPin = 3;
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//--------Global variables--------
const bool isInterrupt = true;
// button state
int buttonState = 0; // current state of the button
// Target
int target;
// Time
unsigned long lastSampleTime = 0;
unsigned long sampleInterval = 5000; // in ms
unsigned long lastSampleTime2 = 0;
unsigned long sampleInterval2 = 250; // in ms
unsigned long lastSampleTime3 = 0;
unsigned long sampleInterval3 = 500; // in ms
// Ultrasonic
long duration;
int distance;
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void SwitchPressed()
{
if (digitalRead(switchPin) == HIGH) {
// this is why people hate C
buttonState == 3 ? buttonState = 0 : buttonState++;
}
// Serial.println(buttonState);
}
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(switchPin, INPUT);
pinMode(trigPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(echoPin, INPUT);
// attach the interrupt pin to a method
if (isInterrupt) {
attachInterrupt (digitalPinToInterrupt (switchPin), SwitchPressed, CHANGE);
}
randomSeed(analogRead(2));
pixels.begin(); // This initializes the NeoPixel library.
}
void loop() {
unsigned long now = millis();
switch (buttonState) {
case 0:
pixelBlinkGreen();
Serial.println ("Ready To Start Game");
break;
case 1:
if (lastSampleTime + sampleInterval < now) {
lastSampleTime = now;
target = random(1, 150);
Serial.print("Target Set");
}
pixels.setPixelColor(0, pixels.Color(0, 255, 0));
break;
case 2:
pixels.setPixelColor(0, pixels.Color(255, 200, 0));
// Serial.print("Find ");
// Serial.println(target);
hotCold(target);
break;
default:
pixelBlinkYellow();
Serial.println("Push Button For New Game");
// statements
}
}
/*
if (buttonState == 0) {
pixelBlinkGreen();
Serial.println ("GREEN BLINK");
}
else if (buttonState == 1) {
if (lastSampleTime + sampleInterval < now) {
lastSampleTime = now;
target = random(1, 150);
Serial.print("Target = ");
Serial.println(target);
}
pixelBlinkYellow();
}
else if (buttonState == 2) {
pixels.setPixelColor(0, pixels.Color(255, 200, 0));
// Serial.print("Find ");
// Serial.println(target);
hotCold(target);
}
}
*/
//------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void hotCold(int x) {
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(trigPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(trigPin, LOW);
duration = pulseIn(echoPin, HIGH);
distance = duration / 10 / 2 ;
unsigned long now2 = millis();
if (lastSampleTime2 + sampleInterval2 < now2) {
lastSampleTime2 = now2;
if ((distance <= (target + 5)) && (distance >= (target - 5))) {
Serial.println("ON FIRE!");
ledOn();
pixelBlinkPink();
} else if ((distance <= (target + 10)) && (distance >= (target - 10))) {
Serial.println("Things are heating up");
ledOff();
} else if ((distance <= (target + 20)) && (distance >= (target - 20))) {
Serial.println("Warmer...");
ledOff();
} else if ((distance <= (target + 30)) && (distance >= (target - 30))) {
Serial.println("Cooler...");
ledOff();
} else if ((distance <= (target + 40)) && (distance >= (target - 40))) {
Serial.println("Pretty Cold");
ledOff();
} else if ((distance <= (target + 50)) && (distance >= (target - 50))) {
Serial.println("Ice Cold, Elsa");
ledOff();
} else {
ledOff();
//Serial.println("Something is wrong");
}
}
}
void pixelBlinkGreen() {
pixels.setPixelColor(0, pixels.Color(0, 255, 0));
pixels.show(); // This sends the updated pixel color to the hardware.
delay(500);
pixels.setPixelColor(0, pixels.Color(0, 0, 0));
pixels.show(); // This sends the updated pixel color to the hardware.
delay(500);
}
void pixelBlinkYellow() {
pixels.setPixelColor(0, pixels.Color(255, 200, 0, 75));
pixels.show(); // This sends the updated pixel color to the hardware.
delay(250);
pixels.setPixelColor(0, pixels.Color(0, 0, 0));
pixels.show(); // This sends the updated pixel color to the hardware.
delay(250);
}
void pixelBlinkWhite() {
pixels.setPixelColor(0, pixels.Color(255, 255, 255));
pixels.show(); // This sends the updated pixel color to the hardware.
delay(300);
pixels.setPixelColor(0, pixels.Color(0, 0, 0));
pixels.show(); // This sends the updated pixel color to the hardware.
delay(250);
}
void pixelBlinkPink() {
pixels.setPixelColor(0, pixels.Color(254, 6, 141));
pixels.show(); // This sends the updated pixel color to the hardware.
delay(300);
pixels.setPixelColor(0, pixels.Color(0, 0, 0));
pixels.show(); // This sends the updated pixel color to the hardware.
delay(250);
}
void pixelOff() {
pixels.setPixelColor(0, pixels.Color(0, 0, 0));
pixels.show(); // This sends the updated pixel color to the hardware.
}
void ledOn() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
}
void ledOff() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
}
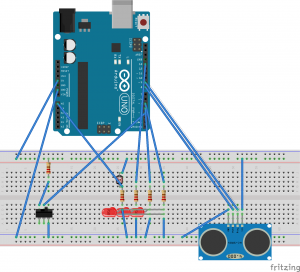
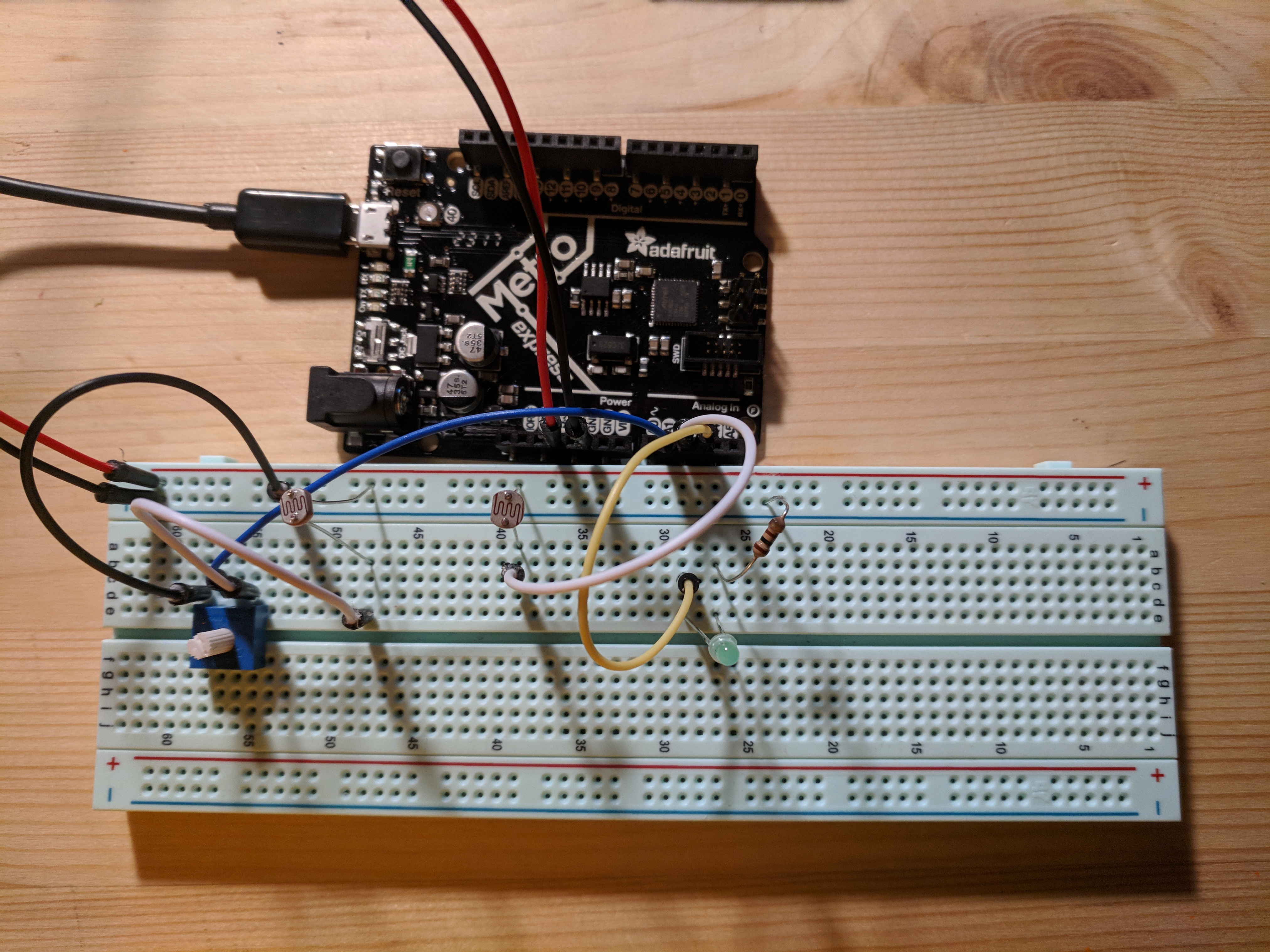
 (every time I upload)
(every time I upload) which I’ve never seen before,
which I’ve never seen before,