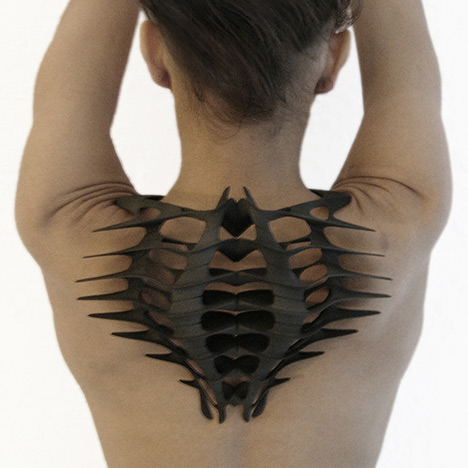
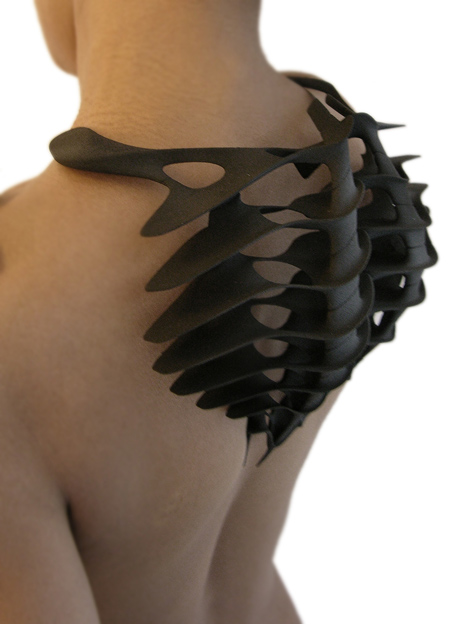
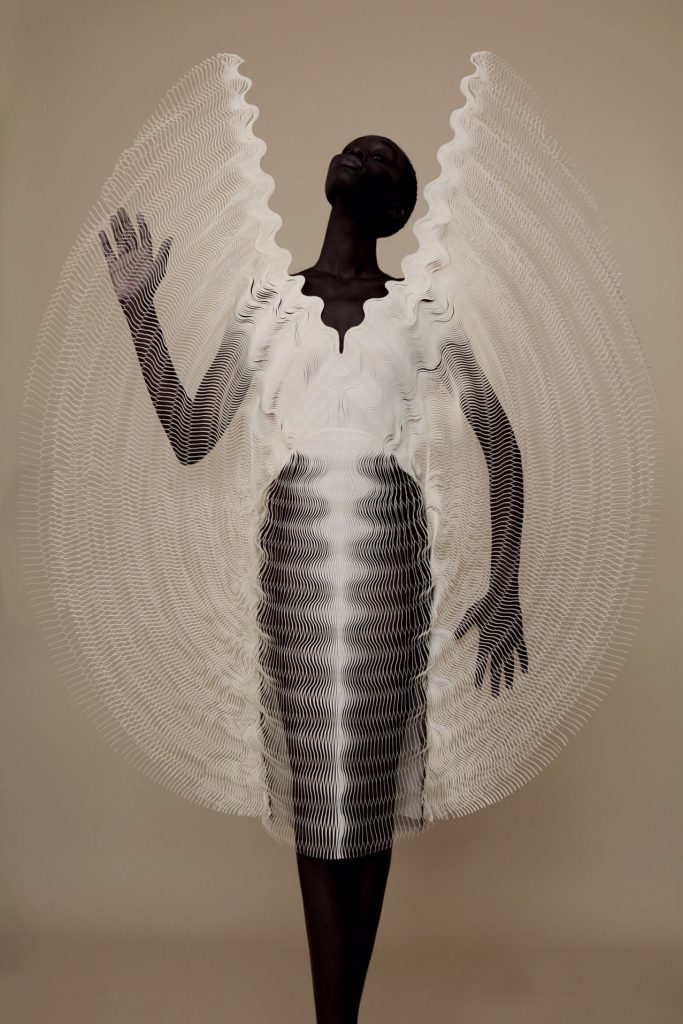
Iris van Herpen is one of the most avant garde designers known in the industry of fashion design. She has been innovating new methods in both design and garment construction techniques to fuse the past and future of couture craftsmanship. In her Hypnosis 2019 collection, collaborating with the architect Anthony Howe, she applies her design in using parametric patterns to the fabric that’s generated through 3D printing. The Hypnosis collection can be called as “kinetic couture,” since the garments move as models walk the runway. I believe the algorithms on generating these patterns were inspired by the complexity forms that is in nature, such as wind and fluidity of water. The kinetic movement and form was also adapted from the mechanisms of Howe’s sculptures. Howe’s design uses computational aid in creating parametric installation work. I admired this collection and collaboration between fashion designer and an architect, where they applied architectural form using computational distortion to experiment on bringing into creation of haute couture.

![[OLD FALL 2019] 15-104 • Introduction to Computing for Creative Practice](../../../../wp-content/uploads/2020/08/stop-banner.png)