Problem
In recent weeks, workplace safety standards have come under scrutiny, after an incident where an Amazon employee suffered a fatal heart attack while on the floor with no one around to help for twenty minutes after the fact. The labor sector of the economy can cause a variety of health risks, caused by falls, drops, and repetitive stress. Additionally, accidental misuse of heavy machinery, or lack of awareness of ones surroundings can lead to fatal consequences. There are a variety of technologies that can tackle workspace related injury, this experiment covers responding and communicating physical stress.
Solution
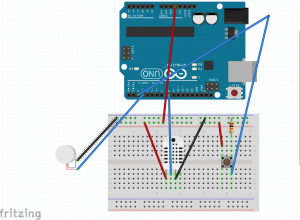
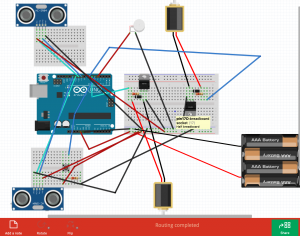
An suite of auditory and visual feedback systems would allow workers to maintain there safety in an intuitive fashion. The first device is a fingerless glove wearable that reads the temperature of an object, and indicates that temperature to the user in the form of color. Green implies handilability, red implies heat, and blue implies cold. If the object is not handleable, the wearable will vibrate as a warning.
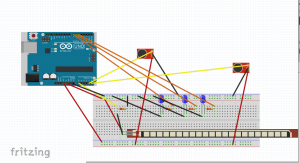
The second device is a stress sensor. If the user is physically stressed, or if the user is experiencing and irregular heartbeat, the sensor will begin playing a patterned noise, indicating to others that they are either performing a laborious task, or that they need assistance.
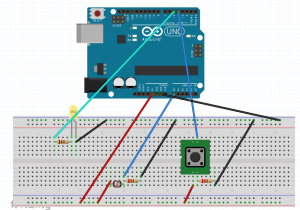
The third device is a personal alarm, embedded into a vest or article of clothing. It requires two distinct buttons to be pressed at the same time. If the user feels that they are having a serious medical event, or are injured, or see another person that is in need of assistance, the user can press these buttons, which will trigger an alarm.
Proof of Concept
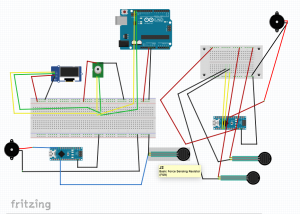
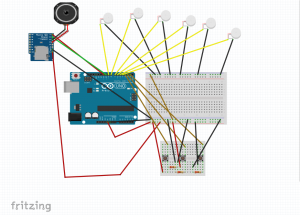
The first device was prototyped using the onboard neopixel from a redboard turbo, an I2C OLED, and a tactor motor. The I2C OLED stated the current temperature, read from an MLX non contact temperature sensor. The neopixel and tactor perform as noted above.
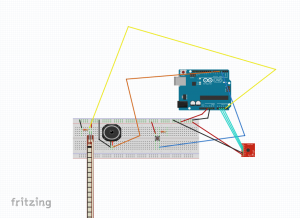
The second device prototype utilizes an electromyograph sensor, which reads signals from muscle impulses. When the rating reaches a threshold, a piezo speaker plays a tune.
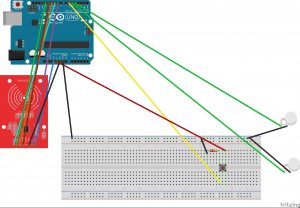
The third device uses two force sensors as push buttons, and uses a speaker to play an alarm.